The Evolving Nature of Cyber Threats
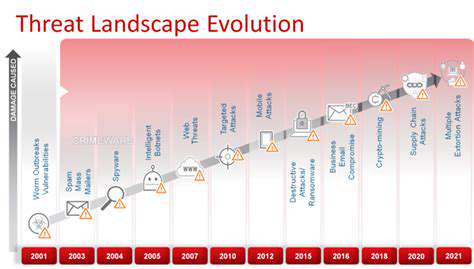
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the tactics and strategies employed by cybercriminals. Traditional security measures are often inadequate in addressing the sophisticated and increasingly complex threats emerging today. This necessitates a proactive and adaptable approach to cybersecurity, requiring constant vigilance and the adoption of cutting-edge technologies to mitigate risks effectively. Cyberattacks are no longer isolated incidents but rather a continuous, evolving threat that demands a comprehensive and layered security strategy.
Cybercriminals are constantly seeking new vulnerabilities and exploiting weaknesses in systems and networks. This includes the rise of ransomware attacks, sophisticated phishing campaigns, and the exploitation of software vulnerabilities. The proliferation of IoT devices and the increasing reliance on cloud-based services introduce new vectors for attack, demanding a broader understanding of the threat landscape and a more comprehensive security posture.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rapid advancement of technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is both a boon and a challenge for cybersecurity. While these technologies can be leveraged to enhance security measures, they can also be employed by malicious actors to create more sophisticated and targeted attacks. This creates a complex dynamic, where the very tools used to defend against cyber threats can also be used to launch them. Understanding the potential implications of these technologies on the threat landscape is crucial for effectively addressing the evolving risks.
The increasing use of cloud computing and the proliferation of mobile devices are further complicating the security landscape. These advancements create new attack surfaces and require organizations to adapt their security strategies to protect data and assets across diverse platforms and environments. These technologies offer unprecedented opportunities for efficiency and innovation but also introduce new vulnerabilities that require careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies.
The Human Factor in Cybersecurity
Despite the sophistication of cyber threats, a significant portion of security breaches still stems from human error. Phishing attacks, social engineering tactics, and the careless handling of sensitive information often play a critical role in compromising systems. Educating employees on cybersecurity best practices and fostering a culture of vigilance are essential components of a robust security posture. It is crucial to remember that human factors are often the weakest link in the security chain, and proactive training and awareness programs are vital to mitigate risks.
The human element in cybersecurity extends beyond employee training. It encompasses the need for strong security policies, procedures, and incident response plans. These elements are crucial for effective and efficient response to security breaches and for maintaining a secure environment. Effective communication and collaboration between security teams, employees, and stakeholders are also key to preventing and managing cyber threats effectively.
Strengthening Collaboration and Information Sharing Among Stakeholders

Strengthening Communication Channels
Effective communication is paramount to any successful collaboration initiative. Clear and consistent communication channels are essential for ensuring everyone involved understands their roles and responsibilities, and for fostering a sense of shared purpose. This includes establishing designated communication platforms, whether email, instant messaging, or project management software, and defining clear guidelines for how and when to use them. Regular updates and progress reports are crucial for keeping everyone informed and aligned.
Using collaborative tools can significantly improve efficiency and reduce misunderstandings. Prompt responses and active listening are key components of effective communication, fostering a supportive and productive environment. Encouraging open dialogue and feedback mechanisms will help to address concerns and resolve conflicts proactively.
Fostering Trust and Respect
A collaborative environment thrives on trust and respect among all participants. Building rapport through regular interactions, recognizing individual contributions, and actively listening to diverse perspectives are crucial elements in fostering a positive and inclusive atmosphere. This means valuing everyone's opinions and ensuring that every voice is heard and respected, regardless of their role or background. Creating a safe space for open communication and feedback is paramount to successful collaboration.
Promoting mutual understanding and empathy is vital for building trust and respect. By acknowledging and appreciating different work styles, backgrounds, and perspectives, participants can collaborate more effectively. This includes actively seeking to understand the motivations and challenges of others, which in turn facilitates stronger relationships and a shared sense of purpose.
Defining Clear Roles and Responsibilities
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities are fundamental to effective collaboration. This involves outlining specific tasks and expectations for each team member, ensuring everyone understands their individual contributions to the overall project goals. By establishing clear expectations upfront, you can prevent misunderstandings and ensure that everyone is working towards a common objective. Transparent communication regarding individual responsibilities fosters accountability and allows for effective delegation of tasks.
It's crucial to outline decision-making processes and establish clear lines of authority. This helps to ensure that everyone understands who is responsible for making which decisions, preventing overlaps or delays in critical stages of the project. This clarity also contributes to a more efficient and effective collaborative process.
Implementing Effective Conflict Resolution Mechanisms
Disagreements and conflicts are inevitable in any collaborative environment. Having pre-defined strategies for conflict resolution is essential to navigate these situations constructively. Establishing clear protocols and processes for addressing disagreements promptly and fairly will help prevent minor issues from escalating into major problems. This includes designating mediators or conflict resolution teams to help facilitate productive dialogue and find mutually agreeable solutions.
Creating a culture of open communication and active listening is crucial in resolving conflicts. Encouraging respectful dialogue and focusing on finding common ground can help to mitigate tensions and foster a more productive and collaborative environment.
Promoting Continuous Improvement and Feedback
Collaboration is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and feedback. Regular reviews and evaluations of the collaborative process are essential to identify areas for optimization and refinement. Seeking feedback from all participants, analyzing patterns and trends, and adapting strategies accordingly will lead to enhanced collaboration. Implementing a system for gathering and addressing feedback can help identify areas where communication could be improved, where roles and responsibilities need clarification, or where trust and respect need to be reinforced.
Regularly assessing the effectiveness of collaboration initiatives allows for proactive adjustments to improve communication, resolve conflicts, and optimize team dynamics. By continuously refining the process, teams can maximize their efficiency and achieve optimal results.