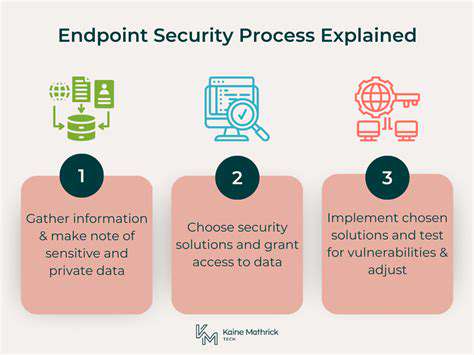
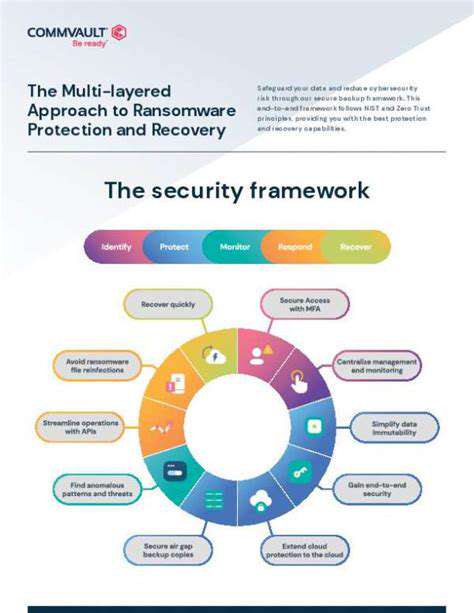
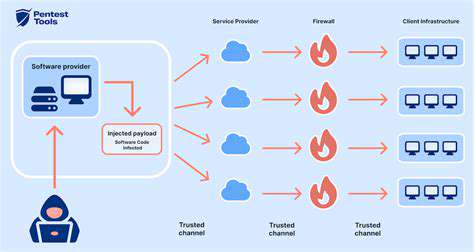
Establishing Clear Security Requirements and Agreements

Establishing Robust Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is crucial for maintaining security. This involves carefully defining user roles and permissions, ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data and resources. This granular control is essential to limit the potential damage from unauthorized access or malicious activity. Properly configured access controls significantly reduce the attack surface and protect against data breaches.
Furthermore, regularly reviewing and updating access controls is vital. As organizational needs and threats evolve, access permissions must adapt to maintain a secure environment. This proactive approach minimizes vulnerabilities and ensures that access rights remain aligned with current security requirements.
Developing Comprehensive Security Policies
Establishing comprehensive security policies is paramount. These policies should outline acceptable use guidelines, data handling procedures, and incident response strategies. Clearly defined policies provide a framework for all employees to understand and adhere to security best practices. This proactive approach helps prevent security breaches and promotes a culture of security awareness.
Implementing Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Robust authentication mechanisms are critical for verifying the identity of users accessing systems and resources. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly enhances security by requiring multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, security tokens, or biometric data. This layered approach makes it considerably harder for unauthorized individuals to gain access. Implementing strong authentication minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and protects sensitive data.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Regular security audits and assessments are essential for identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in security systems. These assessments should encompass both technical and procedural aspects of the security posture. Regular audits help proactively address emerging threats and ensure that security measures are effective in mitigating risks. The findings from these assessments can then be used to refine security policies and procedures, thereby strengthening the overall security posture.
Maintaining Up-to-Date Security Software
Ensuring that all security software, including antivirus, firewalls, and intrusion detection systems, is up-to-date is of paramount importance. This proactive approach helps protect against emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Outdated software often leaves systems exposed to exploits and malware, increasing the risk of data breaches. Keeping software current is a fundamental step in maintaining a strong security posture.
Enforcing Security Awareness Training
Regular security awareness training is a vital component of a comprehensive security strategy. This training educates employees about potential threats, phishing scams, and best practices for safe computing. By empowering employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and avoid security risks, the overall security posture improves dramatically. This proactive approach significantly reduces the likelihood of employees falling victim to social engineering attacks. Furthermore, consistent training reinforces the importance of security within the organization.
Establishing a Robust Incident Response Plan
A comprehensive incident response plan is crucial for handling security incidents effectively. This plan should outline procedures for detecting, containing, analyzing, and recovering from security breaches. This well-defined plan ensures a structured response, minimizing damage and facilitating a swift recovery. A robust plan helps maintain business continuity during security incidents and is crucial for mitigating the impact of a security breach. Thorough preparation and planning ensure that the organization can effectively respond to and recover from incidents.