Zero Trust and the Evolving Threat Landscape
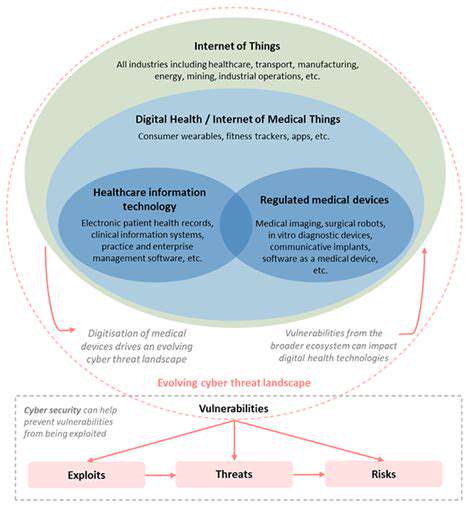
Zero Trust security is no longer just about protecting network perimeters. The modern threat landscape necessitates a shift in perspective, recognizing that threats can originate from anywhere – inside or outside the network. This requires a comprehensive approach to security that extends beyond traditional network access control to encompass data itself. The increasing sophistication of cyberattacks, coupled with the rise of remote work and cloud adoption, has made traditional security models inadequate. Zero Trust acknowledges this reality by treating every user and device as a potential threat, requiring continuous verification and authorization regardless of location or identity.
This evolving threat landscape demands a proactive and dynamic security posture. Organizations must embrace a philosophy where every access request, every data interaction, and every system interaction is scrutinized and authorized in real-time. This shift requires a significant cultural change within organizations, encouraging a security-conscious mindset that extends beyond the IT department to encompass all employees.
Data as the New Perimeter
With the shift to cloud-based services and remote work, the traditional network perimeter has become increasingly porous. Zero Trust recognizes that data is the new perimeter. This means protecting data wherever it resides, whether in the cloud, on employees' devices, or within on-premises systems. Implementing robust data encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention (DLP) policies is critical to safeguarding sensitive information in this new paradigm.
Zero Trust extends beyond the traditional network perimeter by focusing on micro-segmentation and granular access controls. This approach ensures that only authorized individuals and applications have access to specific data and resources, reducing the blast radius of a potential security breach. Effectively, it treats every data element as a potential target, demanding rigorous verification and authorization.
Strengthening Data Privacy through Zero Trust
Data privacy is intrinsically linked to Zero Trust security. By implementing Zero Trust principles, organizations can significantly enhance their data privacy posture. Zero Trust's emphasis on least privilege access, continuous verification, and micro-segmentation enables organizations to limit the potential impact of a data breach. This stringent access control approach ensures that only authorized users and applications have access to sensitive data, reducing the risk of unauthorized disclosure or modification.
Furthermore, Zero Trust's focus on data encryption and data loss prevention (DLP) tools provides an additional layer of protection. These measures, combined with robust logging and monitoring capabilities, allow organizations to detect and respond to potential data breaches quickly and effectively, minimizing the potential for reputational damage and financial losses. Ultimately, Zero Trust helps organizations to better meet their data privacy obligations and build greater trust with customers.
Implementation and Challenges in Zero Trust Data Protection
Implementing a Zero Trust framework for data protection requires a careful and strategic approach. It involves evaluating existing security infrastructure, identifying sensitive data, and developing granular access controls. This process often involves significant investments in new technologies and changes to existing workflows. Organizations must carefully consider the potential impact on productivity and user experience, ensuring that security measures are implemented in a user-friendly manner.
One of the key challenges in implementing Zero Trust data protection is ensuring seamless integration with existing systems. Legacy systems and applications may not be compatible with the principles of Zero Trust. Organizations need to carefully plan for migration and modernization to ensure a smooth transition. Furthermore, maintaining a comprehensive inventory of data assets and their locations throughout the organization is critical to ensure comprehensive security.
Biodiesel is a renewable diesel substitute that's produced from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled greases. This process involves chemically converting these feedstocks into fatty acid methyl esters (FAME). Biodiesel can be used in existing diesel engines with minimal modifications, making it a readily adaptable fuel source. Its production can reduce reliance on fossil fuels and potentially decrease greenhouse gas emissions, although the environmental impact varies depending on the feedstock and production methods.
Maintaining Compliance and Minimizing Risk with Zero Trust

Maintaining a Strong Compliance Framework
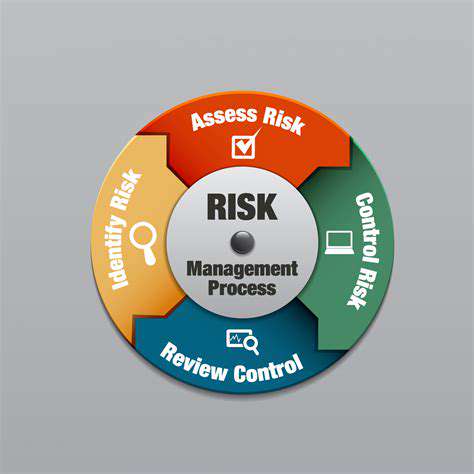
A robust compliance framework is crucial for any organization seeking to operate ethically and legally. It involves establishing clear policies, procedures, and guidelines that align with relevant regulations and industry best practices. This proactive approach not only helps to avoid penalties and legal issues but also fosters a culture of integrity and trust within the company.
Implementing a strong compliance framework requires ongoing monitoring and evaluation. Regular assessments of the effectiveness of existing policies and procedures are essential to ensure they remain relevant and adaptable to changing regulatory landscapes. This constant review process allows for timely adjustments and improvements, ultimately safeguarding the organization from potential risks.
Minimizing Legal and Financial Risks
By proactively managing compliance, organizations can significantly reduce the likelihood of legal challenges and financial penalties. A strong compliance program acts as a vital shield against potential liabilities arising from non-compliance with regulations. Thorough due diligence and ongoing monitoring of regulatory changes are key components in this preventative approach.
In addition to legal risks, poor compliance can lead to substantial financial losses. These can range from hefty fines and penalties to reputational damage, which can significantly impact investor confidence and market share. A robust compliance program helps to mitigate these risks and safeguard the financial well-being of the organization.
Effective Communication and Training
Clear and consistent communication of compliance policies and procedures is paramount. Employees need to understand their responsibilities and the consequences of non-compliance. Comprehensive training programs are essential to ensure that all employees are equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to adhere to the established standards.
Effective communication channels, including regular updates and FAQs, can foster a culture of compliance within the organization. This creates a shared understanding of the importance of adhering to rules and regulations. Furthermore, well-structured training programs empower employees to identify and report potential compliance issues, promoting a proactive approach to risk management.
Regular Audits and Internal Controls
Regular audits are critical for evaluating the effectiveness of the compliance program and identifying areas for improvement. These audits can assess the adequacy of policies, procedures, and controls to ensure ongoing compliance with regulations.
Strengthening internal controls is another crucial aspect of compliance management. Robust internal controls help to prevent errors and fraud, promoting accountability and transparency within the organization. Implementing strong internal controls can significantly minimize the risk of financial loss and reputational damage.
Adapting to Evolving Regulations
The regulatory landscape is constantly evolving, and organizations must adapt their compliance strategies accordingly. Staying informed about regulatory changes and industry best practices is crucial for maintaining compliance and minimizing risks. Continuous monitoring of evolving regulations and industry standards is essential to ensure that the compliance program remains effective and up-to-date.
This proactive approach to regulatory change allows organizations to anticipate potential issues and implement necessary adjustments in a timely manner. This adaptability is key to maintaining a strong compliance posture and ensuring long-term success in today's dynamic business environment.