Defining the Digital Supply Chain Landscape
Understanding the Components
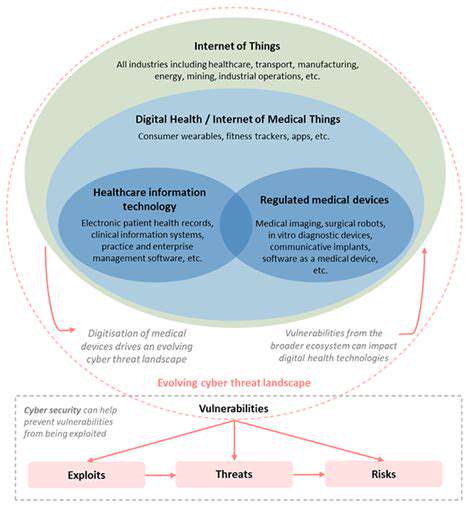
The digital supply chain represents a highly interconnected ecosystem of systems, workflows, and technologies. It spans from product conception through to final delivery, involving multiple stakeholders including manufacturers, distributors, and end-users. Grasping these interconnections proves essential for spotting vulnerabilities and deploying appropriate safeguards.
Every stage in the digital supply chain features distinct digital interactions and information exchanges. While cloud platforms and APIs enable automation and real-time tracking, they simultaneously create potential entry points for security breaches that require diligent monitoring.
Identifying Potential Risks
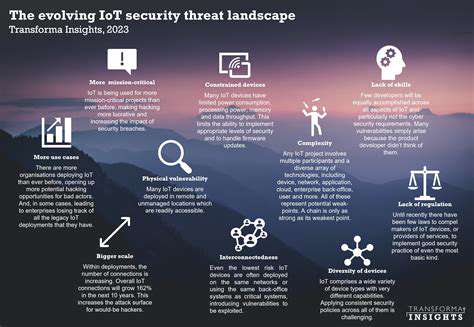
Securing digital supply chains presents unique challenges due to their complexity. Weaknesses might emerge from various sources - flawed third-party software, insecure APIs, or compromised vendors. A single breach can ripple across the entire network with devastating consequences.
The constantly evolving threat landscape introduces fresh challenges regularly. Supply chain attacks, where hackers target vendors to infiltrate client systems, have grown alarmingly common. Organizations must adopt dynamic security strategies to counter these emerging threats effectively.
Implementing Robust Security Measures
Comprehensive security requires a layered defense strategy incorporating secure development practices, vulnerability scanning, and penetration testing. Regular audits of all components and partners help identify and rectify weaknesses before exploitation occurs.
Stringent access controls and authentication protocols form the backbone of supply chain security. These measures protect sensitive information while preventing unauthorized system access. Continuous monitoring systems provide immediate alerts about potential breaches, enabling swift response.
Addressing Third-Party Risk
Third-party vulnerabilities represent one of the most significant supply chain threats, as they can compromise entire networks. Thorough vendor assessments, including security audits and contractual obligations, help mitigate these risks.
Clearly defined security requirements in vendor contracts ensure alignment with organizational standards. Ongoing communication and collaboration with partners strengthen overall security posture across the supply chain ecosystem.
Building a Culture of Security
Effective supply chain security requires organizational commitment at all levels. Employee education about security best practices and threat awareness fosters proactive risk management. Encouraging staff to report concerns without fear supports early threat detection.
Regular training, incident response drills, and security evaluations create an environment where security remains top priority. This cultural approach, combined with technical measures, builds resilience against evolving digital threats.
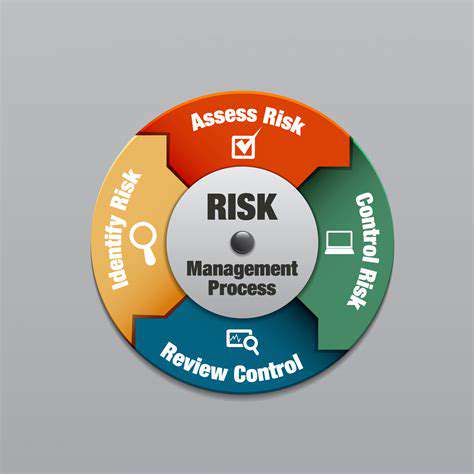
Implementing Robust Security Controls
Implementing Robust Access Control Mechanisms
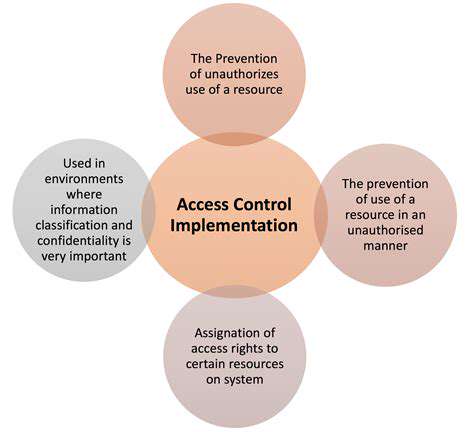
Access control systems form the foundation of data protection by regulating resource access and user permissions. Precise control mechanisms dramatically reduce the potential damage from security incidents. Well-designed systems ensure data confidentiality by restricting access to authorized personnel only.
Employing Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA significantly bolsters security by requiring multiple verification factors. Combining knowledge-based (passwords), possession-based (devices), and biometric elements creates formidable barriers against unauthorized access. Universal MFA implementation across critical systems represents a security best practice.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Proactive security assessments through audits and penetration tests reveal system vulnerabilities. These simulated attacks evaluate existing controls and highlight areas needing improvement. Timely vulnerability remediation remains crucial for maintaining strong defenses.
Data Encryption and Protection
Encryption transforms sensitive data into unreadable formats without proper keys, protecting information during transmission and storage. This fundamental security measure safeguards against data breaches while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Security Awareness Training for Staff
Employee education plays a pivotal role in organizational security. Training programs covering phishing, social engineering, and incident reporting empower staff to recognize and report threats. Knowledgeable employees serve as the first line of defense against security breaches.
Incident Response Planning and Procedures
Predefined incident response protocols enable efficient breach management. Clear escalation paths and containment procedures minimize damage during security events. Regular plan testing and updates ensure readiness for emerging threat scenarios.
Collaboration and Communication for Enhanced Security
Effective Communication Strategies
Clear communication forms the backbone of successful collaboration. Active engagement with team members promotes mutual understanding and effective teamwork. Selecting appropriate communication channels for different contexts prevents misunderstandings and ensures message clarity.
Building Strong Relationships
Trust and mutual respect create the foundation for productive collaboration. Team members who feel valued contribute more effectively to shared objectives. Informal interactions and team-building activities strengthen working relationships.
Establishing Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Well-defined responsibilities prevent task duplication and confusion. Clear decision-making protocols streamline operations and reduce conflicts. This structured approach enhances overall team efficiency.
Utilizing Technology for Enhanced Collaboration
Modern collaboration tools facilitate seamless information sharing and project coordination. Cloud platforms and project management software enable real-time updates and document sharing.
Overcoming Challenges in Collaboration
Diverse perspectives and working styles inevitably create challenges. Proactive conflict resolution and open dialogue maintain productive working relationships. Regular feedback sessions help address concerns before they escalate.
Maintaining Transparency and Accountability
Open information sharing builds trust among collaborators. Clear performance metrics and regular progress updates keep teams aligned. Defined reporting procedures ensure individual accountability.
Promoting a Culture of Innovation and Creativity
Collaborative environments thrive when encouraging creative problem-solving. Supportive feedback mechanisms help refine innovative ideas. Recognizing both successes and learning opportunities fosters continuous improvement.