The Rise of Zero Trust Architectures
Understanding the Core Principles of Zero Trust
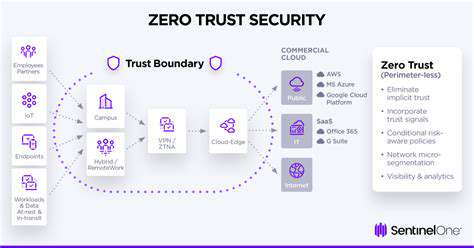
Zero trust is a security model that operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. This contrasts sharply with traditional network security models that often assume trust within a defined perimeter. Crucially, zero trust doesn't inherently trust any user, device, or application, regardless of its location within the organization's network or outside of it. Instead, it demands continuous verification and authorization for every access request, ensuring that only authenticated and authorized entities can access resources.
A key component of zero trust is the granular control it provides over access. This granular control allows organizations to precisely define what resources each user or device can access, minimizing the potential damage from a compromised account or device. This meticulous approach contrasts sharply with traditional security models that often rely on broad access rights, which can create significant vulnerabilities if a single point of failure occurs.
The Role of Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) plays a critical role in implementing a zero trust architecture. IAM systems are essential for verifying the identity of users and devices, and for managing their access privileges. Effective IAM systems provide the foundation for zero trust by enabling organizations to track and manage access requests in real-time, ensuring that only authorized individuals and devices can access sensitive data and resources.
Zero trust architectures heavily rely on strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA). This approach significantly strengthens security posture by requiring multiple forms of verification to confirm a user's identity, effectively mitigating the risk of unauthorized access attempts. Implementing robust IAM practices is crucial for establishing a secure zero trust environment.
Benefits of Zero Trust for Organizations
Implementing zero trust architectures offers a multitude of benefits for organizations. These include enhanced security posture, reduced attack surface, and improved compliance with regulatory requirements. By minimizing the attack surface and strictly controlling access to resources, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. This approach helps companies better meet regulatory requirements and maintain compliance standards.
Moreover, a zero trust architecture enables organizations to better adapt to evolving security threats. The dynamic nature of modern cyber threats necessitates a security model that can quickly adapt to new vulnerabilities and threats. Zero trust's granular control and continuous verification allow organizations to respond quickly and effectively to emerging security risks.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
Despite the numerous benefits, implementing a zero trust architecture presents certain challenges. One significant hurdle is the complexity of managing the increased number of access points and policies. The granular control required for zero trust necessitates a sophisticated approach to access management, which can be challenging for organizations with complex infrastructures and numerous users.
Another challenge lies in the potential cost associated with implementing and maintaining zero trust solutions. Implementing the necessary tools and technologies, along with the training required for personnel to manage the new system, can represent a significant investment. Careful planning and budgeting are crucial to mitigate these financial concerns.
Security Considerations in a Cloud Environment
Zero trust principles become even more critical in cloud environments, where access to resources can be highly distributed and dynamic. The distributed nature of cloud environments requires a robust security posture to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access sensitive data. Zero trust solutions help organizations maintain control and visibility over access in these environments.
Integration with Existing Systems and Technologies
Integrating zero trust with existing security systems and technologies is crucial for a smooth transition and successful implementation. A well-defined integration strategy ensures minimal disruption to ongoing operations while maximizing the benefits of a zero trust architecture. This often requires careful planning and consideration of existing infrastructure and security protocols.
Monitoring and Maintaining a Zero Trust Environment
Monitoring and maintaining a zero trust environment is an ongoing process. Continuous monitoring of user and device activity is essential to detect anomalies and potential security threats. Regular security audits and updates are also necessary to ensure the long-term effectiveness of the zero trust framework. This ongoing process is vital for maintaining a robust and secure environment.
The Crucial Role of Identity Management
The Foundation of Zero Trust
Zero Trust security fundamentally shifts the paradigm from a perimeter-based approach to one that assumes no implicit trust. This necessitates a meticulous understanding of every user, device, and application within the network. A robust identity management system serves as the cornerstone of this trustless model, providing the granular visibility and control needed to verify and authorize access in real-time. Without a comprehensive identity management framework, Zero Trust principles become significantly more challenging to implement and maintain, leading to increased security vulnerabilities.
