Introduction to Lunar Subsurface Exploration

Understanding Lunar Subsurface Environments
Lunar subsurface environments present a fascinating and complex area of scientific inquiry. These regions, shielded from the harsh radiation and extreme temperature fluctuations of the lunar surface, hold potential clues about the Moon's formation, evolution, and even past habitability. Understanding the composition and structure of these subsurface layers is crucial for future lunar exploration and potential resource utilization.
The subsurface environments are not uniformly distributed across the Moon. Different regions, influenced by geological processes and impact events, exhibit varying degrees of subsurface complexity, from shallow regolith layers to deeper, potentially more substantial formations. This diversity necessitates a nuanced approach to study.
Exploring the Regolith Layer
The lunar regolith, a layer of pulverized rock and dust, forms the uppermost layer of the lunar subsurface. Its thickness varies significantly, ranging from a few centimeters to tens of meters, depending on the specific location and geological history. This layer is crucial to understanding the Moon's surface history and provides a valuable archive of micrometeorite impacts and solar wind interactions.
The regolith layer plays a vital role in protecting underlying materials from direct exposure to the harsh lunar environment. It also acts as a significant reservoir of volatiles and potentially valuable resources, including water ice, which is of interest for future human settlements and resource extraction.
Investigating Potential Ice Deposits
The presence of water ice in permanently shadowed craters near the lunar poles is a significant discovery. These deposits, shielded from direct sunlight, could represent a substantial source of water for future lunar missions. The ice, if found in significant quantities, would have profound implications for sustaining human activity on the Moon and facilitating resource utilization.
The precise extent and distribution of these ice deposits remain a major focus of ongoing research and exploration. Understanding the conditions that allowed these deposits to form and persist is vital for developing strategies for accessing and utilizing them.
Importance of Lunar Subsurface for Resource Utilization
The lunar subsurface holds the potential for a variety of resources crucial for sustaining human activity on the Moon. These resources include not only water ice, but also potentially valuable minerals and elements, which could be extracted and utilized for construction materials, fuel, or life support systems.
Extracting these resources in a sustainable and responsible manner is a key consideration for future lunar development. Innovative technologies and strategies need to be developed to ensure efficient and environmentally sound extraction methods.
Lunar Subsurface and Habitability
Understanding the lunar subsurface environment is also essential for evaluating the potential for past or present habitability. The presence of water, the shielding effect of the regolith, and the stability of subsurface environments could have influenced the possibility of past microbial life or future human colonization.
Examining the subsurface for signs of past or present life is a critical scientific goal. The results of such investigations could have profound implications for our understanding of planetary evolution and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Challenges in Exploring the Lunar Subsurface
Exploring the lunar subsurface presents significant technical challenges. The harsh lunar environment, the depth and complexity of the subsurface, and the need for advanced drilling and sampling technologies all contribute to the complexity of this endeavor.
Developing innovative technologies and strategies to overcome these challenges is critical for advancing our understanding of the Moon and enabling future human exploration and resource utilization. This includes developing advanced robotic systems for deep drilling and sample return.

Potential Benefits of Lunar Subsurface Habitats
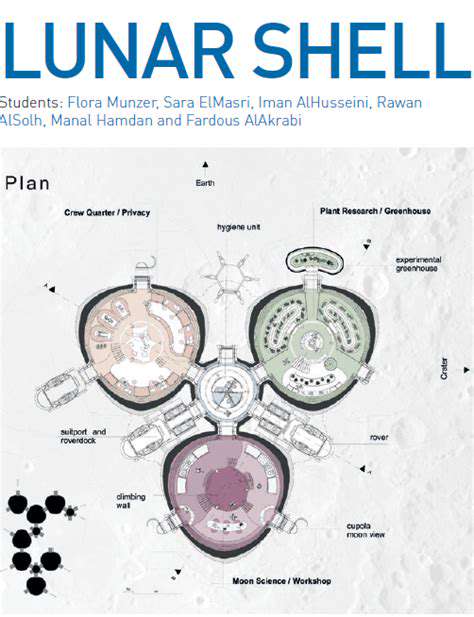
Potential for Resource Extraction
The lunar subsurface holds a wealth of potential resources, including water ice, which could be vital for future lunar settlements and space missions. Extracting these resources on-site would significantly reduce the need to transport materials from Earth, thus lowering costs and increasing the sustainability of lunar operations. This would also free up valuable space and resources on spacecraft, potentially allowing for the transport of more scientific equipment or larger payloads.
Furthermore, the presence of various minerals and elements in the lunar regolith could provide valuable raw materials for construction, fuel production, and other industrial processes. The ability to process these resources locally is a crucial step towards establishing a self-sustaining lunar presence. This could pave the way for a future where lunar operations are largely independent of Earth, fostering a new era of space exploration and utilization.
Scientific Research Opportunities
The lunar subsurface provides a unique environment for scientific research, offering insights into the Moon's formation, evolution, and composition. Studying the subsurface layers can reveal crucial information about the early solar system and the processes that shaped celestial bodies. Analyzing the composition of the lunar subsurface materials can provide a detailed understanding of the Moon's geological history.
Furthermore, the potential presence of previously unknown minerals or compounds in the subsurface could revolutionize our understanding of planetary science and geology. These discoveries could have significant implications for our knowledge of planetary formation and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Development of Lunar Infrastructure
Establishing a lunar base requires a robust infrastructure, and the lunar subsurface could play a crucial role in its development. Utilizing the subsurface for housing, storage, and infrastructure support could create a more secure and sustainable base camp. This could lead to the creation of advanced facilities designed to withstand the harsh lunar environment, potentially opening up opportunities for long-duration human missions.
The excavation of the subsurface could also provide ample space for establishing tunnels and underground structures, offering protection from the extreme temperature fluctuations and radiation that characterize the lunar surface. These structures could serve as essential components of a self-sufficient lunar colony, supporting essential functions and activities.
Potential for Future Space Activities
The existence of resources within the lunar subsurface opens doors to a wide range of future space activities. It could pave the way for establishing manufacturing facilities on the Moon, allowing for the production of components and tools for future space missions. This would create a more dynamic and sustainable space economy, allowing for the exploration of further celestial bodies and the expansion of human presence beyond Earth.
The utilization of lunar subsurface resources could potentially revolutionize space travel and exploration. This could lead to the development of advanced technologies and innovations that will benefit both lunar and terrestrial societies, significantly advancing humanity's ability to explore and understand the universe.