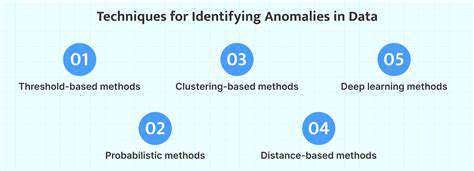
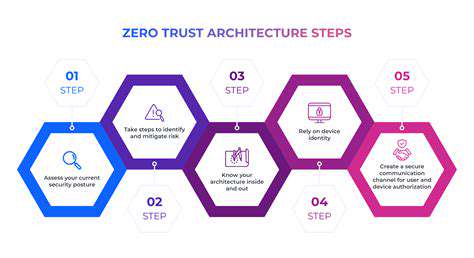
Private space missions aren't solely focused on reaching the stars. They're exploring a vast spectrum of applications, from satellite deployment and Earth observation to resource extraction and even tourism. These diverse applications highlight the versatility and potential of private companies in space, demonstrating how space technology can benefit industries on Earth in countless ways.
For example, private companies are developing constellations of satellites for internet access in remote areas, revolutionizing communication in underserved regions. This innovative approach to space utilization underscores the transformative potential of the private sector in tackling global challenges.
Reusable Rockets: Revolutionizing Launch Costs
The development of reusable rockets, spearheaded by SpaceX, represents a significant advancement in space exploration economics. These rockets dramatically reduce the cost of space travel, making space missions more accessible and affordable. This cost reduction opens the door to more frequent and varied missions, enabling scientific research, resource exploitation, and further exploration of our solar system.
The ability to reuse rockets not only lowers launch costs but also reduces the environmental impact of space travel. This crucial aspect aligns with growing concerns about sustainability, making private space initiatives more environmentally responsible in the long run.
Commercial Space Stations: Expanding Human Presence
The vision of commercial space stations is rapidly materializing. These privately funded stations offer a unique platform for scientific research, technological development, and potentially, human settlement in space. Imagine research facilities in orbit, enabling experiments in microgravity and studying the effects of space on the human body. This would unlock new frontiers in medicine and biology.
Beyond research, commercial space stations could also serve as vital hubs for space tourism and commercial activities, further extending human presence beyond Earth's atmosphere. This development marks a substantial step toward a more permanent human presence in space.
Space Tourism: Expanding Horizons
Private companies are not only focused on scientific and commercial applications but also on fulfilling a fundamental human desire: exploration and experience. Space tourism, made possible by advances in rocket technology and the commercialization of space, is becoming a reality. Space tourism offers a unique opportunity to experience the breathtaking beauty of our planet from orbit, fostering a deeper appreciation for the universe.
This emerging sector has the potential to generate significant revenue and attract even more investment in the space industry. The ability to offer space travel experiences will undoubtedly pique the interest of individuals seeking new and unique adventures.
Resource Extraction in Space: The Future of Materials
The concept of asteroid mining, a key element of resource extraction in space, is no longer confined to science fiction. Private companies are actively exploring the possibility of extracting valuable resources from asteroids and other celestial bodies. These resources could include rare earth minerals, water ice, and other materials that are scarce on Earth.
This potential for resource extraction in space could revolutionize industries on Earth, supplying critical materials for technology and manufacturing at significantly lower costs. Furthermore, it could potentially address resource scarcity issues on our planet, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Addressing Challenges in Private Space Missions
While the private sector's advancements in space exploration are remarkable, challenges remain. Regulations and safety protocols for private space missions must be developed and enforced to ensure the safe and responsible utilization of space. International cooperation and standardization are essential for the smooth operation of this rapidly evolving industry.
Ensuring the long-term sustainability of private space initiatives, including mitigating potential environmental impacts, requires careful consideration and proactive measures. The potential benefits of private space exploration must be balanced against the need for responsible stewardship of our shared space environment.
Commercialization of Space: From Satellites to Space Stations

