The emergence of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has fundamentally altered the landscape of cybercrime. Instead of individual hackers developing and deploying ransomware, RaaS platforms act as a service, allowing even less technically skilled individuals to participate in Ransomware attacks. This democratization of ransomware has dramatically increased the number of attacks, as individuals or smaller groups can now leverage sophisticated tools and techniques without extensive expertise, creating a significant threat to organizations of all sizes. This new business model significantly expands the reach and impact of ransomware, as the barrier to entry is dramatically lowered, empowering a larger pool of attackers.
This model also fosters a more sophisticated and organized approach to cybercrime. RaaS providers often offer support services, including technical assistance, negotiation strategies, and even access to victim databases, creating a well-oiled criminal enterprise. This level of organization and support, previously seen only in more established criminal enterprises, is now prevalent in the ransomware space, further increasing the complexity and effectiveness of these attacks. The availability of these services allows individuals or groups with limited technical skills to successfully execute attacks that were previously impossible.
The Impact and Implications of RaaS
The rise of RaaS has had a profound impact on the cybersecurity landscape, forcing organizations to rethink their security strategies. The increased frequency and sophistication of ransomware attacks, coupled with the ease of access to these tools, necessitates a proactive and multi-layered approach to security. Organizations need to prioritize robust data backups, implement strong access controls, and educate their employees on recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics. Furthermore, organizations must invest in advanced threat detection and response capabilities to effectively identify and mitigate ransomware attacks.
Beyond the direct financial losses from ransom payments, the impact of ransomware extends to reputational damage, operational disruption, and legal liabilities. Maintaining data integrity and business continuity is paramount, especially in sectors like healthcare and finance, where data breaches can have catastrophic consequences. The implications of RaaS reach far beyond the immediate victim, impacting the overall security posture of the digital world.
The proliferation of RaaS has also led to a surge in demand for cybersecurity professionals and solutions. Organizations are actively seeking experts to implement robust security protocols, conduct penetration testing, and develop incident response plans. This increased demand underscores the critical need for a skilled and adaptable cybersecurity workforce to combat the evolving threat landscape.
The long-term implications of RaaS are still unfolding, but one thing is clear: the threat of ransomware is no longer confined to highly skilled hackers. It has become a more accessible and organized criminal enterprise, requiring a comprehensive and proactive approach to cybersecurity from both individuals and organizations.

The Future of Ransomware and Countermeasures

The Evolving Tactics of Ransomware
Ransomware attacks are no longer limited to simple encryption; attackers are increasingly sophisticated, employing techniques like data exfiltration, double extortion, and supply chain attacks to maximize their impact and profitability. This evolution necessitates a proactive, multi-layered security approach that goes beyond traditional endpoint protection. Understanding the motivations and methodologies behind these advanced attacks is critical for effective defense strategies.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) are playing an increasingly important role in detecting and preventing ransomware attacks. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of network traffic and user behavior to identify anomalies that may indicate malicious activity. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the attack surface and allow for faster response times.
AI-powered threat intelligence platforms are becoming crucial tools in the fight against ransomware. They can identify emerging threats and provide valuable insights into the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by attackers.
The Growing Importance of Data Backup and Recovery
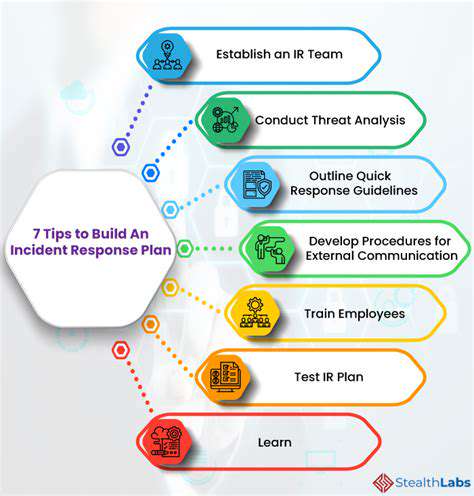
Robust data backup and recovery plans are paramount in mitigating the impact of a ransomware attack. Organizations need to implement a comprehensive strategy that includes regular backups, off-site storage, and verified recovery procedures. This ensures that even if data is encrypted, it can be quickly restored from a secure backup.
The Human Element in Ransomware Defense
Human error remains a significant vulnerability in ransomware attacks. Phishing emails, malicious links, and social engineering tactics are often used to gain initial access to a network. Employee training and awareness programs are essential to educating users about these threats and promoting responsible online behavior.
A strong security culture, where employees feel empowered to report suspicious activity, is also crucial. This empowers employees to become part of the defense mechanism.
The Impact of Regulatory Compliance
Stringent regulatory requirements, such as GDPR and HIPAA, are driving organizations to enhance their data security practices. These regulations often mandate specific measures to protect sensitive data, which can inadvertently strengthen defenses against ransomware. Compliance frameworks can serve as a blueprint for developing comprehensive ransomware response plans.
The Need for International Cooperation
Ransomware attacks are a global issue that requires international cooperation and information sharing. Collaboration between law enforcement agencies, cybersecurity firms, and affected organizations is essential to identifying and disrupting ransomware operations. Effective communication channels and standardized reporting mechanisms are critical to combating this threat effectively. Sharing intelligence and best practices across borders will be crucial for developing a unified front against ransomware.