Understanding the Foundation of Zero Trust
IAM, or Identity and Access Management, is the bedrock upon which a Zero Trust security strategy is built. It's the crucial first step in establishing a comprehensive security posture by meticulously controlling access to resources. Properly implemented IAM policies ensure that only authorized individuals and systems can access sensitive data and applications, thereby minimizing the attack surface.
By meticulously defining who has access to what, and when, IAM empowers organizations to significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized data breaches and insider threats. This proactive approach to security is a fundamental component of a robust Zero Trust framework.
Defining and Enforcing Access Policies
A core aspect of IAM lies in defining and enforcing granular access policies. These policies specify which users, roles, and applications have permission to interact with specific resources. This detailed control extends to defining the types of actions permitted, such as reading, writing, or executing operations.
This granular control is essential for minimizing the blast radius of a security incident. If a breach occurs, the damage is contained because only the compromised user or application has limited access.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Security Awareness Training
IAM systems frequently incorporate multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security. MFA adds an extra layer of verification beyond a simple username and password, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access. This additional layer of security is crucial in a Zero Trust environment.
Complementing MFA, effective security awareness training plays a vital role in IAM. Educating users about phishing attempts, social engineering tactics, and the importance of strong passwords creates a human firewall, making it harder for attackers to exploit vulnerabilities in human behavior.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) for Enhanced Security
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a critical component of IAM, allowing administrators to assign specific roles to users, each with a defined set of permissions. This approach ensures that employees only have the access needed to perform their job functions, minimizing the risk of accidental or malicious data breaches.
Centralized Identity Management for Streamlined Operations
Centralized identity management within an IAM system streamlines operations by providing a single source of truth for user identities and access permissions. This centralized approach simplifies administration, reduces redundancies, and allows for more efficient management of user accounts and access rights across the organization.
Continuous Monitoring and Auditing for Proactive Security
A robust IAM system must incorporate continuous monitoring and auditing capabilities. This involves tracking user activities, reviewing access logs, and identifying suspicious patterns or anomalies. This proactive approach to security allows organizations to swiftly detect and respond to potential security breaches, ensuring the integrity of their data and systems.
Regular audits and reviews are essential to ensure the effectiveness of the IAM policies and to proactively identify and address any potential vulnerabilities.
Integrating IAM with Zero Trust Principles
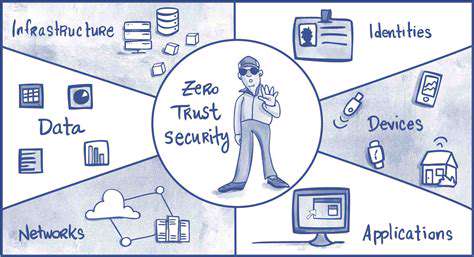
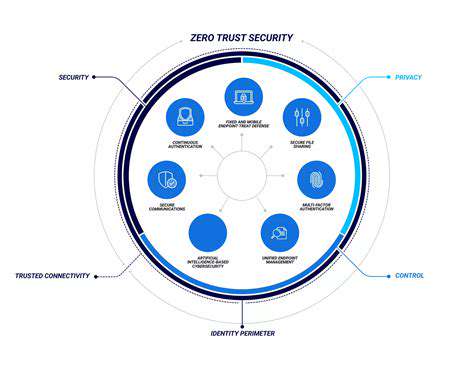
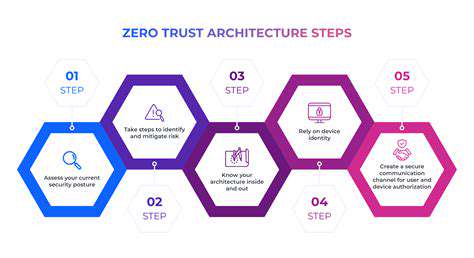
IAM is intrinsically linked to Zero Trust principles by providing the foundation for enforcing least privilege access. Zero Trust assumes no implicit trust in any user or device. IAM ensures that access is continuously verified and authorized, aligning perfectly with the Zero Trust approach of never trust, always verify. This collaborative relationship between IAM and Zero Trust is essential for modern security architectures.

Continuous Monitoring and Adaptive Responses

Continuous Monitoring for Enhanced Performance
Continuous monitoring is crucial for maintaining optimal system performance and identifying potential issues proactively. By constantly tracking key metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory consumption, and network traffic, organizations can detect anomalies and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed. This proactive approach allows for swift intervention, preventing performance degradation and minimizing downtime.
Implementing a robust continuous monitoring system ensures that applications and infrastructure are consistently operating at peak efficiency. This proactive approach not only improves performance but also significantly reduces the risk of unexpected failures and associated costs. Furthermore, continuous monitoring facilitates data-driven decision-making, enabling organizations to optimize resource allocation and fine-tune their systems for maximum efficiency.
Adaptive Strategies for Dynamic Environments
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, static configurations are often insufficient. Adaptive strategies are essential for dynamically adjusting to changing conditions and maintaining optimal performance. These strategies leverage real-time data to modify system parameters and configurations, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.
Real-Time Data Analysis for Immediate Action
Real-time data analysis is paramount for effective continuous monitoring. By processing data as it's generated, systems can identify anomalies and potential problems immediately. This rapid identification allows for immediate corrective action, minimizing the impact on performance and ensuring a seamless user experience.
Effective real-time analysis tools provide a comprehensive view of system health, enabling quick responses to emerging challenges. This agility is vital in modern applications that demand high availability and responsiveness.
Proactive Issue Identification and Resolution
Continuous monitoring facilitates proactive issue identification, allowing for the resolution of problems before they impact users. By detecting potential issues early, organizations can implement preventative measures and avoid costly downtime. This proactive approach significantly improves overall system reliability and user satisfaction.
Identifying issues before they escalate is critical to maintaining a stable and reliable system. This preventative approach saves valuable time and resources that would otherwise be spent on reactive measures.
Integration with Automation for Enhanced Efficiency
Integrating continuous monitoring with automation tools further enhances efficiency. Automated responses to identified issues streamline problem resolution, reducing manual intervention and minimizing downtime. This integration allows for a more robust and reliable monitoring system.
Automated responses to issues are critical for maintaining optimal performance and minimizing downtime. The integration of monitoring with automation creates a self-healing system, capable of adapting to changing conditions and minimizing the impact of potential disruptions.