Grasping Vendor Risk Concepts
Vendor risk evaluation forms a fundamental element of any thorough vendor risk management initiative. The process involves recognizing, examining, and addressing potential hazards connected with suppliers. This undertaking extends further than verifying financial soundness; it includes numerous considerations such as regulatory compliance, operational effectiveness, and possible reputation damage. Complete understanding of these elements becomes essential for making educated partnership decisions and managing relationships efficiently.
Insufficient vendor risk assessment might result in major financial consequences, reputation harm, and business operation interruptions. Early detection and mitigation of potential problems proves crucial for sustaining a dependable supply network.
Recognizing Primary Risk Types
Vendor risk assessment should include various possible threats. These consist of financial instability, regulatory violations, operational shortcomings, and reputation concerns. Economic difficulties, for example, might cause payment failures or contract fulfillment problems. Regulatory non-compliance could subject the organization to penalties and legal consequences. Operational challenges could create product delivery delays or quality reductions.
Reputation risks, frequently ignored, may originate from vendor unethical behaviors or adverse publicity. A complete risk evaluation must account for these diverse aspects to provide thorough understanding of potential vulnerabilities.
Assessing Financial Health
Evaluating a vendor's economic condition represents a vital step in vendor risk management. This process involves reviewing important financial indicators like credit ratings, debt amounts, and cash flow forecasts. Analyzing vendor financial documentation and comparing against industry standards offers valuable perspective on their capacity to meet contractual duties and survive economic challenges. These analyses should remain continuous, adjusting as market situations and vendor performance change.
Examining Operational Capacity
Assessing a vendor's operational capabilities helps determine their ability to consistently provide products or services. This includes reviewing their physical infrastructure, operational processes, and workforce. A thorough evaluation would examine elements like supply chain robustness, emergency recovery strategies, and quality assurance methods. Understanding these operational components helps anticipate potential problems and prepare backup plans.
A vendor's adaptability to market changes and technological developments also represents an important consideration during assessment. This factor should be weighed alongside current infrastructure and procedures.
Analyzing Compliance and Legal Exposures
Adherence to applicable regulations and legal standards remains essential for any vendor relationship. A complete evaluation must examine vendor compliance with industry-specific rules, data protection laws, and other relevant legal structures. This includes identifying possible legal vulnerabilities and associated risks.
Understanding the regulatory environment pertinent to the vendor's industry becomes crucial for comprehensive compliance risk assessment. This proactive strategy helps avoid potential legal complications and reputation damage.
Assessing Reputation Factors
Beyond financial and operational considerations, a robust vendor risk evaluation must account for reputation concerns. A vendor's historical conduct, public perception, and ethical standards require examination. Negative media coverage, unethical behaviors, or controversies could substantially affect organizational reputation and cause significant financial and operational consequences. Detailed research into vendor public presence and perception becomes essential for identifying and reducing these risks.
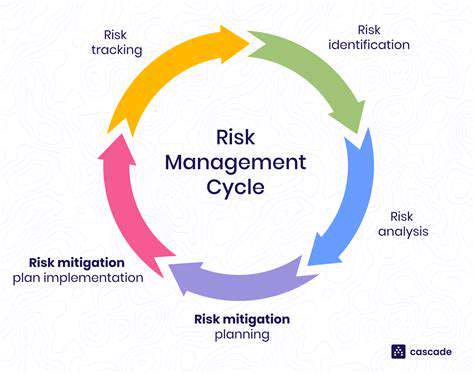
Creating Risk Reduction Plans
After identifying and analyzing risks, developing effective mitigation strategies becomes imperative. This involves formulating contingency plans to handle potential supply chain interruptions or failures. These plans should specify concrete actions for critical situations, including alternative sourcing possibilities, communication methods, and financial protections. Regular review and updates of these strategies remain essential to maintain effectiveness in a changing business environment.
Executing Effective Risk Mitigation Approaches
Comprehending Threat Environments
Successful mitigation techniques demand deep understanding of specific threats facing an organization. This includes pinpointing potential vulnerabilities, analyzing attack methods, and recognizing attacker motivations. Thorough threat analysis becomes crucial for prioritizing resources and developing focused defenses. Reviewing historical incidents and emerging cyberattack trends provides valuable insight for anticipating future threats and adjusting security measures accordingly.
A complete threat assessment should account for both internal and external dangers. Internal threats, including malicious employees or accidental data leaks, can prove equally damaging as external attacks. Understanding human error potential and harmful intentions remains vital for implementing strong security controls.
Building Strong Security Frameworks
Effective security architecture forms the basis for any successful mitigation approach. This involves establishing layered security measures, incorporating network protection, endpoint security, data safeguards, and access controls. Each layer should reinforce the others, creating multi-dimensional defense against various threats. A robust security framework should incorporate scalability and flexibility to accommodate future requirements and evolving risks.
