The Evolving Threat Landscape for Web Applications
The Rise of Sophisticated Attacks
Modern web applications are growing increasingly intricate, revealing vulnerabilities that malicious actors exploit with highly refined methods. These threats often utilize zero-day exploits, advanced persistent threats (APTs), and credential stuffing, rendering conventional security defenses insufficient. The escalating frequency of data breaches and the growing financial incentives for attackers highlight the urgent need for comprehensive security solutions that go beyond traditional perimeter defenses.
Cybercriminals continuously refine their tactics, employing social engineering and targeting weaknesses in third-party libraries or APIs embedded within web applications. This demands a forward-thinking and adaptable security approach, shifting from mere access prevention to identifying and neutralizing potential risks throughout the entire application lifecycle.
The Expanding Attack Surface
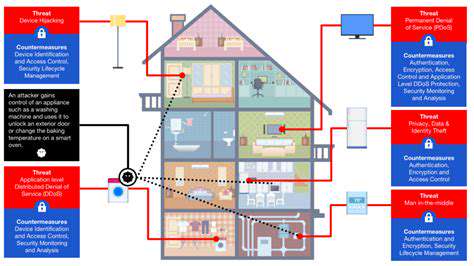
Web applications now face a rapidly widening attack surface due to the widespread adoption of APIs, microservices, and cloud-based infrastructures. While these elements are essential for functionality, they also create new entry points for attackers. Addressing this expanded threat landscape requires a holistic security strategy that incorporates secure coding standards, robust API gateways, and consistent vulnerability evaluations.
Moreover, the rise of mobile devices and IoT integrations adds further complexity to security efforts. Safeguarding these diverse access points necessitates a multi-layered defense strategy tailored to the distinct security challenges posed by each component in the web application ecosystem.
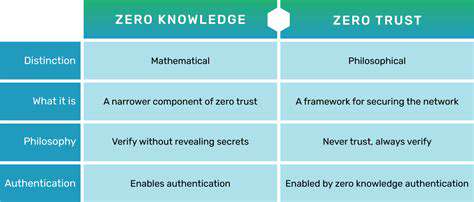
The Importance of Zero Trust
Conventional security frameworks often depend on network segmentation and perimeter-based defenses, which are increasingly ineffective against modern threats. Zero Trust, a security paradigm that operates on the principle of never trust, always verify, is becoming indispensable for web applications. This model mandates ongoing authentication and authorization for every user and device, significantly reducing the potential fallout from security breaches.
Protecting Sensitive Data
Web applications frequently manage highly sensitive data, including financial records, personal identifiers, and proprietary information. Ensuring this data remains secure from unauthorized access, leaks, or tampering is critical. Implementing strong encryption, data obfuscation methods, and stringent access controls forms the backbone of an effective security strategy. Additionally, deploying comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) solutions is vital to curbing the risk of sensitive data exposure.
Mitigating the Impact of Breaches
Even with stringent security protocols, breaches can still occur. Developing a detailed incident response plan is essential for minimizing disruption. This plan should outline clear procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from security incidents while ensuring compliance with regulatory and legal obligations. A proactive stance on incident response is key to limiting damage and sustaining operational continuity.
The Role of Security in Application Development
Security best practices must be woven into every phase of the web application development lifecycle. This includes adopting secure coding standards, conducting regular security audits, and performing ongoing vulnerability assessments. By embedding security into the development process, teams can preemptively address risks and reduce the likelihood of exploits. This fosters a culture of security awareness that permeates the entire organization.
Implementing Zero Trust for Enhanced Web Application Resilience
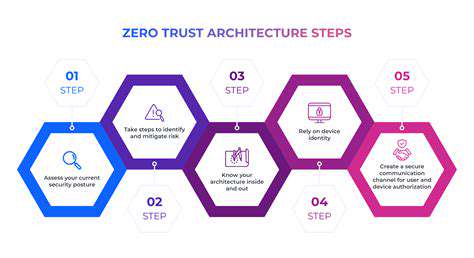
Implementing Zero Trust for Enhanced Security
Zero Trust security represents a fundamental shift in cybersecurity strategy, abandoning the outdated notion that internal users or devices are automatically trustworthy. Instead, it operates on the principle that all access attempts must be continuously verified and authorized. This approach is particularly vital in today’s rapidly evolving threat environment.
Adopting this model requires a thorough overhaul of existing security protocols. Organizations must deploy advanced identity and access management systems, paired with robust threat detection and response mechanisms. This extends security measures beyond the network level to encompass individual applications and data assets.
Defining Trust Boundaries
A cornerstone of Zero Trust is establishing precise trust boundaries. This involves classifying users, devices, and applications into distinct trust tiers based on their risk levels. This granular approach enables customized security controls, allowing organizations to apply appropriate measures based on perceived threats.
Creating these boundaries demands careful evaluation of factors such as data sensitivity and required access levels. This process typically involves a detailed audit of existing infrastructure and workflows.
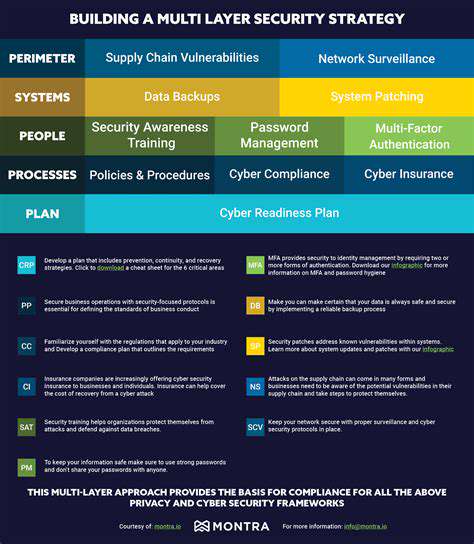
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is indispensable in a Zero Trust framework. By requiring multiple verification steps beyond simple passwords, MFA dramatically lowers the risk of unauthorized access. Strengthening security through MFA is a non-negotiable element in protecting critical resources.
Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Network segmentation and micro-segmentation play pivotal roles in containing breaches. Dividing the network into isolated segments prevents attacks from spreading system-wide. This meticulous approach to segmentation is a defining feature of effective Zero Trust implementation.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Zero Trust necessitates relentless monitoring and real-time threat identification. Systems must constantly scan for anomalous behavior to enable swift responses to emerging threats. Advanced detection capabilities are essential for minimizing operational impact during security incidents.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
A sophisticated Identity and Access Management (IAM) system is central to Zero Trust security. It provides centralized control over user identities and permissions, ensuring only authorized access to sensitive data. Implementing a robust IAM solution is foundational to protecting critical assets.
Security Awareness Training
Comprehensive security training for all personnel is crucial in a Zero Trust environment. Employees must understand security best practices and how to recognize potential threats. Educating staff about phishing and social engineering tactics is fundamental to a successful security strategy. This cultivates a security-aware culture and reduces human error risks.