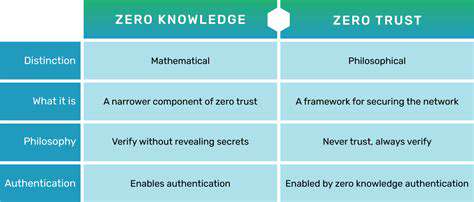
Zero Trust security operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. Instead of assuming trust based on location or network access, Zero Trust verifies every user, device, and application attempting to access resources. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface by limiting access privileges and enforcing strong authentication mechanisms.
Implementing Zero Trust in a Cloud-Native Environment
Zero Trust principles are perfectly aligned with the dynamic and distributed nature of cloud-native environments. By implementing micro-segmentation, identity and access management (IAM) solutions, and advanced threat detection systems, organizations can effectively protect their cloud resources. This approach enables granular control over access, minimizing the impact of a potential breach.
The implementation of Zero Trust in cloud-native environments requires a comprehensive strategy that considers the specific needs of the organization. Careful planning, thorough testing, and ongoing monitoring are essential elements of a successful deployment.
Benefits of a Zero Trust Approach
Adopting a Zero Trust approach delivers significant benefits, including enhanced security posture, reduced attack surface, improved visibility into user and device activity, and increased agility in responding to emerging threats. It also fosters a culture of security awareness and promotes proactive risk management.
The benefits of Zero Trust extend beyond improved security. It can also lead to increased operational efficiency and reduced costs associated with security incidents. This proactive approach will help to minimize the overall impact of security breaches.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementing Zero Trust
Implementing Zero Trust requires significant investment in infrastructure, tools, and personnel. Organizations need to consider the integration challenges between existing security systems and new Zero Trust solutions. The complexity of managing granular access controls can also be a challenge, requiring careful planning and ongoing monitoring.
Furthermore, establishing a culture of security awareness and training across the organization is critical for a successful Zero Trust implementation. Ongoing education and communication are vital for maintaining a robust security posture.
Beyond the Perimeter: Implementing Zero Trust Principles

Securing the Supply Chain
A robust cybersecurity posture extends far beyond the traditional corporate perimeter. Modern threats frequently exploit vulnerabilities in supply chains, targeting not only the final product but also the entire ecosystem of suppliers, vendors, and partners. This necessitates a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating these risks, including rigorous vendor due diligence, secure communication protocols, and regular vulnerability assessments across the entire supply chain. Understanding the intricacies of your supply chain is paramount to securing your organization's data and assets. Furthermore, regular security training and awareness programs for all supply chain partners are crucial to prevent human error-based vulnerabilities.
Implementing strong security measures throughout the supply chain is not just a good practice; it's a necessity in today's interconnected world. Failing to do so exposes your organization to significant risk, including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage. Comprehensive security protocols and continuous monitoring of supply chain activities are essential to prevent malicious actors from exploiting weaknesses and gaining unauthorized access to sensitive information or critical infrastructure.
Protecting Remote Workers
The rise of remote work has significantly broadened the attack surface for many organizations. Employees working from home or in different locations often access company resources through less secure networks and devices. This creates a critical need for robust remote access solutions, employing strong authentication methods, encryption, and network segmentation to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access. Ensuring that remote workers have the necessary tools and training to maintain a secure work environment is also vital in this context.
Implementing Zero Trust security principles is particularly crucial for remote work environments. Zero Trust assumes that no user or device is inherently trustworthy and mandates continuous verification and authorization for access to resources. This approach is critical in securing corporate data and preventing unauthorized access by malicious actors or compromised devices.
Enhancing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures
Data loss prevention (DLP) is no longer a stand-alone solution but rather an integral component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. Organizations need to proactively identify sensitive data across their entire environment, from databases and file systems to cloud storage and employee devices. Implementing robust DLP tools and policies is critical to prevent unauthorized data breaches and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. This involves continuous monitoring and enforcement of access controls to mitigate the risk of data exfiltration.