Adopting Secure Development Methods
Security integration should occur throughout the entire software development lifecycle, beginning with initial design stages. This includes incorporating security considerations during requirements definition, testing, and deployment. Proactively identifying and resolving potential vulnerabilities during development can significantly decrease exploit and data breach risks.
Utilizing secure coding practices, conducting rigorous penetration testing, and implementing automated security testing tools represent critical components of secure development.
Implementing Strict Access Controls
Limiting access to sensitive systems and information represents a crucial mitigation component. Establishing strict access controls involves defining clear responsibilities, assigning appropriate permissions, and regularly reviewing access privileges. This ensures only authorized individuals can access critical data, reducing unauthorized access and data breach risks.
Conducting Regular Security Evaluations
Periodic security assessments and audits help identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in existing protections. These evaluations should occur regularly to ensure security measures remain effective against evolving threats. Routine reviews can detect security gaps and facilitate necessary updates and enhancements.
These assessments should cover multiple areas, including network infrastructure, applications, data storage, and access controls.
Developing Incident Response Procedures
A well-structured incident response plan proves essential for effectively managing security incidents. This plan should outline processes for detecting, containing, responding to, and recovering from security breaches. Creating and maintaining an incident response strategy becomes critical for minimizing security incident impacts.
Regular employee training on security awareness and incident response protocols remains vital. This ensures staff can identify and report potential threats, and follow established procedures during incidents.
Maintaining Ongoing Monitoring
Security threats continuously evolve, requiring mitigation strategies to adapt accordingly. Continuous monitoring and improvement of security measures remains essential for maintaining strong protections. Regular review of security logs, system performance monitoring, and emerging threat identification represent key components of ongoing enhancement. This cyclical approach enables organizations to stay ahead of evolving risks and refine security strategies.
Staying informed about current vulnerabilities and applying regular system updates represent essential aspects of continuous monitoring.
Sustained Monitoring and Enhancement in Vendor Risk Management
Defining Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring within vendor risk management (VRM) represents an ongoing activity rather than a single event, involving persistent tracking and evaluation of third-party relationship risks. This includes regular examination of vendor performance, compliance status, and emerging threats or operational changes. The objective involves proactively identifying potential concerns before escalation, enabling more responsive vendor risk management that maintains operational stability and reduces financial and reputational impacts.
This proactive approach extends beyond periodic audits. It incorporates real-time or near real-time analysis of critical risk indicators, facilitating quick responses to emerging threats and ensuring VRM programs remain current and effective at addressing vulnerabilities.
Performance Metrics for Monitoring
Effective continuous monitoring requires establishing clear metrics for each vendor. These metrics should reflect specific risks associated with each vendor relationship and track performance against established benchmarks. Examples might include security protocol adherence, financial stability, regulatory compliance, or service agreement fulfillment. Monitoring these metrics helps identify trends and performance deviations, enabling early intervention before operational impacts occur.
Regular review and adjustment of these metrics remains crucial. As vendor relationships or industry standards evolve, metrics must adapt accordingly to maintain monitoring relevance and effectiveness. This dynamic approach to metric management proves essential for successful continuous monitoring.
Incorporating Automation Technology
Modernizing VRM programs with advanced technology enables effective continuous monitoring. Automated tools can track vendor performance indicators in real-time, providing immediate issue alerts. These systems can also streamline the entire VRM process, from initial vendor onboarding through ongoing risk assessment and reporting. Implementing such technology can substantially reduce manual monitoring requirements, allowing teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Establishing Improvement Feedback Mechanisms
Continuous VRM improvement requires feedback loops. Regular input collection from various stakeholders, including internal teams, vendors, and external experts, helps identify VRM program enhancement opportunities. This feedback can improve risk assessment methods, refine vendor selection criteria, and enhance overall risk management approaches.
Actively gathering and analyzing this feedback proves essential. This ensures VRM programs remain adaptable to evolving threats and market conditions. Effective feedback mechanisms foster continuous learning and improvement, strengthening organizational resilience against vendor-related risks.
Strengthening Vendor Collaboration
Successful continuous monitoring relies on strong vendor partnerships and communication. Establishing clear communication channels with vendors promotes transparency and shared risk management responsibility. This includes providing vendors with necessary tools, resources, and training to help manage their own risks effectively. Fostering collaboration creates shared understanding of continuous monitoring importance, ultimately strengthening overall risk management.
Regular vendor check-ins and proactive communication about performance and compliance prove essential. This builds partnership awareness and helps vendors understand their risk management role. Open communication also enables early issue identification and resolution, preventing escalation into major disruptions.