Securing Cloud Workloads with Zero Trust Policies

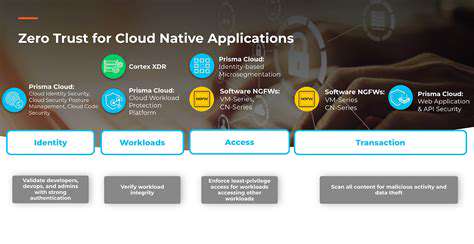
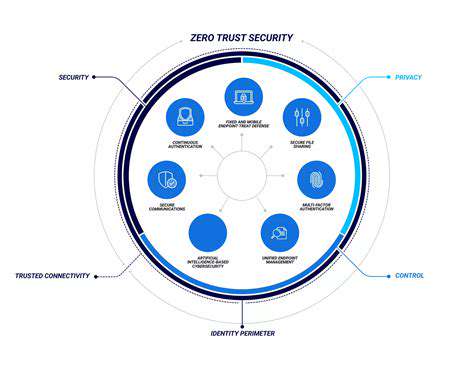
Zero Trust Security for Cloud Workloads
Adopting a zero-trust framework for cloud workloads has become indispensable in our current era of evolving cyber threats. Unlike conventional models, this methodology operates on the principle of never trust, always verify, scrutinizing every access request irrespective of origin. This paradigm shift effectively shrinks potential attack vectors while fortifying organizational defenses.
The distributed nature of cloud resources makes traditional perimeter-based security inadequate. Legacy security approaches frequently prove insufficient for safeguarding decentralized assets, exposing vital systems and information to potential compromise. Zero trust counteracts these vulnerabilities through rigorous access management and ongoing authentication protocols.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Incorporating multi-factor authentication forms the backbone of any comprehensive zero-trust implementation. MFA enhances protection by mandating multiple verification methods, such as combining password entry with device-based codes or fingerprint recognition. This layered approach substantially diminishes the likelihood of unauthorized system access.
The requirement for diverse authentication elements creates formidable barriers for malicious actors, even if they obtain partial credentials. This security measure significantly bolsters data protection while maintaining operational integrity.
Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Implementing network segmentation strategies involves partitioning infrastructure into discrete, protected zones. Such compartmentalization contains potential breaches to isolated sections, obstructing lateral movement across systems. This methodology effectively quarantines critical assets, thereby improving security resilience.
Strategic isolation of sensitive components through segmentation dramatically improves threat containment capabilities. The resultant architecture substantially enhances cloud workload protection by minimizing potential breach consequences.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
DLP mechanisms serve as critical safeguards for confidential information within cloud environments. These systems oversee and regulate data flows, preventing accidental disclosures or unauthorized transfers. Proper DLP implementation not only reduces breach risks but also ensures adherence to privacy mandates.
Comprehensive DLP deployment creates robust barriers against data exfiltration attempts. Additionally, these solutions facilitate regulatory compliance while maintaining stringent information security standards.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
SIEM platforms deliver crucial visibility into cloud workload security events. By aggregating and analyzing security data, these systems flag potential threats and anomalous behavior. This anticipatory methodology enables swift incident response, potentially limiting damage.
Continuous log monitoring through SIEM solutions allows early detection of emerging security concerns. Such proactive surveillance strengthens cloud defenses against sophisticated cyber threats.
Vulnerability Management
Effective cloud security necessitates systematic vulnerability oversight. Routine scanning and remediation of system weaknesses prevents their exploitation by threat actors. This preventive approach reduces exposure while enhancing overall protection.
Establishing thorough vulnerability management processes ensures constant surveillance of cloud assets. Timely identification and resolution of security gaps significantly diminishes potential attack success rates.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Periodic security evaluations represent a cornerstone of robust cloud protection. These examinations assess control effectiveness, pinpoint vulnerabilities, and recommend enhancements. The iterative refinement process builds resilient defenses against emerging threats.
Consistent security audits uncover critical gaps in protective measures. Addressing these deficiencies substantially strengthens organizational security posture against potential intrusions.
Protecting Cloud Applications and APIs
Securing Infrastructure
Cloud application security begins with comprehensive infrastructure protection. Effective defense requires a holistic strategy encompassing all infrastructure components. Stringent security measures must permeate every phase, from initial architecture through continuous maintenance. This includes safeguarding VMs, network components, storage systems, and supporting elements—any vulnerability in these foundational pieces can compromise entire applications.
Implementing granular access controls remains paramount. The principle of least privilege significantly reduces risks associated with credential compromise. Preventive security measures, including regular audits, prove far more effective than reactive responses to security incidents.
Protecting Application Logic
Application code security demands equal attention to infrastructure concerns. Secure development practices must include thorough input validation, robust authentication frameworks, and vetted code libraries. These measures collectively mitigate common application vulnerabilities.
Timely application updates and patches neutralize known security weaknesses in codebases. Comprehensive testing methodologies, including penetration assessments, reveal potential logic flaws before deployment. This proactive identification and resolution of issues prevents subsequent exploitation.
Data Protection and Compliance
Cloud-based data security requires multilayered protection strategies. Encryption protocols for both stored and transmitted information create fundamental security barriers. Adherence to regulatory standards (HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS) maintains legal compliance while preserving organizational reputation.
Verified data recovery procedures ensure business continuity following system failures or attacks. These safeguards, combined with proper encryption and access governance, satisfy both security and compliance requirements.