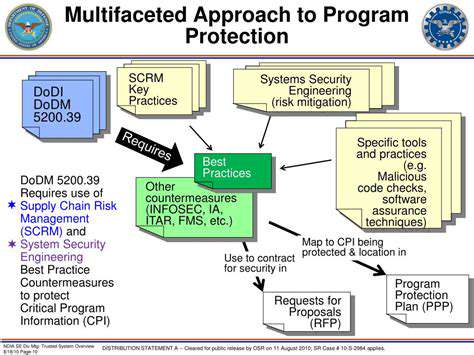
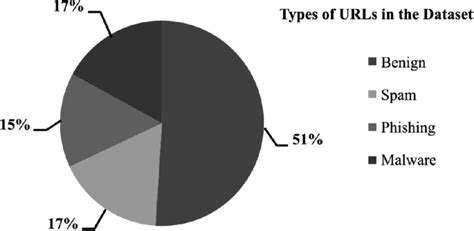
Vertical landing systems are rapidly transforming the aviation industry, offering a paradigm shift in aircraft operations. These systems promise increased safety, reduced congestion at airports, and the potential for more efficient and sustainable air travel. The ability to land and take off vertically allows for the utilization of smaller, more nimble aircraft, which can access a wider range of locations and operate in environments previously inaccessible to traditional aircraft.
From small personal aircraft to larger cargo planes, vertical landing technology is proving adaptable to a diverse range of applications, opening up exciting possibilities for urban air mobility and logistics solutions. The advancements in this field have been nothing short of remarkable, showcasing the power of innovation to solve complex problems.
Advanced Propulsion Systems: The Heart of Verticality
The core of vertical landing capabilities lies in advanced propulsion systems, capable of generating significant thrust for vertical ascent and descent. Electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft, for example, utilize electric motors and batteries to achieve vertical movement, offering significant environmental benefits compared to traditional jet engines. This approach minimizes noise pollution and reduces harmful emissions, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable future for air travel.
Further advancements in engine design and materials science are leading to lighter, more efficient propulsion systems, allowing for smaller, quieter, and more economical aircraft. The pursuit of lighter and more powerful components is crucial for the development of practical vertical takeoff and landing vehicles.
Autonomous Navigation and Control: Precision in the Air
Autonomous navigation and control systems are essential for vertical landing operations. These systems enable aircraft to precisely navigate and maneuver during vertical landings, ensuring safe and accurate positioning on landing pads or designated areas. Sophisticated algorithms and sensors allow the aircraft to adjust to changing wind conditions and other environmental factors, maintaining stability and precision throughout the entire operation.
Payload Optimization and Cargo Handling: Streamlining Logistics
Vertical landing technology is not just about passenger transport; it's about revolutionizing cargo handling as well. Optimized payload systems allow for efficient loading and unloading of cargo, streamlining logistics and reducing transit times. The ability to land and take off vertically opens up new possibilities for delivering goods to remote or congested areas, enhancing accessibility and efficiency in supply chains.
This technology allows for more agile and flexible cargo transport, particularly in urban and remote environments. Improved cargo handling systems play a critical role in the overall success of vertical landing technologies.
Sensors and Perception Systems: Enhancing Safety and Reliability
Advanced sensors and perception systems are crucial for safe and reliable vertical landing operations. These systems provide aircraft with real-time data on their surroundings, including obstacles, wind patterns, and other relevant environmental factors. This information allows the aircraft to make informed decisions and react appropriately to changes in the environment, ensuring a smooth and safe landing process.
The integration of sophisticated sensors and perception systems is vital for navigating complex urban airspace and ensuring the safety and reliability of vertical landing procedures. This advanced technology is crucial for operating in urban environments with close proximity to buildings and other obstacles.
Infrastructure Development: Paving the Way for Vertical Landing
To fully realize the potential of vertical landing technology, comprehensive infrastructure development is essential. This includes the creation of designated landing pads and charging stations for electric aircraft, as well as the modification of existing airports to accommodate vertical landing operations. Furthermore, the development of robust communication and control systems is critical for coordinating multiple aircraft in close proximity during operations.
The future of vertical landing is inextricably linked to the development of supportive infrastructure. This includes not only physical infrastructure but also the development of regulations and safety protocols to ensure the safe and smooth integration of these technologies into the existing aviation landscape.
Applications and Future Implications of Vertical Landing
Vertical Landing in Urban Environments
Vertical landing technology presents a compelling solution for the growing challenges of urban airspace management. The limited horizontal space in cities necessitates innovative approaches to aircraft operations. Vertical landing systems offer a significant advantage by reducing the need for extensive runways and taxiways, enabling more efficient and compact airport designs, and potentially allowing for the construction of vertical landing pads in densely populated areas. This could revolutionize air travel in metropolitan centers, providing greater accessibility and reducing congestion at existing airports. Imagine a future where personal aircraft can land directly in your backyard or on rooftop platforms, transforming the urban landscape and our daily routines.
