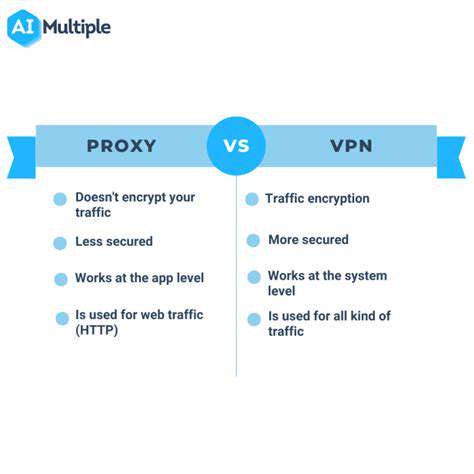
Traditional VPN Protocols: A Historical Overview
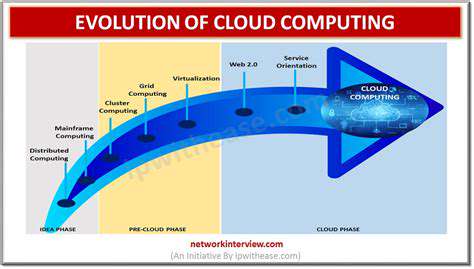
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have been a cornerstone of secure communication for decades, evolving from simple point-to-point connections to sophisticated, multi-layered systems. Understanding their historical development provides crucial context for appreciating the challenges and advancements in modern VPN technology. Their initial implementations focused primarily on establishing secure tunnels between geographically dispersed networks, a crucial need for businesses and organizations needing to share sensitive data.
Early VPN protocols, such as PPTP and L2TP/IPSec, were relatively straightforward in their design and implementation. However, they often lacked the robust security features of later protocols like OpenVPN and WireGuard. This legacy of simpler protocols continues to impact the VPN landscape, with some older technologies still in use, albeit with growing security concerns.
Security Considerations in Traditional VPNs
A critical aspect of traditional VPNs is their security model. Early protocols often relied on less sophisticated encryption methods, making them vulnerable to various attacks. The lack of robust authentication mechanisms and the potential for weak encryption algorithms are significant security flaws. This highlights the importance of choosing modern VPN providers and protocols that prioritize security.
The security considerations extend beyond encryption. Factors like key management, authentication protocols, and the overall architecture of the VPN infrastructure all contribute to the overall security posture. Carefully considering these factors is crucial for implementing a robust and trustworthy VPN solution.
Performance and Speed in Traditional VPNs
Performance has always been a significant concern with VPNs. Traditional VPN protocols, particularly those relying on older encryption standards, can introduce latency and reduce overall network speed. This can negatively impact user experience, especially for applications requiring real-time performance, like video streaming or online gaming.
Increased network traffic and complex tunneling protocols can sometimes lead to slower speeds. This is a common drawback of traditional VPN solutions. Modern VPNs are continuously working to improve speed and performance through optimized protocols and efficient server locations.
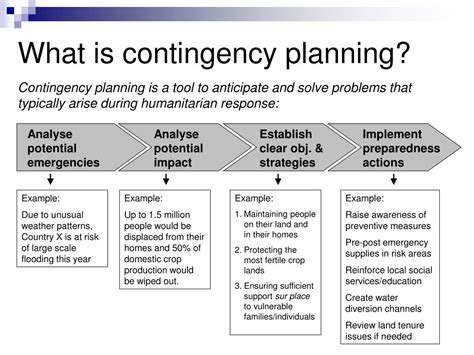
Scalability and Maintainability Challenges
Traditional VPN implementations often faced difficulties in scaling to meet the increasing demands of today's interconnected world. The complex configurations and potential for bottlenecks in larger networks made management and maintenance challenging. This scalability issue was a major hurdle for enterprises with vast and distributed networks.
Maintaining a robust VPN infrastructure across numerous locations and users required significant IT resources. This often translated into high costs and complexity for organizations. The need for consistent updates and security patches across a vast network also added to the maintenance burden.
The Evolution of VPN Protocols: An Overview
The VPN landscape has witnessed significant advancements since its inception. New protocols, such as OpenVPN and WireGuard, have emerged, offering improved security, performance, and scalability. These newer protocols address many of the limitations of traditional VPNs.
The evolution of VPN protocols reflects the ongoing need for more secure, efficient, and adaptable solutions in the ever-changing digital environment. This ongoing evolution is crucial for keeping pace with emerging threats and maintaining strong security standards.
The Future of Traditional VPNs
While traditional VPN protocols still have a place in certain niche applications, their widespread adoption is likely to decrease in favor of newer, more advanced solutions. The increasing emphasis on security, performance, and user experience is driving the shift towards more modern VPN technologies.
The future of VPNs is likely to be dominated by newer technologies. However, understanding the strengths and weaknesses of traditional VPNs provides a crucial foundation for navigating the complexities of modern network security.
Virtual Reality (VR) is rapidly transforming the architectural design and planning process. VR technology allows architects and clients to experience spaces in a truly immersive way, going beyond traditional 2D blueprints and 3D models. This immersive experience enables a deeper understanding of spatial relationships, lighting, and overall ambiance, leading to more informed design decisions and ultimately, more satisfying final products. The ability to virtually walk through a building before its construction significantly reduces the risk of costly revisions and design misinterpretations.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Needs

Choosing the Right Software Solution
Selecting the appropriate software solution is crucial for any business, as it directly impacts efficiency, productivity, and overall success. A poorly chosen solution can lead to wasted resources, frustrated employees, and ultimately, a diminished bottom line. Careful consideration and thorough research are essential steps in this process. Understanding your specific needs and requirements is paramount before even beginning to explore potential solutions.
A robust software solution should streamline workflows, automate repetitive tasks, and provide valuable data insights. It should also be scalable to accommodate future growth and adapt to changing business needs. Investing time in evaluating different options and considering long-term implications is key to avoiding costly mistakes.
Evaluating Key Features
When evaluating potential software solutions, carefully consider the specific features that align with your business needs. Does the software offer the tools you need to manage customer relationships effectively? Does it provide robust reporting capabilities to track key performance indicators (KPIs)? Thoroughly examine the features to ensure they align with your current processes and future goals.
Look for solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing systems, reducing data silos and improving overall efficiency. This seamless integration is critical for minimizing disruption and maximizing the value of your investment. Features like customizable dashboards and user-friendly interfaces are also important factors to consider.
Understanding Cost Implications
Beyond the initial software purchase price, consider the ongoing costs associated with maintenance, updates, and potential technical support. A comprehensive cost analysis should include all these factors to ensure you're making a financially sound decision. Understanding the total cost of ownership is crucial for evaluating the long-term financial impact of a software solution.
Consider factors such as licensing fees, user accounts, and potential add-on costs. Thoroughly researching and comparing pricing models is essential to ensure the solution aligns with your budget. Don't forget to factor in potential training costs for your employees to ensure smooth adoption.
Considering Vendor Reliability and Support
Choose a vendor with a strong reputation for reliability and excellent customer support. Consider their track record, industry experience, and commitment to ongoing service. A reliable vendor can be invaluable during implementation and troubleshooting phases.
Look for vendors who offer various support options, including documentation, online resources, and dedicated technical assistance. This support will be crucial for any issues that may arise during the software's lifecycle. A strong support network can significantly ease the transition and ensure a positive experience.