Cryptocurrency and the Dark Web: Facilitating Anonymous Operations
The Dark Web's Embrace of Crypto
The dark web, a hidden network accessible only through specific software, has long been associated with illicit activities. Cryptocurrencies, with their decentralized nature and potential for anonymity, have become a crucial tool for facilitating transactions on these platforms. The lack of centralized control over crypto transactions allows users to operate with a degree of anonymity, making them attractive to those seeking to evade traditional financial tracking systems. This anonymity is a key driver for the dark web's adoption of crypto, enabling the exchange of goods and services that would be impossible or extremely difficult within the traditional financial landscape.
Cryptocurrency's pseudonymous nature allows users to obscure their identities. This anonymity, combined with the decentralized nature of crypto networks, provides a haven for those involved in illegal activities, including drug trafficking, weapons sales, and the exchange of stolen data. While proponents of cryptocurrency often highlight its potential for financial inclusion and empowerment, the dark web's embrace of crypto underscores its potential for misuse and the challenges of regulating transactions without compromising user privacy.
Crypto's Role in Facilitating Illegal Activities
The use of cryptocurrency on the dark web goes beyond simple anonymity. It facilitates the purchase and sale of illegal goods and services, enabling a level of transaction speed and security that traditional methods often lack. Cryptocurrency's ability to circumvent traditional banking systems makes it particularly attractive for those seeking to conduct illicit transactions without detection.
Furthermore, the decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies makes it difficult for law enforcement agencies to track and seize funds involved in illegal activities. This lack of centralized control hinders efforts to identify and prosecute individuals involved in these crimes. The ease of transferring funds across borders, without the need for intermediaries, also exacerbates the problem of tracing illicit transactions.
This lack of regulation and oversight creates an environment ripe for exploitation. The potential for laundering illicit funds, financing criminal organizations, and facilitating other illegal activities is significant, raising concerns about the overall impact of cryptocurrency on the security and integrity of the financial system.
The Challenges of Regulation and Enforcement
The use of cryptocurrency on the dark web poses significant challenges for law enforcement and regulatory bodies. The decentralized nature of cryptocurrencies makes it exceptionally difficult to trace transactions and identify individuals involved in illegal activities. Traditional methods of financial investigation often fail to penetrate the layers of anonymity provided by the crypto ecosystem.
Developing effective regulatory frameworks to address the use of cryptocurrency in illicit activities is a complex undertaking. Governments worldwide are grappling with the need to balance the potential benefits of cryptocurrencies with the risks of their misuse. Finding a regulatory approach that effectively combats criminal activity while respecting user privacy remains a major challenge.
The Future of Cryptocurrency and the Dark Web
The interplay between cryptocurrency and the dark web is likely to continue evolving. As technology advances, so too will the methods used to obscure transactions and facilitate illicit activities. This necessitates a proactive and adaptive approach to regulation and enforcement, requiring constant innovation in investigative techniques and partnerships between law enforcement agencies and crypto experts.
The future likely involves a more sophisticated interplay between cryptocurrency and the dark web. The development of new crypto technologies and the refinement of dark web platforms will likely create new challenges in the fight against crime. It's crucial for governments and law enforcement to stay ahead of these developments to mitigate the risks and maintain the integrity of the financial system.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) and Nation-State Involvement: A New Era of Cyber Warfare
Understanding the Threat Landscape
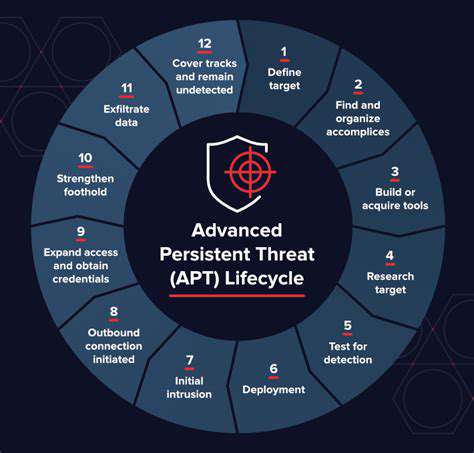
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) represent a sophisticated and evolving cyber threat landscape. These attacks are often orchestrated by state-sponsored actors or highly skilled criminal organizations, targeting specific high-value assets or sensitive information. Understanding the motivations behind these attacks is crucial for effective mitigation strategies. These actors typically operate with stealth and patience, aiming for long-term access and influence over their victims.
The diverse range of tactics employed by APTs makes them particularly challenging to detect and defend against. They often exploit vulnerabilities in software, utilize social engineering techniques, and employ sophisticated malware to maintain persistence within a compromised network. This level of planning and execution necessitates a multi-layered approach to cybersecurity defense.
Technical Sophistication and Tactics
APTs are characterized by their technical sophistication. They employ advanced tools and techniques, often leveraging zero-day exploits and custom malware designed to evade traditional security solutions. These attacks are often highly targeted and tailored to exploit specific vulnerabilities within the victim's infrastructure or processes. Furthermore, their operational approach often involves multiple stages, enabling them to penetrate and maintain access within a network for extended periods.
The tactics employed by APTs are often highly nuanced and can include spear-phishing campaigns to gain initial access, credential stuffing to compromise accounts, and leveraging vulnerabilities in network protocols to escalate privileges. These attacks are designed to evade detection and persist within the network until their objectives are met.
Impact and Consequences
The consequences of an APT attack can be devastating for organizations. They can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and loss of sensitive data. The long-term impact of these attacks can be particularly damaging to the victim's operations, affecting productivity and potentially impacting their ability to maintain trust and confidence from their stakeholders. Furthermore, the access gained by APTs can lead to the unauthorized exfiltration of intellectual property or trade secrets.
Beyond financial implications, APTs can also result in legal ramifications and regulatory penalties. Compliance with data protection regulations and industry standards becomes paramount in the wake of an APT attack. Organizations need to develop robust incident response plans to mitigate the impact and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Mitigation and Prevention Strategies
Implementing robust security measures is crucial for mitigating the risk of APT attacks. This includes implementing strong access controls, regularly patching software vulnerabilities, and deploying advanced threat detection and prevention systems. Organizations should also invest in employee training to raise awareness of social engineering tactics and phishing attempts.
Proactive security measures, like penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, can help identify potential weaknesses in the network infrastructure and allow for the implementation of appropriate safeguards. A layered security approach that combines technical controls, process improvements, and human element considerations is vital for effectively preventing and responding to APT attacks. Continuous monitoring and adaptation to the evolving threat landscape are essential elements of a proactive security posture.
Incident Response and Recovery
Having a well-defined incident response plan is critical in the event of an APT attack. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, containing, and eradicating the threat, as well as procedures for recovering from the attack. A well-orchestrated response is critical to minimize the impact and ensure a swift recovery.
The recovery phase should include steps to restore compromised systems and data, assess the damage, and implement measures to prevent future attacks. Collaboration with security experts and law enforcement agencies can be essential in addressing the complexities of an APT attack. Building resilience against these sophisticated threats requires a holistic approach that combines technical expertise with organizational preparedness.