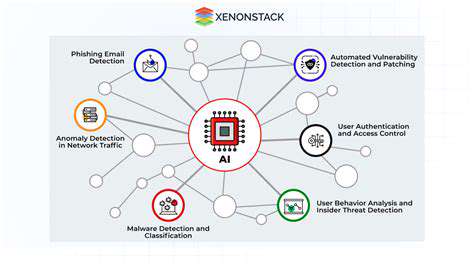
The Financial Burden
Beyond the immediate payment of the ransom, organizations face significant financial repercussions. The costs extend far beyond the ransom amount itself, encompassing forensic analysis to identify the extent of the breach, data recovery efforts, and potential legal fees. These expenses can cripple a business, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) lacking robust financial reserves.
Recovering lost data and systems can be a protracted and expensive process. Companies often need specialized services to restore their operations to pre-attack functionality, potentially impacting productivity and revenue streams for an extended period. The damage to reputation can also lead to lost future revenue and customer trust, a cost difficult to quantify but potentially devastating in the long run.
Reputational Damage
The public perception of a victimized organization takes a severe hit. News of a ransomware attack can tarnish the company's image, leading to a loss of customer trust and loyalty. This can manifest in decreased sales, difficulty attracting new clients, and a decline in brand value.
Damage to reputation is often long-lasting and difficult to repair, impacting the company's future prospects. Restoring trust with customers and stakeholders requires significant effort and investment, including public apologies, strengthened security measures, and potentially even a change in corporate strategy.
Operational Disruption
A ransomware attack disrupts normal business operations. Systems are compromised, and critical data is held hostage, effectively halting workflows and impacting productivity. This disruption can lead to significant delays in project completion, missed deadlines, and a cascade of downstream problems.
Teams are forced to scramble, often with limited resources and expertise, to restore essential functions. This often requires extensive troubleshooting, system reconfiguration, and the implementation of new security protocols. The operational downtime can be measured not only in hours or days but also in lost revenue and decreased efficiency.
Security and Compliance Implications
A ransomware attack highlights the vulnerability of an organization's security posture. This often necessitates the implementation of enhanced security measures, such as improved firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and multi-factor authentication. These measures, while necessary, can come at a considerable cost, both financially and in terms of time and effort.
Beyond immediate security concerns, companies face stricter compliance regulations. The incident may trigger investigations and audits by regulatory bodies, demanding documentation and potentially hefty fines for non-compliance. This adds another layer of complexity and cost to the recovery process.
Loss of Sensitive Data
Ransomware attacks can compromise sensitive data, including customer information, financial records, and intellectual property. This can lead to significant legal and financial liabilities, including potential lawsuits and regulatory penalties.
The leak or exposure of sensitive data can have disastrous consequences, affecting individuals and organizations. This includes potential identity theft, financial fraud, and damage to reputation, requiring significant resources for remediation and damage control.
Employee Morale and Productivity
The stress and anxiety associated with a ransomware attack can negatively impact employee morale and productivity. Workers may experience fear, uncertainty, and a sense of helplessness, leading to decreased engagement and motivation.
The disruption to their work routines and the uncertainty surrounding the future can have a significant impact on their well-being. Addressing these concerns and restoring a sense of normalcy within the organization is crucial for maintaining productivity and preventing long-term issues.
The Limitations and Caveats of Insurance Coverage

Understanding the Core Constraints
Ins, a powerful tool for streamlining various tasks, isn't a magic bullet. It's crucial to understand the inherent limitations of any technology, especially in complex systems. These limitations often stem from the underlying data structures and algorithms, and recognizing them is essential for effective utilization. Ins's capabilities are defined by the scope of its design and the data it processes, and exceeding these boundaries can lead to unexpected results or errors.
Acknowledging these boundaries is the first step toward using Ins responsibly and efficiently. A thorough understanding of Ins's functionalities and limitations helps users tailor their approach, ensuring they achieve their goals within the tool's capabilities. This proactive approach minimizes frustration and maximizes the return on investment.
Data Integrity and Accuracy
Data integrity is paramount for any system, and Ins is no exception. The accuracy of the results depends heavily on the quality of the input data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to flawed outputs, potentially impacting downstream processes and decisions. Users must meticulously validate and clean their data to ensure reliable results from Ins.
Regular checks and audits of the data used within Ins are crucial to maintaining its reliability. This proactive approach not only ensures the quality of the output but also safeguards against costly errors and misunderstandings further down the line.
Scalability and Performance
The scalability of Ins is a key consideration, particularly in large-scale applications. As the volume of data or complexity of tasks increases, the performance of Ins may degrade. Understanding the performance characteristics of Ins is essential for predicting and mitigating potential bottlenecks.
Careful planning and optimization strategies are often necessary when dealing with large datasets or complex operations. Solutions like data partitioning or distributed processing might be required to maintain optimal performance as the scope of the project expands.
Compatibility and Integration
Compatibility with other systems is another crucial aspect to consider. Ins's ability to integrate seamlessly with existing workflows and applications directly impacts its overall value. Problems can arise if the integration process isn't well-defined or if the systems aren't compatible. Thorough testing and validation are essential to avoid unexpected disruptions or errors.
Addressing integration issues early on is critical, as it can prevent significant disruptions and delays. Developing robust integration strategies ensures a smooth workflow and avoids conflicts between different systems, maximizing efficiency.
User Experience and Training
A positive user experience is essential for successful adoption and ongoing use. A user-unfriendly interface or lack of adequate training materials can hinder the effective utilization of Ins. Intuitive design and comprehensive documentation are crucial for minimizing user frustration and maximizing productivity.
Providing clear and concise instructions, along with interactive tutorials, can significantly improve user understanding and proficiency. An effective training program should equip users with the necessary skills to handle a variety of tasks within Ins efficiently.
Security Considerations
Data security is paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Ensuring the security of data processed by Ins is critical. Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access or breaches is paramount for maintaining trust and compliance. Implementing robust security measures is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of the data.
Regular security audits, adherence to industry best practices, and the implementation of security protocols are vital for safeguarding the data handled by Ins. This proactive approach minimizes risks and safeguards against potential threats.
Maintenance and Updates
The ongoing maintenance and updates of Ins are critical to its long-term viability. Regular updates often address bugs, enhance performance, or introduce new functionalities. Staying current with updates ensures that the tool remains effective and reliable. Keeping up with the latest updates is vital for maintaining optimal functionality and security.
Ignoring updates can lead to vulnerabilities and decreased efficiency. A proactive approach to software maintenance and updates ensures a smooth and reliable experience for users and safeguards against potential issues. Implementing a clear update strategy is vital for maintaining the integrity and safety of your systems.