Early Stages of Commercialization
The initial stages of space commercialization were largely driven by the desire to develop and test technologies that could eventually be applied to both terrestrial and extraterrestrial endeavors. Early ventures focused on satellite applications, particularly in telecommunications and Earth observation. These early endeavors laid the groundwork for the private sector's eventual foray into space, demonstrating the viability of commercially launching and operating satellites, and establishing the crucial infrastructure for future expansion.
Private companies began experimenting with small-scale projects, demonstrating the feasibility of using space for various purposes. These early successes, while often limited in scope, were crucial in building momentum and attracting further investment in the burgeoning field of commercial space activities.
Satellite Technology Advancements
Significant advancements in satellite technology have been instrumental in propelling the commercialization of space. Miniaturization of satellites, often referred to as CubeSats, has drastically reduced the cost of developing and deploying these crucial components of space-based infrastructure. This has opened up unprecedented opportunities for smaller companies and research institutions to participate in space exploration and research.
Furthermore, improvements in satellite communication and data processing capabilities have enabled the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data from space, providing critical insights into Earth's systems and potentially revolutionizing industries like agriculture, environmental monitoring, and disaster relief.
Space Tourism and Exploration
The allure of space tourism has captured the imagination of the public, and the potential for commercial space travel is driving innovation in rocketry and spacecraft design. Companies are actively working to make space travel more accessible, although the cost remains a significant hurdle. Several companies are actively pursuing the development of reusable rockets and spacecraft, aiming to reduce the expense of space travel and make it more practical for commercial purposes.
Beyond tourism, the commercialization of space is fostering new opportunities in space exploration. Private companies are now involved in endeavors such as lunar resource extraction and asteroid mining, creating new frontiers in the commercial sector and potentially providing crucial resources for future human endeavors in space.
Infrastructure Development
The successful commercialization of space relies heavily on the development of robust and reliable space infrastructure. This includes the creation of launch facilities, ground stations, and maintenance networks, all of which need to be designed to support the growing demands of commercial space activities. The establishment of these facilities is critical to ensuring the smooth operation and scalability of space-based ventures.
This infrastructure development is not only crucial for the present but also for the future of space exploration. As space-based activities expand, the need for advanced and reliable support systems will become even more pronounced. This ongoing development is crucial to the long-term sustainability of commercial ventures in space.
Economic Impacts and Future Prospects
The commercialization of space is expected to have a profound impact on the global economy, creating new jobs, stimulating innovation, and driving technological advancements. The sector promises to be a major economic driver in the coming decades, fostering competition and promoting creativity in the aerospace industry.
Future prospects for commercial space activities are bright, with ongoing development of new technologies and applications. The potential for space-based resources, manufacturing, and research is vast, and this sector will likely continue to grow and evolve, shaping the future of human activity in the cosmos.
Flour, water, yeast, and salt—these are the foundational elements of most breads. But beyond these basic ingredients lies a fascinating world of variations and possibilities. Different flours, from strong bread flours to delicate whole wheat varieties, affect the texture and flavor of the final product. Each ingredient contributes to the overall experience, and understanding their roles is key to crafting exceptional bread.

The Future of Space Exploration: Public-Private Partnerships and Collaboration

The Expanding Frontier of Space Tourism
The burgeoning space tourism industry promises revolutionary experiences for the public. Companies are actively developing suborbital and orbital flights, offering unique opportunities to witness the Earth from a new perspective. This burgeoning sector is expected to generate substantial economic activity, driving innovation and creating new jobs in the aerospace sector. Beyond the thrill of space travel, space tourism could open up avenues for scientific research and education, bringing a new generation of enthusiasts into the field.
The potential for private investment in space travel is immense. This investment will likely lead to a greater emphasis on cost-effective and sustainable space travel solutions. This trend could lead to a decrease in the price of space travel for the average person, making space travel more accessible to a much wider audience.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Space Missions
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming space exploration. AI-powered systems are enhancing the capabilities of spacecraft, allowing for more complex and efficient missions. AI can autonomously navigate and analyze data, significantly reducing the need for human intervention in many tasks. This automation leads to increased efficiency and drastically reduced mission costs.
Spacecraft equipped with AI can process vast amounts of data in real-time, enabling faster decision-making. This capability is particularly crucial in situations requiring quick responses, such as reacting to unexpected events or celestial phenomena.
Advancing Spacecraft Technologies
Significant advancements in spacecraft technology are paving the way for more ambitious missions. The development of reusable rockets and advanced propulsion systems is reducing the cost and complexity of space travel. This allows for more frequent and cost-effective launches, potentially accelerating the exploration of the solar system and beyond.
Innovative materials and designs are improving the resilience and efficiency of spacecraft. These advancements are crucial for withstanding the harsh conditions of space, extending the lifespan and capabilities of spacecraft.
The Search for Extraterrestrial Life
The quest for extraterrestrial life is an ongoing endeavor. New telescopes and instruments are constantly being developed, designed to detect signs of life beyond Earth. This ongoing search will likely yield significant discoveries in the years to come.
The discovery of even microbial life on another planet would revolutionize our understanding of the universe and our place in it. This could have profound implications for our scientific community and our cultural perception of the cosmos.
International Collaboration in Space
International cooperation is vital for advancing space exploration. Sharing resources, expertise, and knowledge fosters innovation and accelerates progress. Collaboration allows for the development of larger and more complex projects that would be impossible for any single nation to undertake.
International partnerships can lead to the establishment of joint space stations, observatories, and research facilities. This collaborative effort can lead to the development of new technologies and advancements that benefit all of humanity.
Sustainable Space Exploration
Sustainable space exploration is becoming a critical consideration. Minimizing the environmental impact of space missions is essential for long-term sustainability. Innovative approaches are needed to reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize the risk of contamination of other celestial bodies.
Careful planning and responsible resource management are necessary for ensuring that space exploration does not harm the fragile ecosystems of other planets or compromise the long-term sustainability of space itself.
The Ethical Implications of Space Exploration
Ethical considerations are paramount as we venture further into space. Questions surrounding the ownership of space resources, the potential for conflicts among spacefaring nations, and the responsibility for the protection of space environments are increasingly important. Establishing clear guidelines and international agreements are essential for navigating the ethical complexities of space exploration.
The responsible and ethical development of space technologies is crucial to ensuring that the benefits of space exploration are shared equitably and that the potential risks are mitigated.