The Transformative Potential of AI in GRC
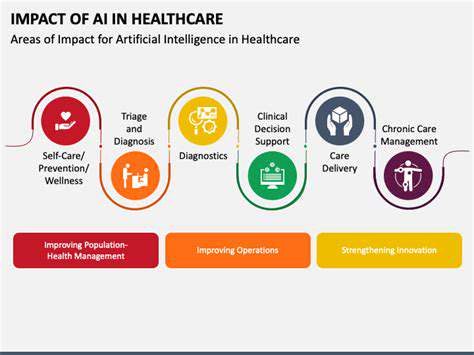
AI's Impact on Various Industries
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming industries across the globe, from healthcare and finance to manufacturing and transportation. AI-powered tools are automating tasks, improving efficiency, and enabling new levels of innovation. This has led to significant cost savings and increased productivity in many sectors.
We're seeing AI applications in healthcare, enabling the development of more accurate diagnostic tools and personalized treatment plans. In finance, AI is revolutionizing fraud detection and risk assessment, while in manufacturing, it's optimizing production lines and improving quality control. This widespread adoption is undeniably reshaping the economic landscape.
Enhanced Customer Experiences
AI is fundamentally changing how businesses interact with customers. From personalized recommendations to chatbots providing instant support, AI-powered systems are making customer interactions more efficient and more satisfying. This personalized approach leads to stronger customer loyalty and increased brand engagement.
Companies are leveraging AI to understand customer preferences and tailor their offerings accordingly. This leads to a more targeted approach, increasing the likelihood of sales and fostering a more positive customer experience. Ultimately, this results in a more profitable business model.
The Rise of Intelligent Automation
AI is driving a wave of intelligent automation in various business processes. This automation frees up human employees to focus on higher-level tasks, such as strategic planning and creative problem-solving. Intelligent automation, therefore, enhances overall employee productivity and job satisfaction.
Repetitive and mundane tasks are often taken over by AI, allowing human employees to concentrate on tasks that require critical thinking and creativity. This shift in the job market requires retraining and upskilling programs to adapt to the changing demands of the modern workplace.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While the potential of AI is immense, it's crucial to address the ethical considerations and challenges that arise with its implementation. Bias in algorithms, job displacement due to automation, and the potential for misuse are all important concerns that need to be carefully managed.
Ensuring fairness and transparency in AI systems is paramount. Robust regulations and ethical guidelines are necessary to mitigate potential risks and ensure responsible development and deployment of AI technologies.
The Future of AI and its Evolution
The future of AI is bright, with continued advancements in machine learning and deep learning promising even more powerful applications. AI will likely play an increasingly important role in addressing global challenges, from climate change to disease eradication. The potential for AI to improve human lives is truly profound.
As AI evolves, it will likely become more integrated into our daily lives, influencing everything from transportation and communication to healthcare and education. This integration will require a proactive approach to adapt and embrace the transformative opportunities AI presents. We must prepare for the inevitable changes and ensure that AI benefits all of humanity.
Automated Compliance Monitoring and Reporting
Automated Compliance Monitoring
Automated compliance monitoring systems are transforming the way organizations approach governance, risk, and compliance (GRC). These systems leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to identify and address potential compliance breaches in real-time, drastically reducing the risk of penalties and reputational damage. By automating the process of monitoring compliance policies and procedures, organizations can significantly improve efficiency and resource allocation, freeing up valuable human resources to focus on higher-level strategic initiatives. This proactive approach allows for early detection of potential issues, enabling swift corrective action and minimizing the impact of compliance failures.
The core function of automated compliance monitoring is to continuously track and assess adherence to various regulations and internal policies. This involves scrutinizing data from diverse sources, including financial transactions, employee activities, and operational processes. Sophisticated algorithms analyze this data to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential violations. This real-time analysis enables organizations to promptly address emerging compliance risks, safeguarding their operations and maintaining a strong ethical posture.
Automated Compliance Reporting
Automated compliance reporting is a critical component of any effective GRC program. AI-powered reporting tools streamline the process of generating and distributing comprehensive compliance reports, significantly reducing the time and resources required for manual reporting. These automated systems provide clear and concise summaries of compliance status, highlighting areas of concern and success. The ability to quickly and accurately generate reports allows organizations to demonstrate their commitment to compliance to stakeholders, including regulators, investors, and customers.
Automated compliance reporting systems typically generate reports in various formats, including dashboards, tables, and charts. These visually appealing and interactive reports offer a clear overview of compliance performance, enabling stakeholders to easily grasp the key metrics and trends. This enhanced visibility fosters transparency and accountability, building trust and confidence in the organization's compliance efforts. Moreover, the ability to generate reports on demand empowers organizations to react swiftly to emerging regulatory changes and maintain a consistent posture of compliance.
Furthermore, these systems can facilitate the generation of customized reports tailored to specific needs and stakeholders. This feature allows for a granular understanding of compliance performance across different departments or functions, enabling targeted interventions and improvements. This level of granularity empowers organizations to proactively address any compliance gaps and maintain a proactive stance on maintaining compliance.
