Strengthening Supply Chain Security Through Proven Strategies

Multi-Layered Authentication Systems
Modern cybersecurity demands more than simple passwords. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has become the industry standard for protecting sensitive accounts. This approach combines multiple verification methods, like biometric scans with temporary access codes, creating multiple barriers against unauthorized entry. Organizations that implement comprehensive MFA solutions see dramatic reductions in account breaches, often cutting incidents by 80-90% according to recent industry reports.
The effectiveness of MFA increases exponentially when paired with proper password hygiene. Rather than reusing credentials, each system should have distinct, complex passwords that follow current NIST guidelines. Many security professionals recommend using passphrases instead of traditional passwords, as they're easier to remember but harder to crack through brute force methods.
Comprehensive Network Defense Tactics
Contemporary network security requires a defense-in-depth approach. Modern firewall solutions now incorporate AI-driven threat detection, while next-generation intrusion prevention systems automatically block suspicious traffic patterns. What many organizations overlook is the critical importance of timely system updates - unpatched vulnerabilities remain the most common entry point for cyber attacks.
Strategic network segmentation has proven particularly effective in recent years. By creating isolated zones for different business functions (finance, HR, operations), companies can limit the blast radius of potential breaches. This containment strategy has become essential in an era where sophisticated attackers often remain undetected for months.
Security-First Development Methodologies
The shift-left movement in software development emphasizes integrating security early in the SDLC. Developers now receive specialized training in OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities, with code reviews focusing as much on security flaws as functionality. Many organizations have adopted automated scanning tools that check for common vulnerabilities during the build process.
Continuous Security Evaluation Processes
Quarterly security audits have given way to continuous monitoring solutions in progressive organizations. These systems provide real-time visibility into security postures, with automated alerts for configuration drifts or new vulnerabilities. Forward-thinking companies now combine automated scanning with regular red team exercises, creating a more realistic assessment of defensive capabilities.
Penetration testing has evolved beyond simple vulnerability scans. Modern ethical hackers use the same advanced techniques as criminal actors, including social engineering and zero-day exploits. These realistic simulations provide invaluable insights that generic scanning tools might miss.
Advanced Data Protection Strategies
Data encryption standards have advanced significantly with the adoption of quantum-resistant algorithms. The current best practice involves encrypting data both at rest and in transit, with separate keys for different sensitivity levels. Many organizations are moving toward homomorphic encryption, which allows processing encrypted data without decryption.
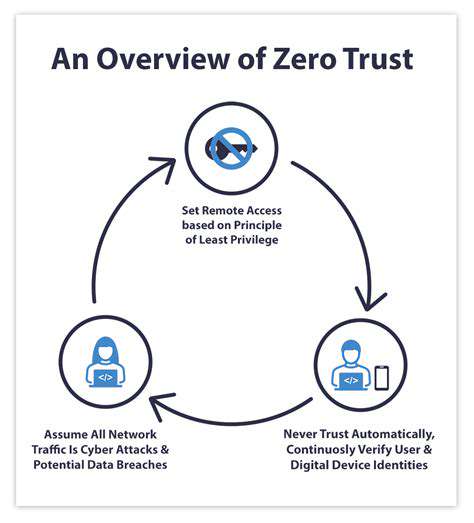
Modern access control systems now incorporate behavioral analytics, detecting unusual access patterns that might indicate compromised credentials. The principle of least privilege has become fundamental, with just-in-time access replacing permanent elevated permissions in many enterprises.
Overcoming Global Supply Chain Complexities
Geopolitical Risk Management
Today's volatile international landscape requires sophisticated geopolitical risk analysis. Leading companies employ dedicated teams to monitor developing situations, with scenario planning for various disruption possibilities. The most resilient organizations maintain diversified supplier networks across multiple regions, avoiding over-reliance on any single geography.
Advanced analytics now help predict potential trade route disruptions weeks or months in advance. Some firms use AI-powered platforms that correlate political events, weather patterns, and economic indicators to forecast supply chain impacts with surprising accuracy.
Regulatory Compliance Frameworks
The regulatory patchwork across jurisdictions has spawned specialized compliance management systems. These platforms track changing requirements in real-time, automatically updating compliance checklists and documentation templates. Many multinationals now maintain local compliance officers in each operating region to navigate nuanced legal landscapes.
Emerging blockchain solutions show promise for simplifying cross-border documentation. Smart contracts can automatically validate compliance at each supply chain node, reducing administrative burdens while improving auditability.
Unified Cybersecurity Standards
Forward-looking organizations are implementing ISO 27001-aligned security frameworks across all international operations. These standardized approaches include mandatory security controls, regular third-party audits, and centralized monitoring of all connected systems. The most advanced implementations use SD-WAN solutions to create secure, encrypted tunnels between global locations.
Employee cybersecurity training has become increasingly sophisticated, with localized content addressing regional threat landscapes and compliance requirements. Many companies now use AI-driven training platforms that adapt content based on individual knowledge gaps and learning styles.
Global IP Protection Strategies
Comprehensive IP protection now begins with thorough audits of all innovations, followed by strategic filings in key jurisdictions. Many companies employ digital watermarking and blockchain timestamping to establish ownership claims. In high-risk regions, some firms implement physical security measures at manufacturing facilities to prevent unauthorized duplication.
Legal teams now work closely with engineering departments to identify patentable innovations early in development cycles. Some organizations maintain defensive publication programs to prevent competitors from patenting similar technologies.
End-to-End Supply Chain Visibility
Modern tracking systems combine IoT sensors, blockchain ledgers, and AI analytics to provide unprecedented supply chain transparency. These systems can trace individual components back to their source materials, with automated alerts for any deviations from expected routes or handling procedures.
The most advanced implementations integrate sustainability metrics, allowing companies to verify ethical sourcing claims in real-time. Some consumer-facing brands now share portions of this tracking data with customers through smartphone apps.
Resilience Planning Methodologies
Contemporary disruption planning uses wargaming techniques to stress-test supply chains against various scenarios. These exercises often reveal unexpected vulnerabilities and dependencies. Many companies now maintain digital twin simulations of their supply networks to model potential disruptions and test mitigation strategies.
The most resilient organizations maintain strategic reserves of critical components while cultivating relationships with alternative suppliers. Some have even invested in small-scale manufacturing capabilities for essential items, creating valuable flexibility during crises.