Infection vectors for IoT devices are diverse and often exploit common weaknesses. One common method involves exploiting default usernames and passwords, which are frequently left unchanged by device manufacturers or users. Furthermore, insecure configurations, poorly secured Wi-Fi networks, and outdated firmware all contribute to the vulnerability of these devices.
Phishing attacks targeting IoT device owners or users are also increasingly common. Malicious software disguised as legitimate updates or applications can be downloaded and installed on susceptible devices, opening the door for remote control.
Command and Control (C&C) Infrastructure: The Brain of the Botnet
The command and control (C&C) infrastructure is the central nervous system of an IoT botnet. This infrastructure acts as a central hub for malicious actors to issue commands to the compromised devices. These commands can range from simple tasks like sending spam emails to more complex operations, such as launching distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
C&C servers are often hosted on compromised servers, hidden within the vast expanse of the internet. Their location and operation are carefully concealed to evade detection by security systems.
The Propagation Mechanism: Spreading the Infection
The propagation mechanism is crucial for the success of an IoT botnet. Attackers leverage various methods to rapidly spread the infection to as many devices as possible. Exploiting vulnerabilities in the devices' communication protocols allows the malware to spread automatically, infecting nearby devices on the same network. This rapid spread often occurs without the knowledge or consent of the device owners.
The nature of IoT devices, frequently relying on open communication channels, significantly facilitates the spread of the infection. This characteristic poses a significant challenge to security measures.
Types of Attacks Enabled by IoT Botnets
IoT botnets can be used to launch a wide range of malicious attacks. Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks are a common tactic, flooding targeted servers or websites with traffic, effectively shutting them down. Spam campaigns are another prevalent form of attack, using compromised devices to send unsolicited emails.
Furthermore, data breaches are a potential outcome, with attackers potentially gaining access to sensitive information stored on or transmitted through compromised IoT devices. Critical infrastructure, including power grids and water systems, could be targeted, potentially causing widespread disruption.
Defenses Against IoT Botnet Attacks
Implementing strong security measures is crucial to defend against IoT botnet attacks. Changing default passwords, regularly updating firmware, and using strong encryption protocols are essential steps. Utilizing intrusion detection systems and firewalls can also help identify and block malicious activity. Education and awareness are vital for users to recognize and avoid potential threats.
Furthermore, manufacturers need to prioritize security in the design and development of IoT devices. Robust security features built into the devices themselves can significantly mitigate the risk of compromise.
The Role of Security in the IoT Ecosystem
The security of the IoT ecosystem relies on a multi-faceted approach. Collaboration between device manufacturers, network providers, and users is essential. Stronger industry standards and regulations are necessary to ensure consistent security practices. Continuous monitoring and proactive measures are vital for identifying and responding to emerging threats.
Ultimately, securing the IoT ecosystem requires a collective effort from all stakeholders to build a more resilient and secure digital landscape.

Mitigating the Risks: Defending Against IoT Botnet Attacks

Agricultural Resilience in the Face of Climate Change
Climate change poses significant and escalating threats to global agricultural systems, demanding proactive measures to enhance resilience. Adapting farming practices to changing weather patterns, such as unpredictable rainfall, extreme temperatures, and increased frequency of droughts and floods, is crucial. Farmers must adopt water-efficient irrigation techniques, drought-resistant crop varieties, and integrated pest management strategies to minimize the impact of these climate shocks.
Developing agricultural systems that are more climate-resilient requires a multifaceted approach. This includes investing in research and development of climate-smart technologies, such as improved crop varieties and livestock breeds, as well as promoting sustainable farming practices that protect soil health and biodiversity. These practices are vital for long-term agricultural sustainability and food security.
Protecting Against Pests and Diseases
Agricultural production is constantly challenged by a wide range of pests and diseases that can decimate crops and livestock. Effective pest and disease management strategies are essential for maintaining agricultural productivity and food security. These strategies should encompass a combination of preventative measures, such as crop rotation, resistant varieties, and biocontrol agents, and timely interventions when outbreaks occur.
Integrated pest management (IPM) approaches offer a promising solution, focusing on minimizing environmental impacts and maximizing long-term effectiveness. This approach incorporates a range of strategies, including biological control, cultural practices, and targeted chemical interventions when necessary. This approach aims to balance agricultural needs with environmental protection and public health concerns.
Strengthening Supply Chains
Robust and resilient supply chains are crucial for delivering agricultural products to consumers efficiently and reliably. Disruptions to these chains, caused by factors such as extreme weather events, political instability, or pandemics, can have severe consequences for food security and economic stability. Strengthening supply chains requires investments in infrastructure, logistics, and diversification of sourcing and transportation options to reduce vulnerabilities.
Diversifying supply chains can enhance resilience by reducing reliance on single sources or regions. This strategy can mitigate the impact of shocks in one region or market, ensuring a more consistent supply of food products.
Sustainable Land Management Practices
Sustainable land management practices are essential for maintaining soil health, water resources, and biodiversity. These practices are crucial for long-term agricultural productivity and environmental protection. Techniques such as conservation tillage, cover cropping, and agroforestry can improve soil structure, reduce erosion, and enhance water infiltration, thus increasing the resilience of agricultural systems to climate change.
Implementing sustainable land management practices can also contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating the effects of climate change and enhancing the overall health of the environment. This is vital for ensuring long-term agricultural sustainability in a changing climate.
Promoting Agricultural Technology Adoption
The adoption of advanced technologies, such as precision agriculture, remote sensing, and data analytics, can significantly improve agricultural efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. These technologies can help farmers optimize resource use, monitor crop health, and manage risks more effectively. Implementing these technologies can increase yields and reduce the environmental footprint of agriculture.
