- Vendor risk profiling with tiered classification systems
- Real-time monitoring of supplier security postures
- Contractual cybersecurity obligations with audit rights
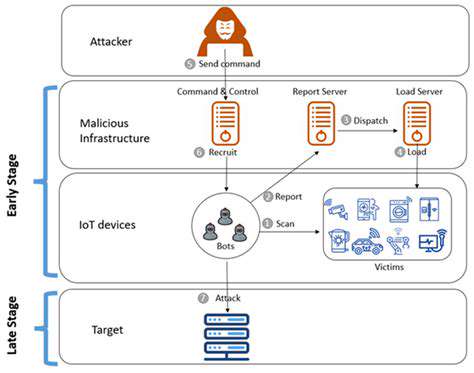
The most resilient organizations implement assume breach mentalities, preparing containment protocols for when - not if - incidents occur. Red team exercises simulating supplier-compromise scenarios help stress-test response capabilities.
Implementing Security Measures Across the Supply Chain
Practical implementation challenges often stem from asymmetrical security maturity across partners. A pharma company might mandate ISO 27001 certification for API manufacturers, while local logistics providers may lack basic cyber hygiene.
Successful programs typically feature:
- Baseline security questionnaires adapted to partner types
- Shared threat intelligence platforms
- Joint incident simulation workshops
The 2023 Microsoft Digital Defense Report highlights that 53% of supply chain attacks now target small/midsize vendors as weaker links - making comprehensive coverage essential.
Choosing the Right Security Framework for Your Business
Framework selection depends heavily on:
- Industry regulatory requirements (e.g., TISAX for automotive)
- Geographic data protection laws
- Supply chain complexity levels
A medical device manufacturer might combine ISO 13485 with NIST SP 800-171 controls, while a financial services firm could overlay PCI DSS requirements. The key is mapping framework elements to actual risk scenarios rather than checkbox compliance.
Staying Updated with Evolving Threats and Technologies
Emerging challenges include:
- AI-powered reconnaissance identifying weak suppliers
- Cryptographic attacks jeopardizing IoT device integrity
- Geo-political factors disrupting trusted vendor relationships
Forward-looking organizations are piloting:
- Blockchain-based provenance tracking
- Predictive analytics for supplier risk scoring
- Secure enclaves for sensitive data sharing
ISO 27001: A Holistic Approach to Information Security
Implementing ISO 27001 in Supply Chains
ISO 27001 implementation demands cultural transformation beyond technical controls. A 2023 ISACA study found organizations extending certification requirements to 78% of critical suppliers within 3 years of their own certification.
Key success factors include:
- Supplier security maturity assessment programs
- Standardized control inheritance mechanisms
- Joint continuous monitoring initiatives
Integrating Security into Supply Chain Processes
Effective integration points occur at:
- Procurement: Security-weighted vendor scoring models
- Development: Secure-by-design contract clauses
- Logistics: Tamper-evident shipment protocols
The Airbus Cyber Security for Suppliers program demonstrates how sector-specific control augmentations (like aviation-specific Annex A.15 controls) can address unique risks.
Benefits and Challenges of Implementing ISO 27001
Tangible benefits observed:
- 38% reduction in supplier-related incidents (Ponemon 2023)
- 2.1x faster contract negotiations with pre-certified vendors
- 17% premium on supplier security ratings post-certification
Persistent challenges include:
- Small supplier resource constraints
- Control interpretation inconsistencies
- Certificate validity period misalignment
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF): A Tailored Approach for Supply Chain Security
Understanding the NIST Cybersecurity Framework
The CSF's outcome-focused approach proves particularly valuable for heterogeneous supply chains. Its Functions (Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, Recover) create a common language bridging diverse organizational security postures.
Tailoring the Framework for Supply Chain Security
Notable adaptation approaches:
- Tiered implementation based on supplier criticality
- Supply-chain-specific subcategories (e.g., SCRM-1 for supplier risk management)
- Integration with other standards like CMMC
Benefits of a CSF-Based Approach
The Department of Defense's Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) program illustrates how CSF adaptations can meet specialized requirements while maintaining flexibility.
Integrating ISO 27001 and NIST CSF for Enhanced Protection
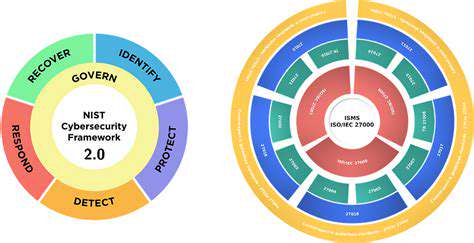
Understanding the Synergies
The integration sweet spot lies in combining ISO 27001's certifiable control rigor with NIST CSF's dynamic risk prioritization. Organizations report 42% greater security ROI from integrated implementations (Gartner 2024).
Practical Implementation Strategies
Effective integration roadmaps typically feature:
- Crosswalk mapping of controls to CSF subcategories
- Unified risk registers
- Combined audit programs
The NSA's Commercial Solutions for Classified (CSfC) program demonstrates how dual-framework approaches can secure sensitive supply chains.