Furthermore, the integration of vertical landing technology into existing urban infrastructure is crucial for its widespread acceptance. Careful consideration must be given to noise pollution, airspace regulations, and potential safety concerns related to the close proximity of buildings and other structures. Collaboration between urban planners, aviation authorities, and technology developers is essential to ensure smooth implementation and address any potential issues that may arise. Such collaboration will be key to realizing the full potential of vertical landing and its integration into the fabric of urban life.
Safety and Reliability Considerations
Ensuring the safety and reliability of vertical landing systems is paramount. Rigorous testing and certification procedures are critical to validate the performance and stability of these systems under various conditions, including extreme weather events, and potential mechanical failures. Advanced sensors, robust control systems, and redundant safety mechanisms are necessary to mitigate risks and maintain a high level of operational reliability. This is vital to building public trust and confidence in this emerging technology. The safety record of these systems will be a major factor in their widespread adoption.
The development of robust emergency procedures and protocols is also essential for vertical landing technology. Clear guidelines for handling malfunctions, unexpected situations, and potential accidents need to be established and rigorously trained for all operators and maintenance personnel. These procedures must address diverse scenarios, from minor malfunctions to more significant emergencies, ensuring that the impact of any incident is minimized. Predictable and swift emergency response procedures contribute to system reliability and public safety.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
The environmental impact of vertical landing systems is a crucial consideration. The reduced noise levels compared to traditional take-offs and landings are a significant advantage, particularly in densely populated urban areas. Furthermore, the potential for reduced fuel consumption and emissions, due to more efficient flight paths and reduced ground operations, could contribute to a more sustainable aviation industry. Careful analysis of the environmental footprint of these systems is vital to their long-term acceptance and to minimizing their impact on the environment.
Exploring alternative energy sources for vertical landing vehicles and optimizing their aerodynamic designs to reduce energy consumption are areas of ongoing research. Implementing environmentally conscious manufacturing processes and utilizing recycled materials in the construction of these systems will further enhance their sustainability credentials. By prioritizing environmental responsibility, vertical landing technology can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future for air travel.
Economic Viability and Market Potential
The economic viability of vertical landing technology is closely tied to its potential to reduce operational costs, increase efficiency, and generate new revenue streams. Reduced ground handling costs, shorter flight times, and the potential for increased passenger capacity are key economic advantages. The development of a robust infrastructure for vertical landing operations, including charging stations, maintenance facilities, and regulatory frameworks, will be crucial to attracting investment and driving market growth. This could lead to a thriving new sector of the aviation industry, with numerous opportunities for jobs and innovation.
The market potential for vertical landing technology is substantial, with the potential for widespread adoption across various sectors, including personal transportation, cargo delivery, and emergency response. The creation of new business models and opportunities related to urban air mobility will be critical in fostering the growth of this sector. The global market for urban air mobility is expected to experience significant growth in the coming years, making vertical landing technology an attractive investment opportunity for both private and public sectors.
The Road Ahead: Challenges and Opportunities

Navigating Economic Uncertainty
The global economy faces a complex and unpredictable landscape, marked by fluctuating interest rates, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. These factors create significant challenges for businesses, impacting investment decisions, production costs, and ultimately, consumer confidence. Businesses must adapt to these shifts by proactively seeking out innovative solutions and strategies to mitigate risks and capitalize on emerging opportunities. This adaptability will be crucial for sustained growth and stability in the face of potential economic downturns.
Technological Advancements and Disruption
Rapid technological advancements are reshaping industries and creating new opportunities across various sectors. Artificial intelligence, automation, and the Internet of Things are transforming processes, demanding new skill sets and fostering a need for continuous learning and development. This rapid pace of innovation necessitates a proactive approach to embrace new technologies and effectively integrate them into existing operations. Moreover, organizations need to address the ethical implications associated with these advancements to ensure responsible and beneficial implementation.
Sustainability and Environmental Concerns
Environmental sustainability is no longer a niche concern but a critical business imperative. Growing public awareness and regulatory pressures are driving organizations to adopt more sustainable practices. This includes reducing carbon footprints, minimizing waste, and embracing circular economy models. Companies that proactively integrate sustainability into their core strategies will likely enjoy a competitive advantage and build stronger relationships with environmentally conscious consumers. This means investing in renewable energy, optimizing resource management, and implementing eco-friendly solutions throughout their operations.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The global talent pool is becoming increasingly competitive, with organizations vying for skilled workers across various disciplines. Attracting and retaining top talent requires a comprehensive approach that addresses compensation, benefits, work-life balance, and career development opportunities. Attracting top talent is becoming a significant challenge for many industries. This requires proactive strategies for employee engagement, creating a positive work environment, and investing in employee training and development programs.
Globalization and International Relations
The interconnected nature of the global economy necessitates a nuanced understanding of international relations and trade dynamics. Geopolitical shifts, trade wars, and fluctuating exchange rates can significantly impact business operations. Navigating these complexities requires adaptability, strategic partnerships, and a proactive approach to mitigating potential risks associated with international trade and investment. Companies need to be mindful of evolving trade policies and regulations and develop strategies to manage risks and optimize returns in diverse global markets.