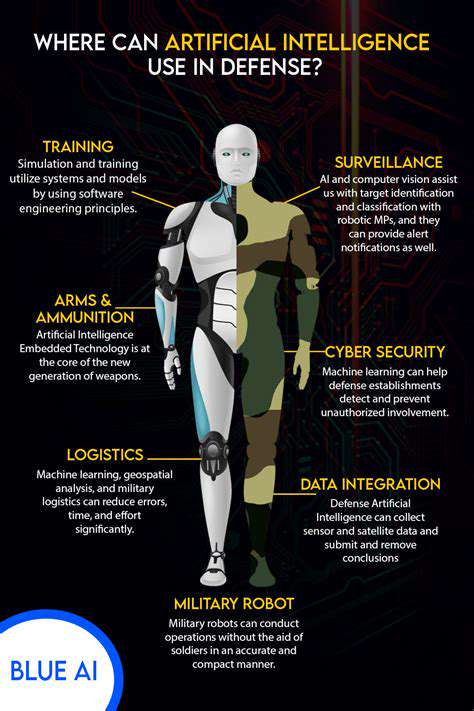
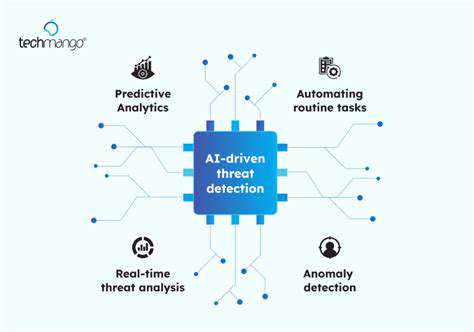
Securing Your Smart Home Network
A crucial aspect of protecting your smart home is securing your network. A strong Wi-Fi password is the first line of defense. Avoid using easily guessed passwords and opt for a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Consider using a password manager to generate and store complex passwords securely, making it easier to manage multiple devices.
Regularly updating your router's firmware is essential. Outdated firmware can introduce vulnerabilities, making your smart devices susceptible to attacks. Check your router's manufacturer website for updates and follow the instructions carefully to ensure a smooth update process. Keeping your router's security settings up-to-date is equally important.
Choosing Secure Smart Home Devices
When purchasing smart home devices, prioritize reputable brands known for robust security features. Read reviews and check for certifications like those from independent security organizations. Look for devices that offer strong encryption and secure authentication protocols, such as two-factor authentication where available. This helps prevent unauthorized access and maintain the privacy of your home data.
Consider devices with a clear security policy and easy-to-understand privacy settings. Understanding how your devices collect and use data is crucial for protecting your privacy. Thoroughly review the device's terms of service and privacy policies. This will help you understand your rights and responsibilities regarding your data.
Implementing Multi-Factor Authentication
Enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for your smart home devices adds an extra layer of security. This means using more than one method to verify your identity, such as a code sent to your phone or an authentication app. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if someone manages to guess your password. Securing access to your smart home network with MFA is a proactive measure to deter potential threats.
This extra security step can be applied to virtually every device, from your smart thermostat to your security cameras. By enabling MFA, you are adding another layer of protection to your smart home ecosystem, making it much more difficult for intruders to gain access.
Regularly Updating and Monitoring
Staying on top of software updates for your smart home devices is critical. Manufacturers often release updates to patch security vulnerabilities, so ensuring your devices are running the latest version is vital. Regularly checking for updates and installing them promptly is a simple but effective way to maintain a strong security posture.
Actively monitoring your smart home devices for unusual activity is also important. Set up alerts and notifications to receive immediate warnings if something seems amiss. Unusual activity, like unexpected power consumption or device restarts, could indicate a security breach, allowing you to take prompt action. Monitoring activity across your smart home devices is a crucial step to ensure your home stays protected.