Investing in agricultural research and development and providing training and support to farmers are essential for successful adoption of these technologies. This ensures that farmers have the knowledge and capacity to fully utilize the potential of these innovations.
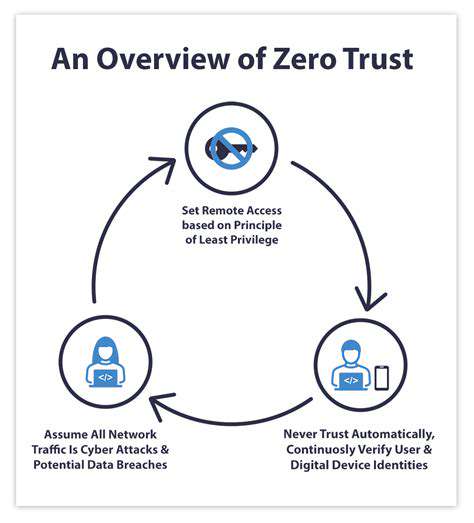
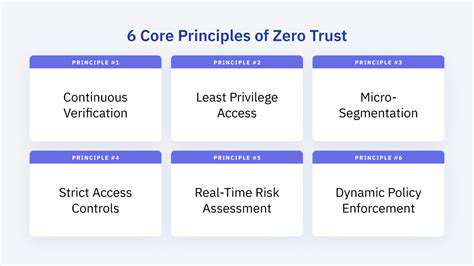
Proactive Security Measures for IoT Devices and Networks
Protecting IoT Devices from Malware
Protecting Internet of Things (IoT) devices from malware requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond simply installing antivirus software. A critical first step is to prioritize strong, unique passwords for each device. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and subsequent compromise. Regularly updating firmware and software is also essential, as these updates often include crucial security patches that address vulnerabilities. Furthermore, implementing robust access controls, limiting network access to only authorized devices and users, is crucial in preventing unauthorized intrusion. This includes configuring firewalls to block suspicious traffic and using virtual private networks (VPNs) for secure remote access. Finally, educating users about potential threats and safe practices is equally vital.
Implementing regular security audits and vulnerability assessments is another key proactive measure. These assessments help identify potential weaknesses in the system before malicious actors exploit them. It's important to understand that IoT devices often come with default configurations that can be easily exploited. Changing these default settings and using strong, unique passwords is a critical step in bolstering overall security. Regularly reviewing and updating security policies is necessary to stay ahead of emerging threats and adapt to changing security landscapes. This process should include implementing security protocols that address data encryption and access control.
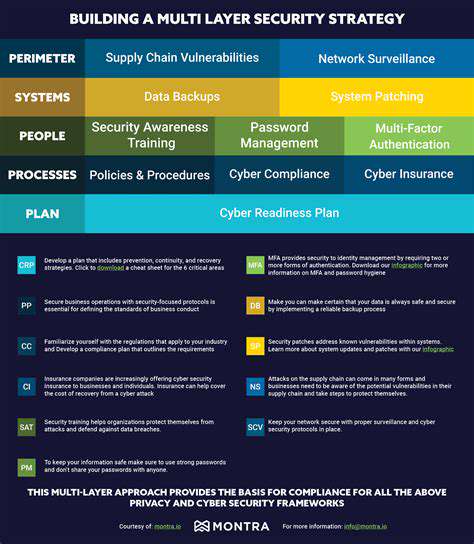
Securing IoT Networks: A Holistic Approach
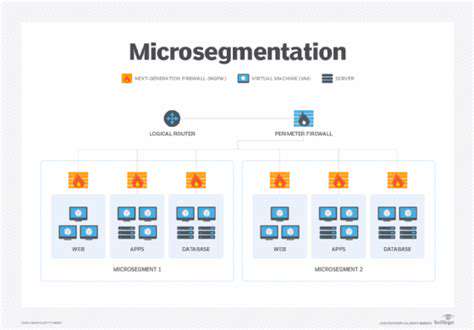
Securing IoT networks requires a holistic approach that considers the entire ecosystem, from individual devices to the network infrastructure itself. This includes implementing robust network segmentation to isolate vulnerable devices from critical systems, thereby containing the impact of a potential breach. Utilizing intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) can help monitor network traffic for malicious activity and block suspicious connections. Employing multi-factor authentication (MFA) for network access adds an extra layer of security, making it more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access. Regularly backing up data stored on IoT devices and network servers is crucial for data recovery in case of a breach or system failure. This backup strategy should be an integral part of the overall security plan.
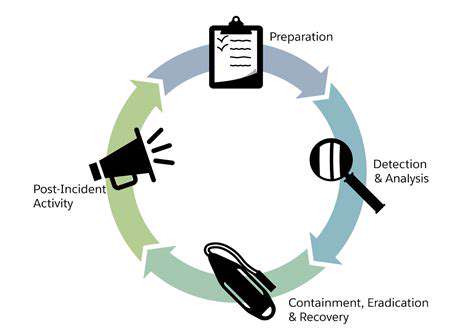
Employing a layered security approach is essential for protecting IoT networks. This involves combining various security measures to create a more robust defense against cyber threats. Regular security awareness training for personnel involved in managing the network is vital to ensure they understand the risks and best practices. Developing and implementing incident response plans is also critical, outlining clear procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from security incidents. It is also important to consider the use of advanced threat detection technologies and threat intelligence to stay informed about evolving cyber threats.