The Evolving Threat Landscape and the Need for Zero Trust
The Rise of Sophisticated Cyberattacks
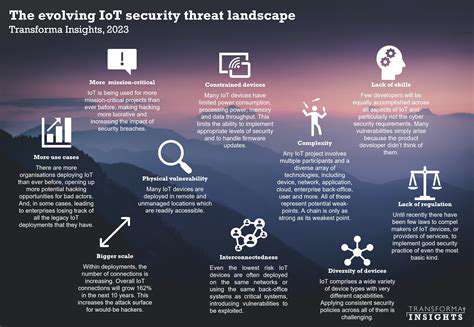
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and with it, the sophistication of cyberattacks. Attackers are increasingly employing advanced techniques to bypass traditional security measures, targeting vulnerabilities in software, hardware, and even human behavior. These attacks are often meticulously planned and executed, leveraging a combination of exploits and social engineering tactics to achieve their objectives. This evolution necessitates a proactive and adaptable approach to cybersecurity, requiring organizations to continuously update their defenses.
Cybercriminals are no longer content with simple data breaches. They are increasingly targeting critical infrastructure, financial institutions, and government agencies, demonstrating the potential for widespread disruption and significant financial losses. The impact of successful attacks can extend far beyond the immediate target, affecting entire industries and economies.
The Growing Importance of Data Protection
In today's interconnected world, data is a valuable asset, and its protection is paramount. Organizations must prioritize the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their data to safeguard sensitive information and maintain operational continuity. This includes implementing robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and data loss prevention strategies, to mitigate the risk of breaches and unauthorized access.
Data breaches can result in significant financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. The increasing regulatory requirements and evolving standards for data protection highlight the critical need for organizations to proactively address data security concerns.
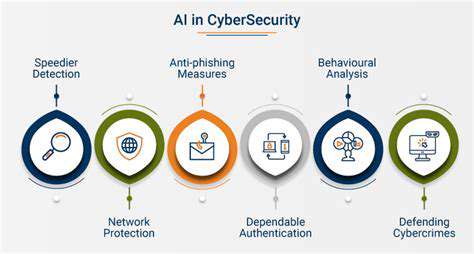
The Expanding Role of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are rapidly transforming the cybersecurity landscape. These technologies are being employed to detect and respond to threats in real-time, automating tasks that were previously time-consuming and resource-intensive for human security analysts. AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of malicious activity, significantly improving threat detection capabilities.
The Human Factor in Cybersecurity
Despite the increasing reliance on technology, the human element remains a critical vulnerability in cybersecurity. Employees may inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities through careless behavior, such as clicking on phishing emails or failing to follow security protocols. Therefore, comprehensive cybersecurity strategies must integrate employee training and awareness programs to educate staff about potential threats and best practices for safe computing habits.
Cybersecurity awareness training can significantly reduce the risk of human error. By equipping employees with the knowledge and skills to recognize and respond to potential threats, organizations can effectively mitigate the human factor risk.
The Need for Multi-Layered Security
Implementing a single security solution is no longer sufficient to protect against the multifaceted threats in today's digital environment. A robust cybersecurity strategy must incorporate a multi-layered approach, combining various security technologies and procedures to create a comprehensive defense. This includes firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and regular security audits. A multi-layered approach can significantly improve the overall security posture of an organization.
The Continuous Evolution of Threats
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, making it imperative for organizations to adopt a proactive and adaptable cybersecurity strategy. Staying abreast of emerging threats, vulnerabilities, and attack vectors is crucial for maintaining a secure environment. This requires organizations to continuously monitor and adapt their security measures to address new challenges and threats.
Regular updates and patching of software vulnerabilities, along with the continuous improvement of security processes, are essential to maintaining a robust defense. Organizations must invest in ongoing cybersecurity training and research to stay ahead of the ever-changing threat landscape.
Implementing Zero Trust for API Protection

Implementing Zero Trust for API Protection
Implementing a Zero Trust security model for APIs is crucial in today's interconnected landscape. This approach shifts the traditional security paradigm, moving away from perimeter-based defenses to a more granular, identity-centric approach. This means verifying every user and device attempting to access API resources, regardless of their location within the network or their prior access history. This rigorous verification ensures that only authorized entities can interact with sensitive data and functionality.
This paradigm shift requires a fundamental change in how we think about API security. Instead of relying on broad network access controls, Zero Trust mandates continuous verification and validation of all API requests, including those from trusted internal sources. This ensures consistent security posture, regardless of the user's location or the device they're using.
Identifying API Assets and Defining Access Policies
A critical first step is meticulously identifying all APIs within your organization. This inventory should encompass every publicly accessible API as well as internal APIs used by applications and services. Understanding the scope of your API ecosystem is paramount to implementing effective Zero Trust controls.
Once identified, define granular access policies for each API. These policies should delineate which users, devices, and applications are permitted to access specific API endpoints and functionalities. Careful consideration should be given to the level of access required for each user group, minimizing privilege escalation and limiting potential attack vectors. This granular control is the cornerstone of a robust Zero Trust architecture.
Utilizing Authentication and Authorization Mechanisms
Implementing strong authentication mechanisms is essential for verifying the identity of users attempting to access APIs. This often involves employing modern authentication protocols like OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect, which provide secure and standardized ways to manage user identities and permissions.
Complementing authentication, robust authorization mechanisms are necessary to control the specific actions that authenticated users can perform. This involves defining granular roles and permissions, enabling fine-grained control over what data and functionality each user can access. These mechanisms ensure that unauthorized actions are blocked, preventing potential breaches.
Enforcing Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege is fundamental to Zero Trust. This means granting users only the minimum access rights needed to perform their required tasks. Restricting access to sensitive data and functionalities significantly reduces the impact of a potential compromise. By limiting what a user can do, the potential damage from a breach is minimized.
This approach prevents attackers from escalating privileges and gaining unauthorized access to critical resources. By adhering to the principle of least privilege, organizations can significantly enhance their overall security posture.
Implementing API Gateway Security
An API gateway acts as a central point of entry for all API requests. This strategic placement allows for the implementation of crucial security controls, including rate limiting, request validation, and authentication/authorization enforcement. The API gateway serves as a critical security layer, protecting your internal systems from external threats.
By centralizing security in the API gateway, organizations can simplify management and enhance their overall security posture. This centralized approach also facilitates the implementation of advanced security features like threat detection and response.
Monitoring and Auditing API Activity
Continuous monitoring of API activity is essential for detecting anomalies and potential security threats. This involves tracking API usage patterns, identifying unusual access attempts, and correlating events to pinpoint potential vulnerabilities. Regular audits of API access logs provide crucial insights into user behavior and identify potential security gaps.
Implementing robust logging and monitoring mechanisms enables rapid detection and response to security incidents. This allows organizations to stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain the integrity of their API infrastructure. Proactive monitoring and auditing are fundamental to a successful Zero Trust API security strategy.