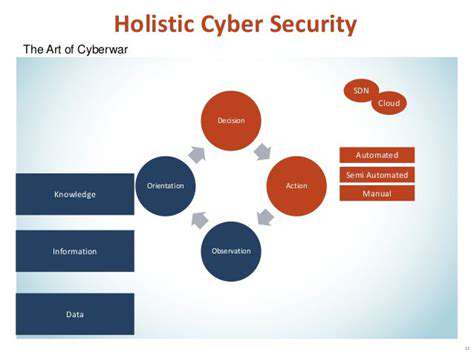
Understanding the Shifting Security Landscape
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and with it comes a rapidly changing threat landscape. Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, employing new and increasingly creative methods to breach security measures. Traditional security models, often relying on perimeter defenses, are proving inadequate in the face of these advanced attacks. This shift necessitates a fundamental reevaluation of security strategies, and the need for a more proactive and comprehensive approach is becoming increasingly apparent. Organizations must move beyond simply protecting their perimeters and embrace a more dynamic and adaptable security posture.
This evolution is driven by several factors, including the rise of cloud computing, the proliferation of mobile devices, and the increasing reliance on interconnected systems. These factors introduce new attack vectors and complexities, making it more challenging to maintain a secure environment. Consequently, organizations are struggling to keep pace with the evolving threats, leading to a growing need for robust and adaptable security solutions.
The Limitations of Traditional Security Models
Traditional security models, often focused on perimeter defenses, are struggling to keep pace with the sophistication of modern cyber threats. These models often rely on a trust but verify approach, assuming that users and devices inside the network are inherently safe. This assumption is increasingly flawed as threats exploit vulnerabilities across the entire attack surface, including internal networks and endpoints.
Furthermore, traditional security measures often lack the contextual awareness needed to identify and respond to sophisticated attacks in real-time. They may struggle to distinguish between legitimate user activity and malicious behavior, leading to excessive false positives and hindering productivity. This reactive approach is simply not enough to mitigate the ever-present risk of cyberattacks in today's dynamic environment.
The Rise of Zero Trust Architecture
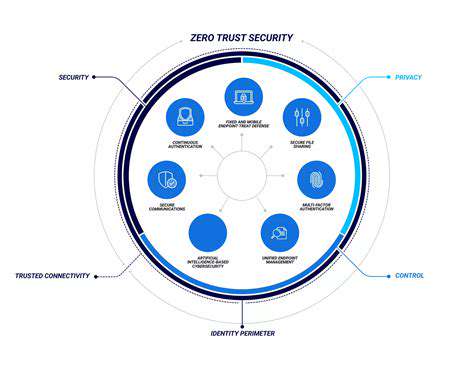
Zero Trust security architecture offers a more comprehensive and proactive approach to safeguarding sensitive data and systems. Instead of trusting anyone or anything within the network, Zero Trust assumes a zero-trust posture and verifies every user, device, and application access request. This approach mandates continuous authentication and authorization, regardless of whether the entity is internal or external.
By implementing micro-segmentation and granular access controls, Zero Trust significantly reduces the attack surface. This enhanced security posture is crucial in today's interconnected world, where threats can originate from anywhere and compromise systems in unexpected ways. Zero Trust architecture strengthens the security posture by creating a more resilient and adaptive security system.
Key Benefits of Adopting Zero Trust
Implementing a Zero Trust framework offers a multitude of benefits, including increased security posture, reduced attack surface, and enhanced data protection. By continuously validating user and device access, Zero Trust significantly minimizes the potential damage from a successful breach.
Beyond enhanced security, Zero Trust also fosters greater operational agility and efficiency. The granular control afforded by Zero Trust allows organizations to more effectively manage and control access to resources, which can lead to improved productivity and reduced operational overhead. It enables organizations to respond quickly to emerging threats and adapt to changing business needs.
The Future of Security: A Zero Trust Approach
The future of cybersecurity hinges on the adoption of Zero Trust principles. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, Zero Trust is emerging as the cornerstone of a robust and adaptable security strategy. This proactive approach allows organizations to mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive data in an increasingly complex and interconnected digital world.
Organizations that embrace Zero Trust are better positioned to defend against sophisticated attacks, safeguard sensitive data, and maintain a secure and productive environment. By adopting a Zero Trust approach, organizations can ensure that their data and systems remain protected, no matter where the threats originate.
Implementing Zero Trust: Key Components and Strategies
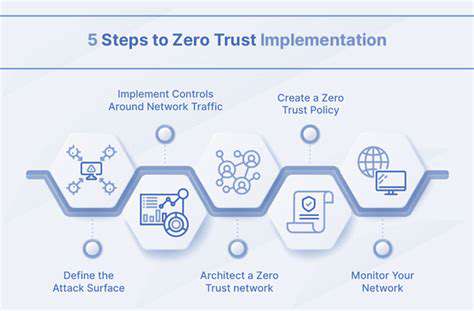
Understanding the Core Principles of Zero Trust
Zero Trust security operates on the principle of never trust, always verify. This fundamentally shifts the traditional network security model, moving away from implicit trust within the network perimeter. Instead, every user, device, and application, regardless of location, is treated as a potential threat and requires continuous authentication and authorization. This approach dramatically reduces the attack surface and enhances the overall security posture.
Implementing Zero Trust necessitates a shift in mindset from a perimeter-based security model to a continuous verification model. This means that even if an entity is inside the network, it still must be verified before accessing any resource or data. This proactive approach to security is essential in today's increasingly complex and interconnected digital landscape.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Robust Identity and Access Management (IAM) is crucial for Zero Trust implementations. This involves implementing strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and providing granular access controls. IAM allows organizations to precisely define who has access to what resources, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data and systems.
Effectively managing user identities is paramount in a Zero Trust environment. Detailed audit trails of user activity, along with real-time access monitoring, are vital for identifying and responding to potential security breaches quickly and efficiently. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the system.
Network Segmentation and Micro-segmentation
Network segmentation, including micro-segmentation, is a cornerstone of Zero Trust security. By dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments, organizations limit the impact of a potential breach. If one segment is compromised, the damage is contained within that segment, preventing the attacker from easily moving laterally throughout the network.
This segmentation approach is essential for isolating sensitive data and applications. Micro-segmentation takes this a step further, dividing networks into even smaller, more granular segments, further reducing the attack surface and improving control over access.
Continuous Monitoring and Threat Detection
Continuous monitoring and threat detection are critical components of a Zero Trust framework. Implementing security information and event management (SIEM) solutions, along with advanced threat intelligence feeds, enables organizations to detect and respond to potential threats in real-time. This proactive approach is vital in stopping attacks before they can cause significant damage.
Real-time threat detection and response mechanisms are crucial in a dynamic security environment. This allows organizations to quickly identify suspicious activity and take swift action to mitigate potential risks. Regular security assessments and penetration testing are also essential for identifying vulnerabilities and improving the overall security posture.
Policy Enforcement and Automation
Zero Trust security relies heavily on well-defined policies and automated enforcement mechanisms. Clear, comprehensive policies should govern access, authentication, and authorization for all users, devices, and applications. These policies should be consistently enforced to ensure that only authorized users and devices can access resources.
Security Posture and Compliance
Maintaining a strong security posture and adhering to relevant compliance standards are crucial aspects of Zero Trust implementation. Regular security assessments and penetration testing are vital for identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring that the security controls are effective. Compliance with industry regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, is also essential.
Adhering to industry best practices and compliance standards is essential for building a trustworthy system. This demonstrates a commitment to robust security and instills confidence in stakeholders and partners.