Effective DLP strategies should go beyond simply identifying sensitive data. They should also include proactive measures to protect against data breaches, such as encrypting sensitive data at rest and in transit, implementing secure deletion protocols, and regularly reviewing and updating DLP policies to adapt to evolving threats and changing data usage patterns. This proactive approach is essential to ensure the long-term security of sensitive information.
Strengthening Incident Response Capabilities
A well-defined incident response plan is critical to effectively mitigate the impact of a security breach. This plan should outline clear procedures for detecting, containing, and recovering from security incidents. Regularly testing and updating the plan is essential to ensure that it remains effective in responding to evolving threats and attack vectors. Proactive training for employees on how to identify and report suspicious activities is paramount. Having a dedicated incident response team with the necessary skills and resources is also essential for handling complex and critical situations.
A robust incident response process not only minimizes the damage caused by a breach but also builds trust with stakeholders and customers. A clear communication strategy during a security incident is crucial to maintaining public confidence and minimizing reputational damage. Furthermore, thorough post-incident analysis is critical to identify weaknesses in the security posture and implement preventative measures to avoid similar incidents in the future.
Zero Trust and Cloud-Native Security Tools
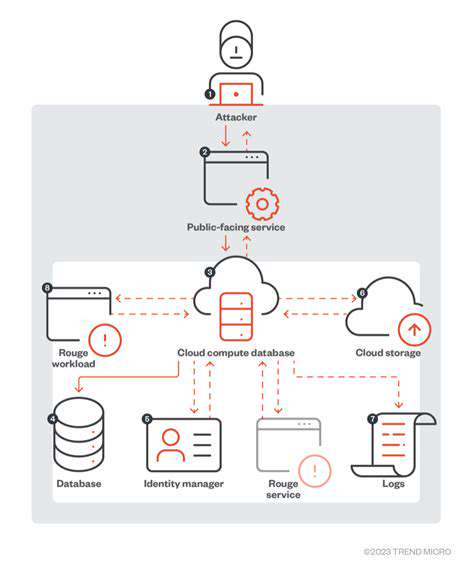
Zero Trust Architecture Fundamentals
Zero Trust security is a security model that assumes no implicit trust, either inside or outside the organization's network perimeter. It mandates continuous verification and authentication of every user, device, and application, regardless of location. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface by requiring strong authentication and authorization policies for all network access, regardless of whether the user or device is on-premises or in the cloud.
Implementing a Zero Trust approach requires a shift in mindset from traditional security models. Instead of relying on a perimeter-based security strategy, Zero Trust mandates a granular and dynamic approach that allows access based on explicit trust relationships. This is crucial for protecting sensitive data and applications in a cloud-native environment.
Cloud-Native Security Challenges
Cloud-native applications, designed for dynamic and scalable cloud environments, often introduce unique security complexities. The distributed nature of these applications, frequently deployed across multiple cloud providers and microservices, can make traditional security tools and processes ineffective. This lack of visibility across the distributed environment is a major security concern.
The rapid pace of deployment and scaling in cloud-native environments can create vulnerabilities if not properly managed. Traditional security approaches may struggle to keep pace with the dynamic nature of cloud-native applications, potentially exposing them to threats. Proactive security measures are critical.
Microservices Security Considerations
The modularity of microservices, while enabling agility and scalability, presents challenges in securing communication and data integrity between these independent components. Implementing secure communication channels and enforcing access controls between microservices is paramount. Properly securing the communication pathways between these independent components is crucial.
Ensuring data integrity and confidentiality throughout the microservices ecosystem requires careful consideration of the security implications of each individual service. This includes robust encryption, access control lists (ACLs), and secure communication protocols. Failing to do this leaves the organization vulnerable to a wide range of attacks.
Network Segmentation and Isolation
Effective network segmentation and isolation are essential to limit the impact of a security breach. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, organizations can contain the damage if one segment is compromised. This restricts the movement of malicious actors within the network.
