Modern urban landscapes are rapidly adopting Internet of Things (IoT) devices across various systems, including traffic control and public lighting infrastructure. While this technological integration delivers substantial benefits in operational efficiency and quality of life improvements, it simultaneously creates new security challenges that demand immediate attention. The protection of essential infrastructure and sensitive data within these networks has become absolutely critical for ensuring reliable smart city functionality. Neglecting these security considerations might result in severe outcomes, spanning from minor service disruptions to catastrophic system failures with potential physical consequences.
The interconnected architecture of smart urban systems means that a single security breach can trigger domino effects across multiple services. For instance, a hacked traffic signal network could create massive congestion and hazardous road conditions. Likewise, security weaknesses in municipal water systems might endanger public health. Understanding these systemic risks is fundamental when designing comprehensive protection strategies.
Protecting Data Integrity and Confidentiality
Safeguarding the accuracy and privacy of information gathered by IoT networks represents a critical priority. Urban IoT applications routinely process sensitive citizen data, including movement patterns, utility usage statistics, and personal behavioral information. Advanced encryption methods and secure data handling procedures form the foundation for preventing unauthorized data access and leaks.
Implementing rigorous verification processes and permission systems proves equally important for controlling sensitive data access. This involves authenticating both human users and connected devices before granting system interaction privileges. Incorporating multiple verification steps and conducting periodic security evaluations represent essential elements of an effective protection framework.
Addressing the Challenges of Device Vulnerabilities
Many IoT components operate with constrained processing capabilities and limited memory, rendering them prone to various security breaches. Manufacturers should emphasize security considerations throughout the entire product development lifecycle to minimize potential weaknesses. Consistent software maintenance and security patches remain vital for resolving identified vulnerabilities.
Additionally, the heterogeneous nature of urban IoT deployments presents significant management difficulties. Coordinating security protocols across diverse hardware from multiple suppliers necessitates a unified approach. Establishing consistent security standards and compatibility requirements helps ensure uniform protection throughout the entire network infrastructure.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
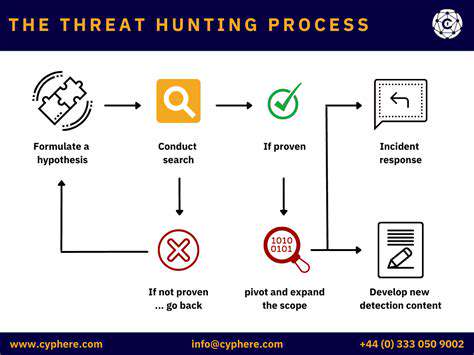
Developing strong security protocols represents an ongoing process rather than a one-time implementation. Regular system evaluations and controlled penetration tests help uncover potential system weaknesses before exploitation occurs. These procedures should incorporate vulnerability assessments, intrusion monitoring, and incident response protocols.
Equally important is educating end-users about fundamental security practices. Residents should understand potential threats and methods for avoiding social engineering attacks. Effective collaboration among all stakeholders - including citizens, municipal authorities, and technology providers - forms the cornerstone of successful security implementation.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Security
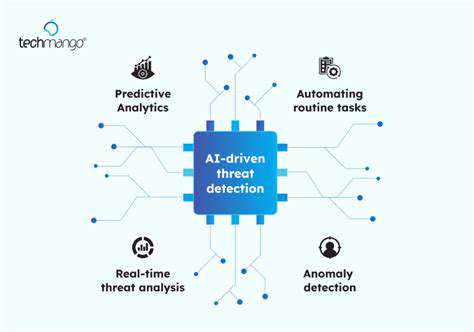
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are playing increasingly significant roles in identifying and responding to security threats within smart urban environments. AI-driven monitoring systems can process enormous data volumes from various IoT endpoints to detect irregularities and potential security incidents as they occur. This capability enables faster response times and reduces the impact of security breaches.
Machine learning models can also be trained to recognize patterns indicative of malicious behavior. This predictive approach can dramatically strengthen urban security postures by preventing attacks before they materialize. Continued advancement in this field remains crucial for enhancing AI-based security applications in city environments.
Identifying Key Vulnerabilities in Smart City IoT Ecosystems
Identifying Common Software Flaws
Software vulnerabilities represent system weaknesses that malicious entities can exploit for unauthorized access or system damage. Recognizing prevalent vulnerability types forms the foundation for implementing effective protective measures. These flaws typically originate from coding errors, insufficient security evaluation, or delayed update cycles.
