Identifying and Mitigating Security Risks in Medical Devices

Identifying Potential Vulnerabilities
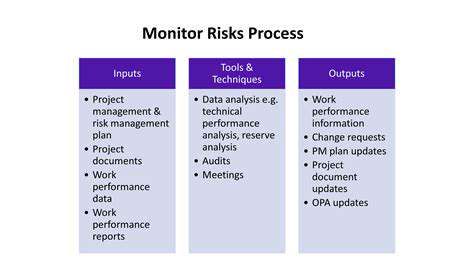
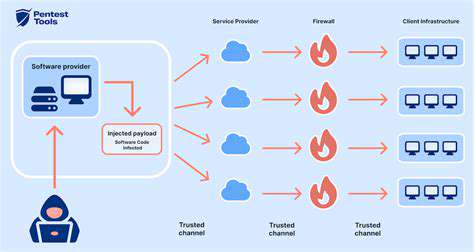
A crucial first step in securing any system is identifying potential vulnerabilities. This involves a thorough assessment of all aspects of the system, from software and hardware components to network configurations and user access controls. A comprehensive vulnerability assessment should consider both known and unknown threats, as well as potential exploits that could be leveraged by malicious actors. This requires a proactive approach that goes beyond simply patching known security flaws; it demands a deep understanding of the system's architecture and potential points of weakness.
Thorough research and analysis are essential. This includes reviewing security best practices, industry standards, and relevant documentation. Staying up-to-date with the latest security threats and vulnerabilities is critical to maintaining a robust security posture. A vulnerability management program should be implemented to track and address identified issues, prioritizing those with the highest potential impact.
Implementing Robust Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is fundamental to mitigating security risks. This involves carefully defining and enforcing rules that govern who has access to what resources within the system. Restricting access to sensitive data and functionality to authorized personnel is paramount to protecting valuable information. This includes using multi-factor authentication, strong passwords, and role-based access control to limit user privileges.
Regular reviews and audits of access controls are crucial to ensuring their effectiveness. Regularly checking for unauthorized access attempts and promptly addressing any detected vulnerabilities is essential. This proactive approach helps maintain a secure environment and prevents unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive data or resources.
Employing Advanced Security Tools
Utilizing advanced security tools can significantly enhance the overall security posture of a system. These tools can include intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS), firewalls, and antivirus software. Employing these tools allows for real-time monitoring and threat detection, enabling prompt responses to potential security breaches.
Implementing security information and event management (SIEM) systems can help analyze security logs to identify patterns and anomalies. This proactive approach to threat detection allows for the identification and mitigation of security risks before they can cause significant damage. Regular updates and maintenance of security tools are essential to ensure their continued effectiveness.
Maintaining Up-to-Date Software
Software updates frequently contain crucial security patches to address vulnerabilities. Regularly updating software is essential to maintaining a strong security posture. Outdated software is significantly more vulnerable to exploitation by malicious actors, making it a critical area for security attention. This is especially true for operating systems, applications, and libraries.
Implementing automated update processes can streamline the update cycle and ensure that systems are always running on the latest, most secure versions. Regular security audits of software components can help identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure that all necessary updates are applied.
Educating Users on Security Best Practices
User education is a critical component of any comprehensive security strategy. Educating users on security best practices, such as strong password creation, safe browsing habits, and recognizing phishing attempts, is essential. Empowering users with the knowledge and tools to protect themselves from potential threats strengthens the overall security posture.
Regular security awareness training can reinforce good security practices and help users recognize and avoid common security pitfalls. This proactive approach reduces the risk of human error in security incidents, thereby reducing the potential for significant breaches. Creating a culture of security awareness throughout the organization is critical.
Establishing a Robust Incident Response Plan
Having a well-defined incident response plan in place is crucial for effectively handling security incidents. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, containing, responding to, and recovering from security breaches. A well-structured incident response plan is essential for minimizing the impact of security incidents and ensuring a swift and controlled recovery.
Regularly testing and reviewing the incident response plan is essential to ensure its effectiveness and relevance in today's ever-evolving threat landscape. This proactive approach helps ensure that the plan can adequately address various types of incidents and that the organization is prepared to respond effectively and efficiently.
The Role of Cybersecurity Professionals and Training in the Healthcare Setting
The Critical Need for Cybersecurity Professionals
The healthcare industry is a prime target for cyberattacks, due to the sensitive patient data they hold. This necessitates a strong presence of cybersecurity professionals within healthcare organizations to proactively identify and mitigate threats. These professionals, armed with the right skills and knowledge, are essential to safeguarding electronic health records (EHRs), protecting patient confidentiality, and ensuring the continuity of crucial medical operations. Their expertise is needed to implement robust security protocols, monitor systems for suspicious activity, and respond swiftly to breaches, minimizing potential damage and reputational harm.
The increasing reliance on digital systems in healthcare, coupled with the ever-evolving nature of cyber threats, demands a dedicated team of cybersecurity experts. These individuals should possess a comprehensive understanding of network security, data encryption, and access controls. Their roles extend beyond simply reacting to incidents; they must also play a crucial part in developing and implementing preventative measures, thus creating a safer and more secure environment for all.
The Importance of Cybersecurity Training
Comprehensive cybersecurity training programs are vital for all healthcare employees, from front-line staff to executives. This training should equip personnel with the knowledge and skills to recognize and report suspicious activity, such as phishing attempts or malware infections, ensuring a strong defense against potential threats. Training programs should cover a wide range of topics, from basic security awareness to advanced threat detection and incident response protocols. This preventative approach fosters a culture of security vigilance throughout the organization.
Regular training sessions and updates are crucial to keep healthcare staff informed about the latest cyber threats and best practices. This ongoing education ensures that employees maintain a consistent level of awareness and preparedness, enabling them to contribute effectively to the organization's overall cybersecurity posture. Successful training programs should include practical exercises, simulations, and real-world case studies to enhance understanding and retention.
Building a Strong Cybersecurity Culture
A robust cybersecurity culture is paramount to safeguarding healthcare organizations from cyberattacks. This culture should foster a sense of shared responsibility, where all employees recognize their role in maintaining data security. Encouraging employees to report suspicious activity and fostering open communication channels are vital aspects of building this culture. Clear policies and procedures, coupled with regular reminders and awareness campaigns, are essential components of a strong security framework.
Promoting a proactive approach to cybersecurity is crucial. Instead of simply reacting to incidents, organizations should actively seek to identify potential vulnerabilities and implement measures to mitigate them before they can be exploited. This proactive approach will contribute significantly to the overall security posture of the organization and minimize the risk of costly and disruptive cyberattacks.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Healthcare
The healthcare sector is facing a continuously evolving landscape of cyber threats. This necessitates a proactive and forward-thinking approach to cybersecurity. Investing in cutting-edge technologies, such as advanced threat detection systems and AI-powered security tools, will be essential to stay ahead of evolving threats. Furthermore, the healthcare industry must adapt to emerging technologies, such as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), and ensure that these technologies are implemented securely.
Collaboration and knowledge sharing among healthcare organizations and cybersecurity experts will be critical for tackling complex cyber threats. Sharing best practices and resources will enable the industry to collectively strengthen its defenses and develop more robust security protocols. This collaborative approach is essential in the face of the ever-increasing sophistication of cyberattacks.