Implementing Zero Trust: Key Considerations for Financial Institutions
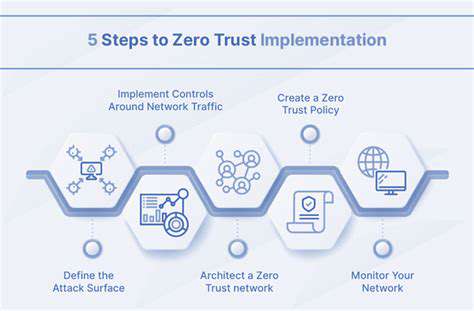
Implementing Zero Trust: A Multi-Layered Approach
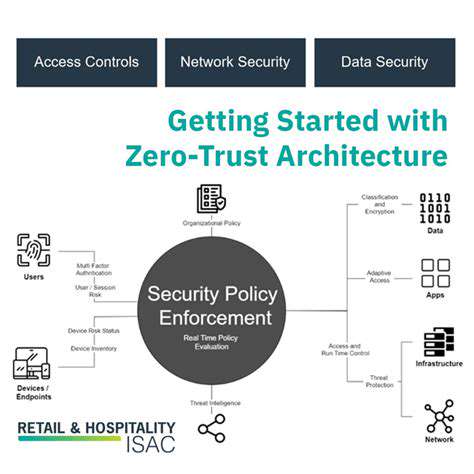
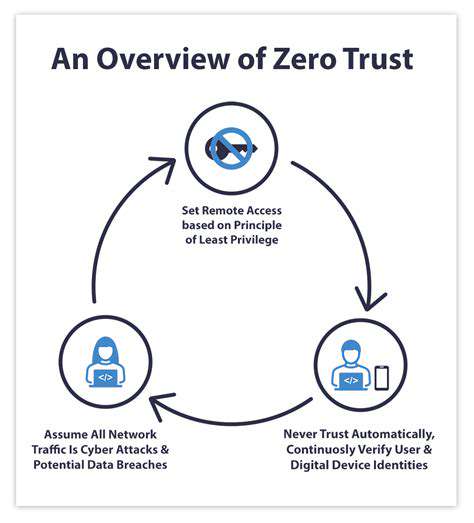
Zero Trust architecture represents a fundamental rethinking of network security. Moving beyond outdated perimeter models, it operates on a verify first, trust never principle where every access request undergoes rigorous scrutiny. This layered security approach minimizes potential attack vectors while significantly strengthening overall protection.
The transition to Zero Trust requires more than new technologies—it demands a complete cultural shift in how organizations approach security. Successful implementation involves integrating identity verification, real-time monitoring, and dynamic security policies into a cohesive defense strategy.
Identifying and Validating Users and Devices
Zero Trust's foundation lies in rigorous identity verification. Implementing multi-factor authentication and robust password requirements forms the first line of defense. Equally important are clearly defined access policies that specify exactly which resources each authenticated entity may access.
Thorough identity verification processes are critical for preventing unauthorized system access. By continuously validating credentials, organizations can stop potential breaches before they gain traction.
Enforcing Micro-segmentation and Access Control
Network micro-segmentation plays a pivotal role in Zero Trust implementations. By creating isolated network zones, organizations can contain potential breaches and limit unauthorized lateral movement. This granular approach to network architecture provides precise control over resource access while dramatically reducing potential attack surfaces.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Zero Trust is an ongoing process requiring constant vigilance. Advanced monitoring tools coupled with sophisticated threat detection systems enable organizations to identify and respond to suspicious activities in real time. This proactive stance significantly reduces potential damage from security incidents.
Immediate threat detection capabilities are indispensable for effective Zero Trust implementations. Rapid identification of anomalies allows security teams to respond before attackers can establish footholds.
Adaptive Security Policies and Response
Effective Zero Trust strategies employ dynamic security policies that evolve alongside emerging threats. Regular policy reviews and updates ensure defenses remain effective against new attack vectors. Automated response mechanisms further enhance security by enabling instantaneous reactions to detected threats.
Security Awareness Training and Incident Response
Human factors continue to represent significant security vulnerabilities. Comprehensive training programs help employees recognize and avoid common threats, while well-practiced incident response protocols ensure swift, effective reactions to security events.
Ongoing security education transforms employees into active participants in organizational defense. When staff members understand their role in maintaining security, they become valuable assets in threat prevention.
Protecting Customer Data with Zero Trust Principles
Implementing Zero Trust for Enhanced Security
Adopting Zero Trust in financial services requires abandoning traditional security assumptions. Instead of relying on network perimeters, it establishes granular access controls that verify every request for sensitive data—regardless of origin. Continuous authentication mechanisms and regular system audits form the backbone of this approach, dramatically reducing potential attack surfaces while addressing both external and internal threats.
The never trust, always verify philosophy extends across all organizational levels. Comprehensive authentication frameworks, including mandatory multi-factor authentication and periodic security evaluations, ensure consistent protection throughout the enterprise.
Data Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Data segmentation strategies provide critical protection for financial institutions. By compartmentalizing sensitive information, organizations can limit breach impacts—ensuring unauthorized access to one dataset doesn't compromise others. This meticulous data management approach proves particularly valuable in financial contexts where data breaches carry severe consequences.
Network micro-segmentation complements data segmentation by creating isolated network zones. This dual approach controls access at both data and network levels, preventing threat movement across systems while enabling precise access management.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Zero Trust implementations require perpetual monitoring to maintain effectiveness. Advanced detection systems and security information platforms provide real-time visibility into network activities, enabling rapid identification of potential threats. This constant vigilance is essential for minimizing breach impacts and maintaining operational continuity.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA solutions add another layer of protection by analyzing behavioral patterns. These systems detect anomalies that may indicate compromised credentials or insider threats, providing early warning for potential security incidents. In financial environments, such proactive detection capabilities are invaluable for preventing fraud and data breaches.
Access Control and Least Privilege
Robust access management systems enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring users access only the resources necessary for their roles. This minimization of access rights significantly reduces potential damage from account compromises while helping maintain regulatory compliance and customer confidence.
Security Awareness Training and Employee Education
Effective Zero Trust strategies recognize the human element in security. Comprehensive training programs equip employees to identify and avoid common threats, while regular reinforcement of security best practices helps build an organizational culture of vigilance. In financial institutions, where human errors can have severe consequences, such education programs provide essential protection.