Protecting Data Through Secure Communication Protocols
Implementing Robust Access Controls
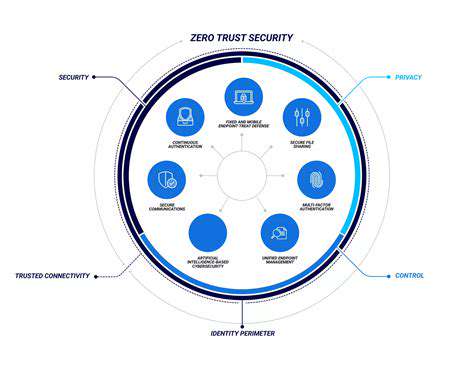
Organizations must prioritize establishing ironclad access management systems to shield confidential information. The foundation lies in crafting precise user roles and permissions, creating digital barriers that keep unauthorized personnel at bay. This meticulous approach acts as the first line of defense against potential breaches. Adding multi-factor authentication transforms security from a simple lock into a complex vault mechanism.
Access control systems aren't set-and-forget solutions. They demand continuous refinement as team structures shift and job responsibilities evolve. Neglecting these updates creates dangerous security gaps where former employees or changed roles might retain inappropriate access levels. Smart organizations treat permission reviews with the same regularity as financial audits.
Employing Encryption Techniques
Modern data protection strategies treat encryption as non-negotiable armor for sensitive information. Whether data travels across networks or rests in storage, encryption scrambles it into unreadable code that only proper keys can decipher. This digital scrambling proves particularly vital for information moving through potentially vulnerable networks or residing on portable devices.
Not all encryption carries equal weight. Security teams must match algorithm strength to data sensitivity - using AES-256 for critical information while potentially lighter options for less sensitive data. The encryption landscape keeps evolving, demanding that security professionals stay current with emerging standards and vulnerabilities.
Utilizing Secure Storage Solutions
Physical security measures form the often-overlooked backbone of comprehensive data protection. From biometric-secured server rooms to tamper-proof storage media, these physical barriers prevent direct access to sensitive information. They serve as the last line of defense when digital protections fail, making their implementation non-negotiable for compliance-focused organizations.
Cloud storage introduces unique security challenges that demand specialized solutions. While providers offer robust tools, their effectiveness depends entirely on proper configuration and active management. Savvy organizations don't just trust cloud security - they verify it through regular audits and penetration testing.
Developing Security Awareness Culture
Human factors represent both the weakest security link and greatest potential strength. Effective training transforms staff from potential vulnerabilities into active defenders. When employees internalize security best practices and develop threat-spotting instincts, they create an organic defense network no software can replicate. This cultural shift turns every team member into a security sensor.
Creating safe reporting channels for suspicious activity completes this human firewall. Organizations that reward vigilance rather than punish false alarms cultivate environments where potential threats surface quickly. This approach catches issues technical systems might miss, particularly sophisticated social engineering attempts.
Conducting Security Audits
Complacency breeds vulnerability in cybersecurity. Regular, rigorous evaluations expose weak points before attackers find them. These assessments should mirror criminal thinking - probing not just for technical flaws but procedural gaps and human factors. Truly comprehensive audits examine both digital infrastructure and the organizational habits surrounding it.
The most effective audits follow through with prioritized remediation plans. Finding vulnerabilities means little without prompt, systematic fixes. Forward-thinking organizations schedule these evaluations with the same regularity as financial reporting, recognizing that digital risks carry equal consequence.
Data Encryption and Storage Security
Advanced Encryption Methods
Modern encryption transforms sensitive health data into indecipherable code that only authorized systems can unlock. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) operates like a digital vault, with 256-bit versions offering bank-level security. These algorithms work constantly in the background, protecting information whether it's moving between devices or resting in databases.
Security teams face complex choices between symmetric and asymmetric encryption approaches. Single-key symmetric systems offer speed advantages but demand military-grade key protection. Dual-key asymmetric solutions enable secure key exchanges while potentially slowing performance. The ideal approach often involves hybrid systems that balance these factors based on specific data sensitivity and usage patterns.
Hardware Security Solutions
Physical security modules represent the gold standard for protecting encryption keys. These tamper-resistant devices create impenetrable vaults within hardware, automatically destroying sensitive information if breached. Their military-grade protection makes them essential for healthcare applications where data breaches carry severe consequences.
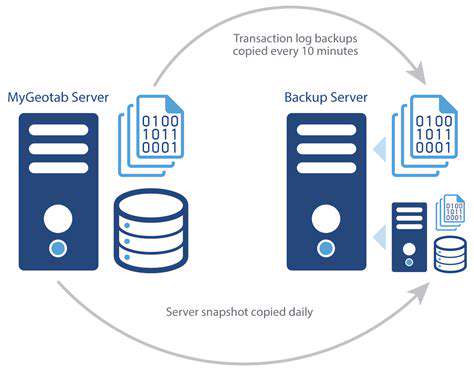
Smart organizations implement layered storage protections that combine encryption with strict access controls. Regular offline backups stored in geographically separate locations provide disaster recovery options. These backups themselves require equal protection, creating concentric circles of security around critical health information.
Network Protection Strategies
Secure communication protocols like TLS/SSL create encrypted tunnels for data transmission. These digital conduits prevent eavesdropping and manipulation attempts during wireless transfers. Proper implementation requires more than just activation - it demands careful configuration and certificate management to avoid potential weaknesses.
Network security extends beyond encryption to include intelligent monitoring systems. Next-generation firewalls and behavior-based intrusion detection create smart perimeters that learn normal patterns and flag anomalies. Continuous traffic analysis spots potential threats in real-time, while comprehensive logging supports forensic investigations when needed.
Comprehensive Data Protection
Effective data loss prevention combines technology with policy. Advanced systems monitor data flows while enforcing strict usage rules, preventing sensitive information from leaving secure environments. These systems grow more sophisticated with machine learning capabilities that understand context and intent.
Tokenization and data masking provide additional protection by replacing sensitive elements with harmless equivalents. When combined with robust audit trails and regular compliance checks, these measures create defense-in-depth architectures. The most secure implementations assume breaches will occur and focus equally on prevention and containment.