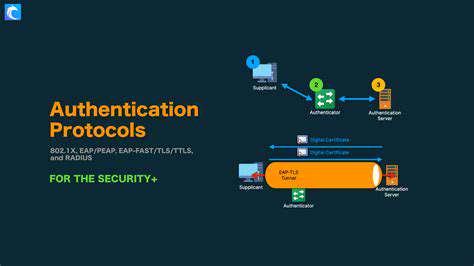
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices into agricultural practices is transforming the industry. From precision irrigation systems that optimize water usage to automated harvesting robots that streamline labor, connected farming offers unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity. This interconnected system collects vast amounts of data, providing farmers with insights into soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health, enabling them to make data-driven decisions that maximize yields and minimize waste. This technological advancement has the potential to significantly increase food production, especially in regions with limited resources or challenging climates.
Furthermore, the implementation of IoT sensors in livestock management allows for real-time monitoring of animal health and behavior. This data-driven approach can prevent disease outbreaks, optimize feeding strategies, and ultimately improve animal welfare. The ability to remotely monitor and manage various aspects of agricultural operations, from field to farm, offers significant benefits in terms of cost savings, resource optimization, and enhanced overall farm management.
Vulnerabilities and the Need for Robust Cybersecurity Measures
While the benefits of connected agriculture are substantial, so are the potential cyber risks. The interconnected nature of these systems creates a complex network susceptible to various threats, including malicious attacks, data breaches, and system failures. Compromised irrigation systems could lead to inefficient water usage and crop damage. Unauthorized access to livestock monitoring systems could result in compromised animal health and welfare. This interconnectedness also means a single point of failure can have cascading effects across the entire operation. Therefore, robust cybersecurity measures are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure the continued success of connected agriculture.
Implementing strong passwords, regular software updates, and intrusion detection systems are crucial steps in securing these systems. Furthermore, establishing clear security protocols and training employees on best practices is paramount to prevent human error. Security audits should be conducted frequently to identify and address vulnerabilities proactively. This proactive approach to cybersecurity is not just about preventing attacks; it's about ensuring the long-term viability and sustainability of connected agriculture in the face of evolving cyber threats.
The increasing reliance on data in agriculture necessitates the development of secure data storage and transmission protocols. Encryption and access controls are vital to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Furthermore, a comprehensive disaster recovery plan must be in place to ensure that critical systems can be restored quickly and efficiently in the event of an attack or failure. Cybersecurity should be considered an integral part of the design and implementation of any connected agricultural system.
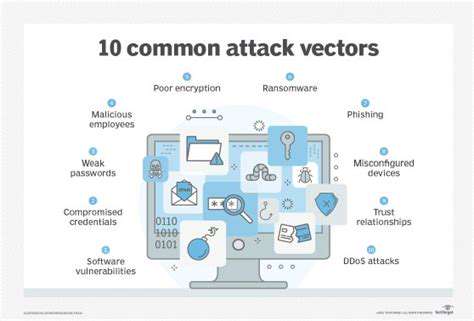
Protecting Data and Critical Infrastructure
Ensuring Data Integrity in Agricultural IoT
Maintaining the accuracy and reliability of data collected by agricultural IoT devices is paramount. Data integrity issues can lead to incorrect decisions regarding crop management, livestock care, and resource allocation. Robust data validation procedures, including redundancy checks and cryptographic hashing, are essential to ensure the trustworthiness of the information used for critical farm operations. Implementing these measures safeguards against errors and malicious manipulation, ultimately maximizing the value derived from the collected data.
Implementing secure data storage solutions is equally crucial. This involves encrypting sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Data encryption protocols should be chosen based on industry best practices and regulations to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access and breaches. This proactive approach not only protects against cyberattacks but also mitigates the potential for data loss and regulatory fines.
Securing Communication Channels
Agricultural IoT systems rely heavily on communication networks to transmit data between sensors, devices, and the cloud. These channels are vulnerable to interception and manipulation. Employing robust encryption protocols, such as Transport Layer Security (TLS), is essential to protect the confidentiality and integrity of the data transmitted. This ensures that only authorized parties can access the information flowing through the network.
Employing secure network architectures, like virtual private networks (VPNs), further enhances the security posture. VPNs create encrypted tunnels between devices, making it significantly more difficult for attackers to eavesdrop on or alter the data being exchanged. These measures are critical to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of communication channels.
Protecting Against Cyberattacks
Agricultural IoT systems are increasingly susceptible to cyberattacks. These attacks can range from simple denial-of-service (DoS) attempts to sophisticated malware infections. Implementing robust security measures, such as intrusion detection systems (IDS) and firewalls, is crucial to detect and prevent malicious activities. Continuous monitoring and proactive threat intelligence are vital to stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical to identifying and addressing potential weaknesses in the system. This proactive approach helps to prevent exploitation by attackers and maintain a strong security posture. Furthermore, training personnel on security best practices and awareness programs will significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
Implementing Access Control Measures
Establishing clear access control policies and procedures is essential to restrict unauthorized access to sensitive data and resources. This includes defining user roles and permissions, implementing multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing and updating access privileges. These measures help to limit the potential impact of a security breach and ensure that only authorized personnel can access critical data and systems.
Hardware Security Considerations
The security of agricultural IoT devices extends beyond the software and communication layers. Physical security measures are also crucial, particularly for devices located in remote or vulnerable locations. Implementing robust physical security measures, such as tamper-proof enclosures, physical access controls, and regular security assessments, is essential to deter unauthorized access to the hardware components. These precautions can prevent attackers from physically altering the devices or stealing sensitive data.
Developing Incident Response Plans
A well-defined incident response plan is crucial to mitigate the impact of a security breach. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from security incidents. It should include clear communication protocols, roles and responsibilities, and a process for notifying affected parties and regulatory bodies. Having a comprehensive incident response plan will allow for a swift and organized response to any potential security incidents, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Staying Updated with Security Best Practices
The agricultural IoT landscape is constantly evolving, and new security threats and vulnerabilities emerge regularly. Staying updated with the latest security best practices and industry standards is essential to maintain a strong security posture. This includes regularly reviewing security advisories, attending relevant training sessions, and participating in industry forums to stay informed about emerging threats and effective mitigation strategies. Continuous learning and adaptation are key to effectively safeguarding connected farm equipment.