Detecting these recurring software issues constitutes the initial phase of any proactive security framework. Comprehensive understanding of these vulnerabilities enables development and security teams to implement preventative measures against potential threats.
Understanding Input Validation Issues
One major vulnerability category involves inadequate input verification, occurring when applications improperly process user-provided data before execution. Attackers can exploit this weakness to inject harmful code, potentially leading to system access, data compromise, or other damaging outcomes. Implementing rigorous input validation procedures remains essential for preventing such attacks.
Exploiting Security Misconfigurations
Frequently, vulnerabilities emerge from improperly configured systems or applications. These configuration errors can range from unprotected network ports to incorrectly managed access permissions. Such oversights may expose sensitive information to unauthorized parties, necessitating regular security configuration reviews and updates.
Insufficient security awareness frequently contributes to these types of vulnerabilities. Periodic security audits and configuration management represent vital practices for reducing these risks.
The Impact of Broken Authentication and Session Management
Faulty authentication and session control mechanisms allow unauthorized users to masquerade as legitimate accounts. This can result in unauthorized data access, information modification, or complete system control acquisition. Implementing strong authentication and session control protocols forms the basis for preventing these attack vectors.
Addressing Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) Vulnerabilities
Cross-site scripting vulnerabilities occur when applications fail to properly sanitize user-provided content, enabling attackers to inject malicious code into web pages viewed by other users. This can facilitate sensitive data theft, account takeover, or malicious website redirection. Preventing XSS attacks demands careful content encoding and comprehensive input validation.
The Risk of Insecure Deserialization
Insecure deserialization vulnerabilities emerge when applications improperly validate external data before reconstruction. This weakness can enable remote code execution or other serious security incidents. Deploying strict input validation and secure deserialization methods proves crucial for preventing exploitation.
The Importance of Using Up-to-Date Libraries and Frameworks
Utilizing outdated software components can expose applications to known security flaws. Attackers frequently target these obsolete elements since they often contain unpatched vulnerabilities. Maintaining current software versions and security updates represents a critical practice for reducing these vulnerabilities. Regular security evaluations and system updates remain essential for preserving strong security postures.
Mitigating Risks Through Robust Security Architectures
Identifying Potential Threats
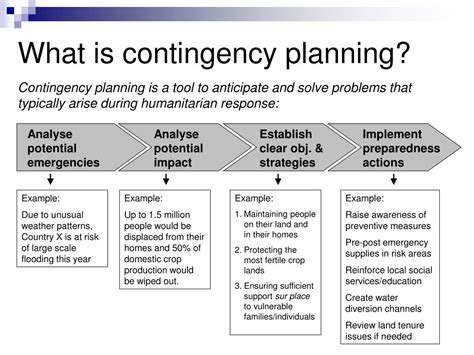
The initial phase in effective risk management involves comprehensive identification of potential threats that could negatively impact organizational operations. This process requires evaluating diverse factors, from internal security gaps to external hazards like cyberattacks or natural disasters. Proactive threat identification enables the development of targeted mitigation strategies. Examining historical incidents and industry standards provides valuable insights into potential risks.
Thorough research and data analysis prove essential for complete threat comprehension. This includes reviewing past incident records, market developments, and regulatory modifications to anticipate emerging challenges. Comprehensive threat understanding allows organizations to strategically allocate protective resources.
Developing Contingency Plans
Following threat identification, creating detailed contingency plans represents the next critical step. These plans should specify exact response procedures for various threat scenarios, ensuring organized reactions. Effective contingency plans clearly define participant responsibilities, required resources, and communication methods. This structured approach facilitates quick, efficient responses that minimize disruption impacts.
Contingency plans require regular review and updates to remain current with evolving threats and environmental changes. This proactive maintenance ensures plan effectiveness and organizational preparedness for various scenarios.
Implementing Protective Measures
Deploying protective measures constitutes a crucial aspect of risk reduction. These implementations range from basic security enhancements to sophisticated protection systems. Implementing these protections demonstrates organizational commitment to asset security and operational stability. This dedication fosters stakeholder confidence and strengthens overall organizational resilience.
Each protective measure requires careful cost-benefit analysis. Comparing implementation expenses against potential financial and reputational damages from security incidents ensures optimal resource allocation.