Implementing a granular network segmentation strategy is vital for mitigating the risk of lateral movement by attackers. This approach reduces the blast radius of an attack, making it more difficult for attackers to propagate malicious activity across the entire network.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) in Cloud
Robust IAM solutions are crucial for managing access to cloud-native applications and resources. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) and least privilege access controls are vital for preventing unauthorized access. This is essential for ensuring that only authorized users and devices have access to sensitive resources.
Modern IAM solutions need to adapt to the dynamic nature of cloud-native environments. Continuous monitoring and auditing of user and application activity are paramount for detecting and responding to security threats promptly and effectively.
Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR)
Security orchestration, automation, and response (SOAR) platforms are vital for automating security tasks, streamlining incident response, and improving overall security posture. SOAR platforms can automate the detection, analysis, and remediation of security threats. They can be used for tasks such as incident response and threat hunting.
The implementation of SOAR tools can significantly improve the speed and efficiency of incident response. This, in turn, minimizes the impact of security incidents and helps organizations recover more quickly. Rapid response to security threats is critical in today's environment.
Enhancing Security Posture with Dynamic Policies

Implementing Robust Access Controls
Implementing robust access controls is crucial for enhancing security posture. This involves carefully defining and enforcing policies that govern who has access to what resources. Clearly defining roles and responsibilities is vital in a secure environment. This allows for granular control over access to sensitive data, applications, and systems, minimizing the potential for unauthorized access and data breaches. Detailed user permissions and authentication protocols are essential components of a comprehensive access control strategy.
Strong access control mechanisms are essential to prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining access to sensitive information. This not only safeguards valuable data but also protects the organization's reputation and operational integrity. Regular audits and reviews of access controls are critical to ensure they remain effective and up-to-date in response to evolving threats and business needs.
Utilizing Multi-Factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) significantly strengthens security posture by adding an extra layer of verification beyond simple passwords. This additional security measure makes it considerably more difficult for attackers to gain access, even if they have compromised a user's password. By requiring multiple forms of authentication, such as a code sent to a mobile phone or a biometric scan, MFA dramatically reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Employing Advanced Threat Detection Systems
Advanced threat detection systems are critical for proactive security. These systems monitor network traffic and system activity for suspicious patterns and anomalies. Early detection of potential threats allows organizations to take swift action to mitigate the risks and prevent incidents before they escalate. This proactive approach to security is essential in today's dynamic threat landscape.
Furthermore, these systems often integrate with security information and event management (SIEM) tools, providing a comprehensive view of security events and improving incident response capabilities. By continuously analyzing system logs and network traffic, organizations can identify potential vulnerabilities and threats before they cause significant damage.
Regular Security Awareness Training
Regular security awareness training is an essential component of a comprehensive security strategy. Employees are often the weakest link in the security chain, making them a prime target for social engineering attacks. Training empowers employees to recognize and avoid phishing attempts, malware, and other security threats. Regular training sessions should cover topics such as password hygiene, safe internet practices, and identifying suspicious emails and attachments.
This proactive approach to educating employees on security best practices will significantly reduce the risk of phishing and malware infections. By fostering a security-conscious culture, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture.
Implementing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures
Data loss prevention (DLP) measures are essential for safeguarding sensitive data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction. These measures can include data encryption, access controls, and data masking techniques. Implementing these measures can protect confidential information from falling into the wrong hands. This is especially crucial in today's digital environment where data breaches can have severe consequences for individuals and organizations.
Maintaining Up-to-Date Security Software
Maintaining up-to-date security software is paramount to a strong security posture. Security vulnerabilities are constantly being discovered and exploited by malicious actors. Regularly updating antivirus software, firewalls, and other security applications is critical to mitigating these threats. Failure to update security software can leave systems vulnerable to known exploits and compromise sensitive data. Organizations should have a well-defined process for patching and updating security software to ensure their systems remain protected.