The integration of AI into compliance reporting also facilitates predictive modeling. By analyzing historical data and current trends, AI algorithms can forecast potential compliance risks and offer proactive recommendations for improvement. This predictive capability is invaluable for long-term compliance strategy and proactive risk mitigation.
Automated reporting also helps ensure compliance with reporting deadlines and regulations. By automating the process, organizations avoid costly delays and penalties associated with late or inaccurate reporting. Furthermore, the data generated through automated reporting systems can be used for continuous improvement by identifying patterns and trends in compliance performance.
The automation of compliance reporting significantly improves the efficiency and accuracy of the process, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring timely reporting to regulatory bodies.
Predictive Risk Analysis and Mitigation
Predictive Modeling Techniques
Predictive risk analysis relies heavily on various statistical and machine learning techniques to forecast potential future risks. These methods, such as regression analysis, time series analysis, and machine learning algorithms like decision trees and neural networks, allow us to identify patterns and trends in historical data, which are then used to predict the likelihood and impact of future events. Understanding these patterns is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies.
A key aspect of predictive modeling is the selection of appropriate variables. Choosing the right variables to include in the model is crucial for accurate predictions. Including irrelevant variables can lead to inaccurate predictions and ineffective risk assessments. Using sophisticated techniques for variable selection and feature engineering is often necessary to achieve reliable results.
Data Collection and Preparation
Accurate risk predictions require high-quality and comprehensive data. This involves collecting data from various sources, including internal databases, external market information, and expert opinions. Thorough data collection is the foundation of a robust risk analysis process.
Data preparation is equally important. This includes cleaning the data to remove inconsistencies, handling missing values, and transforming the data into a suitable format for the chosen predictive model. Data preparation ensures the accuracy and reliability of the analysis.
Risk Assessment and Prioritization
The results from the predictive models need to be interpreted and assessed in the context of the organization's strategic objectives. This involves analyzing the predicted probabilities and impacts of different risks to understand their potential consequences. A clear understanding of the potential impact of each risk is essential for prioritizing mitigation efforts.
Mitigation Strategies and Implementation
Once the risks have been assessed and prioritized, appropriate mitigation strategies need to be developed and implemented. These strategies might include risk avoidance, risk reduction, risk transfer, or risk acceptance. Developing and implementing mitigation strategies is essential to reducing the likelihood and/or impact of the identified risks.
Implementing these strategies often requires adjustments to existing processes and procedures. Careful planning, communication, and stakeholder engagement are vital for successful implementation. This ensures that the organization is well-prepared to handle potential disruptions.
Monitoring and Evaluation
Predictive risk analysis is not a one-time process. Regular monitoring and evaluation of the risk models and mitigation strategies are essential to ensure continued effectiveness. This involves tracking the actual outcomes against the predicted risks to identify any deviations or emerging trends.
By continuously monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of the strategies, organizations can adapt their approaches as needed and enhance their preparedness for future risks. This iterative process allows for proactive adjustments and ensures the longevity of the risk management framework.
Enhanced Decision-Making and Efficiency
Improved Strategic Planning
Enhanced decision-making capabilities directly translate into more robust strategic planning. By leveraging data-driven insights and predictive modeling, organizations can anticipate future trends and challenges more effectively. This proactive approach allows for the development of more adaptable and forward-thinking strategies, ultimately positioning the organization for sustained success in a dynamic market. This improved foresight also allows for better allocation of resources.
Streamlined Operational Processes
Improved efficiency in decision-making often leads to streamlined operational processes. By identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies in existing workflows, organizations can implement changes that optimize resource utilization and reduce redundancy. This streamlined approach results in significant cost savings and increased productivity. Optimizing these processes also enhances employee morale and satisfaction, as it reduces unnecessary tasks and promotes a more efficient work environment.
Enhanced Risk Management
A crucial aspect of enhanced decision-making is the improvement of risk management protocols. By analyzing potential risks and developing mitigation strategies, organizations can protect themselves against unforeseen events and maintain stability. This proactive approach reduces the likelihood of costly errors and disruptions, ensuring business continuity. Implementing effective risk assessments is key to minimizing potential damage.
Improved Resource Allocation
Data-driven decision-making enables organizations to allocate resources more effectively. By analyzing data on project performance, market trends, and resource availability, organizations can optimize their resource allocation strategies. This leads to better utilization of financial and human capital, resulting in a more profitable operation. Efficient resource allocation maximizes returns on investment and ensures that resources are directed towards areas with the highest potential for success.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Improved decision-making can significantly enhance customer satisfaction. By understanding customer needs and preferences through data analysis, organizations can tailor their products, services, and marketing strategies to better meet those needs. This personalized approach fosters stronger customer relationships and loyalty, leading to increased customer retention and advocacy. A more customer-centric approach also opens up opportunities for innovation and product development aligned with actual customer requirements.
Increased Competitive Advantage
Organizations with enhanced decision-making capabilities often gain a significant competitive edge. The ability to quickly adapt to changing market conditions, make informed strategic choices, and optimize operational processes allows them to outperform competitors. This competitive advantage translates to higher market share, increased profitability, and a stronger overall position in the industry. In today's competitive landscape, the ability to make timely and effective decisions is critical for survival and growth.