This shift is crucial because in a Zero Trust environment, every access request, regardless of its origin, needs to be authenticated and authorized. This level of scrutiny demands a sophisticated identity management system capable of handling the complexity of modern, dynamic environments. A well-designed system will automatically assess risk and adjust access privileges accordingly, providing a dynamic security posture that adapts to changing conditions.
Identity as a Key Security Control
Identity management isn't just about user accounts; it encompasses a broader spectrum of identities, including devices, applications, and even network resources. A robust identity management system provides a single source of truth for all these identities, enabling a unified view of access privileges and security posture. This unification streamlines the process of managing and enforcing security policies across the entire organization.
Effective identity management allows for the creation of granular access controls, ensuring that only authorized individuals and entities have access to sensitive data and resources. This granular control is essential for preventing unauthorized access and data breaches, a critical aspect of Zero Trust security.
Enhancing User Experience
While security is paramount, a good identity management system should also enhance the user experience. A user-friendly and efficient authentication process minimizes friction and frustration, preventing users from circumventing security measures due to inconvenience. A system that allows for multi-factor authentication (MFA), but does so seamlessly and intuitively, improves compliance and user satisfaction.
Seamless Integration with Zero Trust Principles
A well-integrated identity management system acts as the engine for Zero Trust. It enables the continuous assessment and dynamic adjustment of access privileges based on real-time risk factors. This constant evaluation ensures that access is granted only when it is absolutely necessary and appropriate, minimizing the attack surface and preventing unauthorized access attempts.
Maintaining Compliance and Governance
Zero Trust mandates a high level of compliance and governance, and a strong identity management system supports this requirement. It provides the necessary audit trails and reporting mechanisms to track access requests, verify compliance with security policies, and facilitate investigations in case of a breach. This ensures accountability and assists in demonstrating compliance to external auditors and regulatory bodies.
Scalability and Adaptability
In today's rapidly changing technological landscape, identity management systems must be scalable and adaptable to accommodate future growth and evolving security needs. A well-designed system can seamlessly integrate with emerging technologies and platforms, ensuring that it continues to provide robust security in the face of constant innovation. Its adaptability is crucial for companies that are constantly adding new users, applications, and devices.

Continuous Monitoring and Adaptive Security Posture

Real-time Data Acquisition and Analysis
Continuous monitoring systems rely heavily on the ability to collect data in real-time. This data, encompassing a wide range of parameters, needs to be meticulously analyzed to identify patterns, anomalies, and trends. This continuous flow of information is crucial for proactive intervention and optimized performance. The analysis process often involves sophisticated algorithms and machine learning models to discern meaningful insights from the raw data.
The speed and accuracy of data acquisition are paramount. Delays in data processing can lead to missed opportunities for intervention, potentially impacting the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the system being monitored. High-speed data pipelines and robust data storage solutions are essential to ensure real-time insights and proactive responses.
Adaptive Algorithms and Machine Learning
Adaptive monitoring systems incorporate machine learning algorithms to continuously learn and improve their performance over time. These algorithms analyze historical data, identify patterns, and predict future outcomes. This allows the system to adjust its monitoring parameters dynamically, focusing resources on areas that require immediate attention.
By leveraging machine learning, continuous monitoring systems can adapt to changing conditions and evolving needs. This adaptability is crucial in dynamic environments where conditions may fluctuate significantly. The ability to adapt to these changes is essential to maintaining optimal performance and preventing critical failures.
Proactive Intervention and Optimization
One of the key benefits of continuous monitoring is the ability to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Early detection allows for proactive intervention, minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency. This proactive approach is critical for maintaining high levels of performance and preventing costly failures.
Furthermore, the insights gained from continuous monitoring can be used to optimize various aspects of the system. By identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas of improvement, optimized solutions can be implemented, leading to significant cost savings and enhanced productivity. Monitoring systems can also be used to collect data for predictive maintenance, further reducing downtime.
System Integration and Scalability
Effective continuous monitoring often necessitates the integration of various systems and components. Data from diverse sources needs to be consolidated and analyzed to provide a holistic view of the system's performance. This integration allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the system's behavior and potential issues.
Scalability is another critical aspect of continuous monitoring. As systems grow and evolve, the monitoring infrastructure must be able to adapt and handle increasing volumes of data. Reliable and scalable monitoring solutions are essential to ensure that the system continues to perform effectively as the organization grows and expands.