Augmented reality (AR) is revolutionizing field service operations by providing technicians with real-time, interactive support during repairs. AR overlays digital information onto the physical world, enhancing the technician's ability to understand complex systems, locate components, and troubleshoot problems with greater efficiency. This streamlined process leads to faster repairs, reduced downtime, and overall improved productivity within the field service team.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Security Strategies

Advanced Security Measures for Enhanced Protection
Implementing robust security measures extends beyond the fundamental principles. Advanced techniques incorporate a layered approach, encompassing not only strong passwords and firewalls, but also proactive threat detection and response mechanisms. This layered defense strategy is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and systems from increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
A comprehensive security strategy must adapt to the evolving threat landscape. This includes continuous monitoring of networks and systems for suspicious activity, as well as regular updates to security software and protocols. Proactive measures, such as penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, are essential for identifying and mitigating potential weaknesses.
Multi-Factor Authentication for Enhanced User Security
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security to user accounts by requiring more than one form of verification. This often involves a combination of something you know (password), something you have (token), and something you are (biometric data). By requiring multiple authentication factors, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if a password is compromised.
MFA provides a strong deterrent to attackers, as gaining access requires overcoming multiple security barriers. This enhanced security is particularly crucial for sensitive data and systems where the consequences of unauthorized access could be severe.
Implementing Secure Coding Practices
Secure coding practices are vital for building applications and systems that are resistant to vulnerabilities. Developers must be trained on secure coding principles to minimize the risk of introducing weaknesses through their code. This includes validating inputs, properly handling user-supplied data, and avoiding common coding errors that can be exploited by attackers.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Regular security audits and penetration testing are critical for identifying and addressing potential security weaknesses. These assessments simulate real-world attacks to evaluate the effectiveness of existing security controls. Understanding the vulnerabilities in your system beforehand allows you to patch them up and mitigate any potential threats.
Regular security assessments provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of security measures. This allows for continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving security threats. Understanding where your vulnerabilities lie is the first step to patching them and strengthening your overall security posture.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Strategies
Implementing robust data loss prevention (DLP) strategies is essential for safeguarding sensitive data. These strategies involve identifying, monitoring, and controlling sensitive data throughout its lifecycle. Effective DLP measures include data encryption, access controls, and secure data handling protocols to prevent unauthorized disclosure or modification.
Data loss can have severe consequences, ranging from financial penalties to reputational damage. By implementing comprehensive DLP strategies, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and protect their valuable assets. The proactive measures taken to safeguard data are critical for long-term security and stability.
The Role of User Education and Awareness
Understanding the Risks
User education is paramount in mitigating the risks associated with smart home devices. Many users overlook the potential vulnerabilities inherent in these interconnected systems. A crucial component of this education involves understanding how data flows between devices, the potential for unauthorized access, and the impact of weak or default passwords. Failing to grasp these fundamentals can expose personal information and create opportunities for malicious actors.
Password Security and Management
Robust password management is a cornerstone of smart home security. Users need to understand the importance of creating strong, unique passwords for each device and service. This practice significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Beyond individual passwords, users should explore password managers that automatically generate and store complex passwords, enhancing security and reducing the burden on memory.
Device Configuration and Updates
Proper configuration of smart home devices is vital. This includes understanding the privacy settings, configuring access controls, and enabling two-factor authentication where available. Regularly checking for and installing software updates is equally crucial. These updates often patch security vulnerabilities, safeguarding devices and networks from known threats. Ignoring these crucial steps leaves devices open to exploitation.
Recognizing Phishing and Social Engineering
Smart home users need to be vigilant against phishing attempts and social engineering tactics. Malicious actors often try to trick users into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, or device credentials. Education on recognizing suspicious emails, messages, or websites is critical. Users should never share personal information with unknown sources and always verify the legitimacy of requests before responding.
Security Protocols and Best Practices
Implementing robust security protocols is an essential aspect of smart home security. This involves utilizing strong encryption protocols, setting up firewalls, and segmenting networks to isolate smart devices from other parts of the home network. The adoption of multi-factor authentication whenever possible adds an extra layer of security, further deterring unauthorized access. These measures significantly improve the overall security posture of the smart home environment.
Staying Informed and Adapting to Evolving Threats
The landscape of cybersecurity is constantly evolving. Users must stay informed about emerging threats and adapt their security practices accordingly. This requires actively seeking out reliable information from reputable sources, such as cybersecurity experts and industry publications. Keeping up-to-date with the latest security advisories and recommendations will enable users to proactively address new threats and vulnerabilities as they arise. This proactive approach is crucial for maintaining a secure smart home environment in the long term.