Zero Trust: A Foundation for Modern Security
The security landscape has outgrown perimeter-based models. Today's digital environments require context-aware protection systems that evaluate each access request independently. Financial institutions implementing Zero Trust architectures report 60% faster threat detection and 45% fewer successful breaches compared to traditional approaches.
Defining the Zero Trust Model
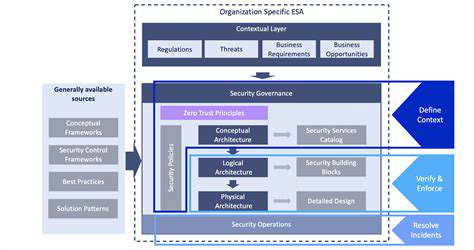
This security philosophy operates on continuous verification principles, treating every access attempt as potentially hostile until proven otherwise. Unlike legacy systems that create trusted zones, Zero Trust environments validate each transaction through multiple security layers, creating defense-in-depth protection.
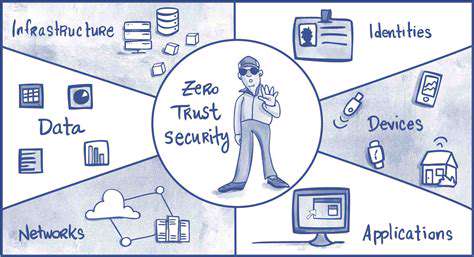
Key Components of Zero Trust
Effective implementations combine identity verification, least-privilege access, and real-time threat monitoring. Successful deployments require careful integration of these components with existing infrastructure, often through phased implementation strategies that minimize operational disruption.
Benefits of Zero Trust Adoption
Organizations gain multiple advantages including reduced attack surfaces and improved regulatory compliance. The financial impact can be significant, with early adopters reporting 30-50% reductions in security incident costs. Additional benefits include streamlined audits and improved customer trust.
Challenges in Implementing Zero Trust
Transition challenges include legacy system integration and user experience considerations. Successful implementations often employ gradual deployment strategies that prioritize critical systems first while maintaining comprehensive change management protocols.
Zero Trust and Cloud Security
Cloud environments particularly benefit from Zero Trust architectures that replace physical perimeters with identity-based controls. Financial institutions leveraging these solutions report improved visibility across hybrid environments and better protection for sensitive customer data.
Key Components and Implementation Strategies for Financial Services
Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)
Modern ZTNA solutions create secure application tunnels based on verified identities rather than network locations. Financial organizations use these systems to eliminate vulnerable VPN infrastructures while providing secure remote access. Implementation typically reduces exposed attack surfaces by 60-80% compared to traditional remote access solutions.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Advanced IAM platforms now incorporate risk-based authentication that evaluates dozens of contextual factors. These systems dynamically adjust security requirements based on real-time threat intelligence, user behavior analytics, and device security posture. Financial institutions report 40% fewer credential-based breaches after implementing such solutions.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Next-generation DLP solutions use machine learning to understand data context and usage patterns. When integrated with Zero Trust architectures, these systems provide intelligent data protection that adapts to emerging threats while maintaining business workflows. Implementation typically reduces accidental data exposures by over 70%.
Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Financial networks now implement application-aware segmentation that automatically adjusts boundaries based on traffic patterns. This dynamic approach to containment prevents the lateral movement characteristic of modern cyberattacks while simplifying network management through policy-based automation.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Modern SIEM platforms incorporate user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) to detect subtle threat patterns. When integrated with Zero Trust controls, these systems provide comprehensive visibility across hybrid environments while automating response to common threat scenarios.
Leveraging ZTA for Enhanced Data Protection

Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) Implementation
Successful ZTA deployments create adaptive security postures that respond to evolving threats. Financial institutions implement these architectures through phased modernization programs that prioritize critical assets while maintaining business continuity. Early adopters report 50-75% reductions in successful breach attempts.
Enhanced Data Protection through ZTA
By replacing broad access permissions with context-aware controls, ZTA implementations dramatically reduce data exposure risks. Protection extends beyond simple access blocking to include usage monitoring and anomaly detection, creating comprehensive data security frameworks.
Data Visibility and Control with ZTA
ZTA solutions provide granular visibility into data flows and access patterns. Security teams use these insights to refine protection strategies and identify potential vulnerabilities before exploitation. This proactive approach significantly improves overall security posture.
Improved Compliance with ZTA
Regulatory frameworks increasingly recognize Zero Trust principles as security best practices. Financial organizations implementing ZTA demonstrate compliance more efficiently through verifiable access controls and comprehensive activity logging. This approach reduces audit costs while improving regulatory relationships.
ZTA Integration with Existing Systems
Effective integration strategies focus on API-based connectivity and policy translation layers. These approaches allow financial institutions to modernize security without disrupting critical business applications or requiring complete infrastructure overhauls.
Performance Considerations in ZTA
Modern ZTA solutions incorporate performance optimization techniques that minimize latency impacts. Through intelligent caching and distributed policy enforcement, financial organizations maintain application performance while significantly improving security controls.