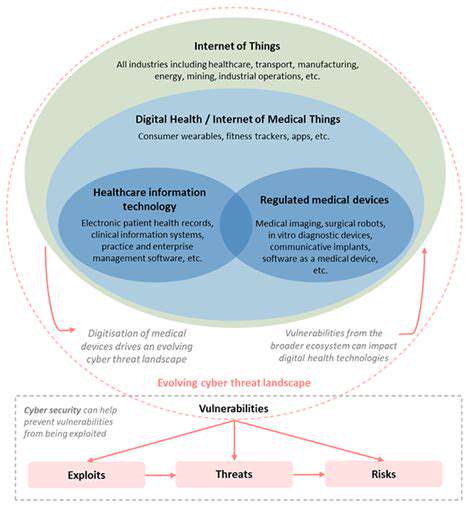
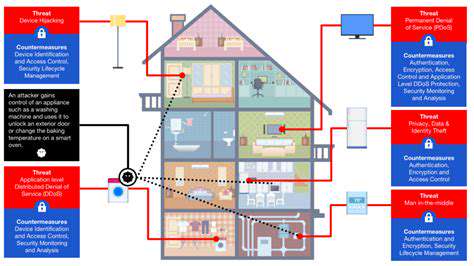
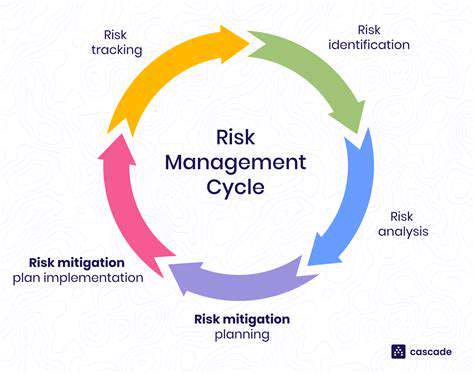
Zero Trust: A Shift in Security Paradigm
The Zero Trust security model represents a radical departure from conventional network security approaches. Rather than granting implicit trust based on network location, Zero Trust mandates rigorous verification for every access request. This paradigm shift is driven by the recognition that traditional perimeter defenses are no longer adequate in today's borderless digital environment. Each user, device, and application must prove its authenticity before accessing resources, creating a more resilient security framework.
Modern cyber threats have evolved to bypass traditional defenses with alarming sophistication. Zero Trust addresses this by eliminating the concept of trusted zones entirely. The never trust, always verify philosophy significantly reduces the potential blast radius of security incidents, making it particularly valuable for protecting sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Effective Identity and Access Management serves as the backbone of any Zero Trust implementation. Modern IAM solutions provide granular control over permissions, ensuring precise alignment between user roles and resource requirements. The principle of least privilege is fundamental here - users receive only the minimum access necessary for their specific duties. This approach dramatically shrinks the attack surface available to potential intruders.
Progressive organizations are implementing adaptive authentication mechanisms that evaluate multiple risk factors in real-time. These systems consider device health, user behavior patterns, and contextual information to make dynamic access decisions. Such intelligent IAM systems can detect and block suspicious activity while maintaining smooth operations for legitimate users.
Continuous Monitoring and Analysis
Real-time monitoring forms the nervous system of Zero Trust architectures. By continuously analyzing user activities, network traffic, and system events, security teams gain unprecedented visibility. Modern monitoring tools leverage machine learning to establish behavioral baselines and flag anomalies with remarkable accuracy. This enables security personnel to identify potential threats before they escalate into full-blown incidents.
The integration of Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems with User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) creates a powerful detection capability. These combined technologies can correlate disparate events to uncover sophisticated attack patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed. When properly implemented, continuous monitoring transforms security from reactive to proactive.
Microsegmentation and Network Segmentation
Microsegmentation revolutionizes traditional network architecture by creating finely tuned security zones. Each application, workload, or data store operates within its own protected segment, isolated from unnecessary network exposure. This containment strategy proves particularly effective against lateral movement attempts, a common tactic in advanced persistent threats.
Implementation requires careful planning to balance security with operational requirements. Modern software-defined networking solutions enable dynamic policy enforcement that adapts to changing conditions. When properly configured, microsegmentation can reduce the impact radius of breaches by up to 80%, according to recent industry studies.
Enforcing Policy and Compliance
Zero Trust demands a policy framework that's both comprehensive and adaptable. Security policies must evolve in lockstep with the threat landscape while maintaining compliance with relevant regulations. Automated policy enforcement mechanisms ensure consistent application across all access decisions, eliminating human error and intentional policy bypasses.
The most effective implementations integrate policy management with other security controls. This creates a closed-loop system where policy violations trigger immediate remediation actions, while compliance reporting happens in near real-time. Such integration significantly reduces the window of vulnerability following policy changes or new threat discoveries.
Device Security: Beyond the Perimeter

Protecting the Network Perimeter
While traditional perimeter defenses remain important, they represent just one layer in a modern security strategy. Next-generation firewalls now incorporate deep packet inspection and threat intelligence feeds to identify sophisticated attacks. However, perimeter defenses alone cannot protect against compromised credentials or insider threats, necessitating a defense-in-depth approach.
