Implementing Strong Security Protocols
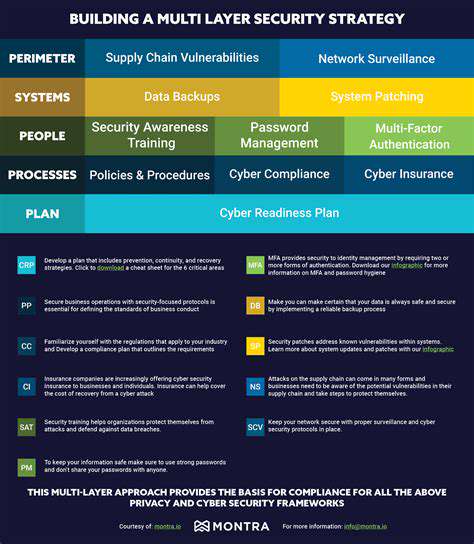
Modern POS security demands defense-in-depth strategies. Tokenization should replace raw card data storage, rendering stolen information useless to attackers. Network segmentation must isolate POS systems from other store networks, while AI-powered anomaly detection monitors for suspicious patterns 24/7.
Physical security is equally vital—tamper-proof hardware modules should encrypt data at the swipe, and surveillance systems must monitor POS terminals for skimming devices. Every firmware update should be cryptographically verified to prevent supply chain attacks.
Regular Security Audits and Training
Quarterly audits must go beyond checkbox compliance, employing forensic tools to uncover hidden vulnerabilities. Employees represent both the weakest link and first line of defense—immersive training simulations should teach staff to recognize advanced social engineering tactics like voice phishing and QR code spoofing.
Tabletop exercises should simulate ransomware attacks on POS systems, testing response teams' ability to maintain operations while containing breaches. Every cashier should complete monthly micro-training sessions on emerging threats.
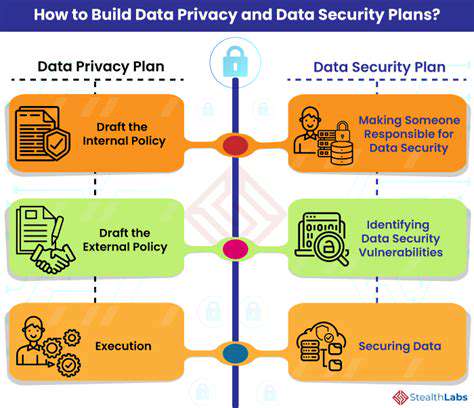
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning
Air-gapped, encrypted backups should occur hourly for critical transaction data, with geographic redundancy to protect against regional outages. Disaster recovery plans must include failover POS systems that can process transactions offline during network outages.
Breach response playbooks should outline precise communication protocols for regulatory bodies, payment networks, and affected customers—delayed or inaccurate disclosures often compound reputational damage. Regular drills must test the organization's ability to restore full POS functionality within predefined recovery time objectives.
Implementing a Comprehensive Security Strategy
Protecting Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems
Next-generation POS security requires hardware-rooted trust mechanisms where cryptographic keys are burned into processor silicon during manufacturing. Behavioral biometrics should analyze typing patterns and touchscreen interactions to detect compromised credentials. All third-party POS applications must undergo sandboxed execution with strict system call restrictions.
Supply chain security is paramount—POS hardware shipments should include tamper-evident packaging with blockchain-verified authenticity certificates. Memory scraping protection must operate at the kernel level to prevent RAM-based attacks. Cloud-based POS systems require attested execution environments that cryptographically verify each transaction's integrity.
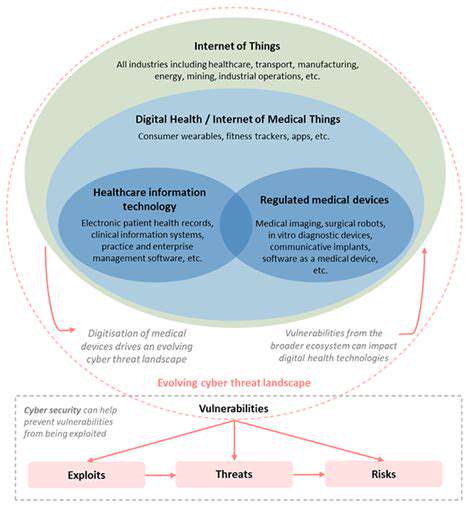
Securing Connected Devices and Networks
IoT device onboarding should incorporate device identity certificates issued by a private PKI infrastructure. Network micro-segmentation must enforce least-privilege access between device classes, with AI-driven traffic baselining to detect lateral movement attempts.
All wireless communications should use quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, with dedicated IoT security gateways performing deep packet inspection. Firmware updates must be delivered via cryptographically signed delta patches with rollback protection. Physical device hardening should include epoxy-sealed components and anti-tamper mesh coatings on circuit boards.
Insider threat programs should implement user behavior analytics that correlate physical access logs with network activity. Privileged access management solutions must enforce just-in-time elevation with multi-party approval workflows. Deception technology should populate networks with realistic honeypot devices to detect and study attacker techniques.
Continuous automated red teaming should simulate advanced persistent threats while maintaining operational systems. Security operations centers must integrate POS, IoT, and network telemetry into unified threat detection platforms powered by machine learning.