Establishing Monitoring Systems
Effective risk management demands continuous evaluation of implemented protections. This involves creating systems to track key metrics like security incidents, event reports, and stakeholder input. Ongoing monitoring enables early threat detection and strategy adjustments. Data collected from these systems informs future planning and process improvements.
Monitoring systems should provide immediate alerts and reports, facilitating rapid response to emerging issues. Quick reaction capabilities remain essential for minimizing damage and maintaining business continuity.
Enhancing Communication Protocols
Clear communication proves critical during security incidents. Well-defined communication procedures ensure rapid, accurate information distribution to all stakeholders, including staff, customers, partners, and regulators. Transparent communication builds trust and reduces confusion during critical situations.
Established communication channels and processes enable coordinated incident responses. This ensures all participants understand their roles, preventing misunderstandings during risk mitigation efforts.
Regular Training and Awareness
Employee education programs play a pivotal role in risk reduction. Regular training sessions inform staff about potential threats, appropriate responses, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities. This proactive approach cultivates security awareness, empowering employees as frontline defenders. A well-trained workforce represents an organization's most valuable security asset.
Ongoing training updates ensure staff remain informed about emerging threats and best practices. Continuous education maintains consistent, informed approaches to risk management.
Prioritizing Data Security and Privacy in Smart City Operations
Ensuring Data Integrity and Confidentiality
Maintaining data accuracy and privacy represents a fundamental requirement for smart city functionality. This necessitates implementing advanced encryption standards to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Data verification procedures are essential to confirm information remains unaltered during transmission or storage. These measures include digital authentication methods and hashing algorithms to validate data authenticity and prevent unauthorized modifications. Comprehensive data protection strategies are crucial for preventing accidental or intentional data leaks, ensuring sensitive information remains accessible only to authorized parties. A multi-layered security approach incorporating various protective controls is recommended to address potential vulnerabilities and maintain optimal data security.
Additionally, maintaining detailed access logs for data interactions is essential for accountability and incident investigation. This enables tracing security breach origins and implementing prompt corrective actions. Regular security testing and penetration assessments are vital for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before exploitation occurs. Establishing clear data management policies and procedures, including access controls and retention schedules, also proves critical for regulatory compliance and best practice adherence. These policies require periodic review and updates to reflect evolving threats and technological advancements.
Implementing Robust Security Measures Across IoT Devices
Smart city operations extensively utilize Internet of Things (IoT) devices that frequently collect and transmit sensitive information. Consequently, securing these devices becomes paramount. Implementing strong authentication protocols for IoT components is essential for preventing unauthorized access. This includes utilizing unique device identification, complex credentials, and multi-step verification where feasible. Regular firmware updates for IoT equipment are crucial for addressing security flaws and implementing the latest protective features. This proactive approach substantially reduces exploitation risks from malicious actors. These devices must undergo thorough security evaluation before deployment to identify and resolve potential weaknesses.
Securing communication pathways between IoT devices and central systems proves equally important. Implementing encryption standards like TLS/SSL for data transmission is essential for preventing interception and tampering. Establishing secure network configurations, including firewalls and intrusion detection systems, is crucial for preventing unauthorized network access. Regular network security audits are necessary for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities, ensuring network reliability and security. IoT device security considerations should begin during the design phase, integrating protection into system architecture rather than implementing it as an afterthought.
Implementing comprehensive access control systems for IoT data is also critical. These systems should restrict access to authorized personnel and systems only. This includes assigning appropriate access levels and regularly reviewing permission assignments. Regular security awareness training for smart city personnel is essential for developing security-conscious cultures and reducing human error risks. This training should cover topics like phishing recognition, suspicious activity identification, and incident reporting procedures.
Deploying comprehensive security measures across IoT devices, from initial design to operational deployment, is critical for maintaining data security. This involves implementing complete security protocols, regular updates, protected communication channels, and rigorous security testing - all designed to ensure smart city ecosystems remain resilient against evolving threats.
Continuous system log monitoring and analysis are equally important for prompt security incident detection and response. This enables rapid identification of suspicious activities and implementation of appropriate countermeasures. This proactive approach helps maintain data integrity and confidentiality throughout smart city networks.
Creating detailed incident response plans is also critical for efficient security breach management. These plans should outline procedures for identifying, containing, and recovering from security incidents. Regular testing and plan updates ensure continued relevance and effectiveness against emerging threats.