Secure access service edge (SASE) architectures are redefining perimeter security by combining network security functions with WAN capabilities. This cloud-delivered model provides consistent security policies regardless of user location, a critical requirement for today's distributed workforce.
Endpoint Security: Securing Individual Devices
Modern endpoint protection platforms have evolved far beyond traditional antivirus solutions. Today's systems employ behavioral analysis, machine learning, and threat intelligence to detect and block advanced threats. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) solutions provide continuous monitoring and forensic capabilities, enabling rapid investigation and remediation of security incidents.
The proliferation of BYOD policies has made endpoint security even more challenging. Mobile device management (MDM) solutions help maintain security standards across diverse device types while respecting user privacy. Containerization technologies have emerged as particularly effective for separating personal and corporate data on employee-owned devices.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Protecting Sensitive Information
Contemporary DLP solutions combine content inspection, contextual analysis, and user behavior monitoring to prevent data exfiltration. Advanced systems can classify data automatically and apply appropriate protection measures based on sensitivity. Integration with cloud access security brokers (CASBs) extends these protections to SaaS applications, closing a critical gap in many security postures.
Data-centric security approaches are gaining traction, focusing protection on the data itself rather than just the containers. Technologies like rights management and encryption follow data wherever it goes, maintaining protection even when it leaves controlled environments.
Insider Threats: Recognizing the Human Factor
Addressing insider risks requires a balanced approach that combines technical controls with organizational culture. User activity monitoring tools can detect anomalous behavior patterns while respecting privacy boundaries. Privileged access management (PAM) solutions are particularly effective at reducing risk from administrative accounts, which are prime targets for attackers.
Building a strong security culture through regular training and clear policies significantly reduces accidental insider threats. Gamification techniques have shown particular promise in improving security awareness and behavior among employees.
Vulnerability Management: Proactive Security Measures
Modern vulnerability management extends beyond periodic scanning to continuous assessment. Threat intelligence feeds help prioritize vulnerabilities based on actual exploit activity in the wild. Automated patch management systems can significantly reduce the window of exposure, with some solutions capable of deploying critical patches within hours of release.
Red team exercises and penetration testing provide validation of vulnerability management effectiveness. These proactive measures identify security gaps before attackers can exploit them, allowing for targeted remediation efforts.
Security Audits and Assessments: Continuous Improvement
Comprehensive security assessments now leverage automation and standardized frameworks like NIST CSF. Continuous control monitoring provides real-time visibility into security posture rather than point-in-time snapshots. Benchmarking against industry peers helps identify areas needing improvement, while compliance automation reduces the burden of regulatory requirements.
Third-party risk assessments have become critical as supply chain attacks increase. Vendor security ratings provide ongoing visibility into partner security postures, enabling informed risk decisions about third-party relationships.
Incident Response Planning: Preparing for the Unexpected
Modern incident response plans incorporate playbooks for various attack scenarios, from ransomware to supply chain compromises. Security orchestration, automation and response (SOAR) platforms streamline incident handling by automating repetitive tasks. Tabletop exercises that simulate realistic breach scenarios are invaluable for testing response readiness, revealing gaps in processes and tools.
Building relationships with law enforcement and industry information sharing groups before incidents occur pays dividends during actual events. Post-incident reviews are equally important, transforming lessons learned into improved defenses.
Beyond the Basics: Enhancing Zero Trust with Advanced Technologies
Advanced Authentication Methods
Passwordless authentication represents the next evolution in secure access, eliminating the vulnerabilities associated with traditional credentials. FIDO2 standards enable secure, phishing-resistant authentication using hardware tokens or platform authenticators. Behavioral biometrics add another layer of security by analyzing unique patterns in how users interact with devices, creating continuous authentication without user friction.
Decentralized identity frameworks based on blockchain technology give users control over their digital identities while providing verifiable credentials. These self-sovereign identity solutions reduce reliance on centralized directories, making identity systems more resilient to attack.
Enhancing Visibility and Control with Network Segmentation
Intent-based networking takes segmentation to the next level by automatically translating business policies into network configurations. Software-defined perimeter (SDP) solutions create dynamic, identity-based network boundaries that follow users and workloads. This approach dramatically reduces the network attack surface while simplifying access management.
Zero Trust network access (ZTNA) solutions provide secure remote access without exposing applications to the public internet. These cloud-native services verify identity and device health before granting access, then enforce least-privilege connectivity. The result is improved security without sacrificing user productivity.
Network detection and response (NDR) solutions analyze traffic patterns to identify stealthy threats that evade other security controls. When integrated with segmentation policies, NDR can automatically contain suspicious traffic, limiting potential damage from breaches.
Artificial intelligence is transforming network security operations by correlating vast amounts of data to detect subtle attack patterns. These AI-driven systems can identify zero-day attacks by recognizing anomalous behavior rather than relying on known signatures, providing protection against previously unseen threats.
The convergence of these advanced technologies creates a security fabric that's both intelligent and adaptive. This represents the future of enterprise security - capable of anticipating threats rather than just reacting to them.